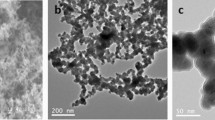
Abstract
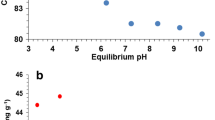
Cadmium (Cd) is a carcinogenic metal contaminating the environment and ending up in wastewaters. There is therefore a need for improved methods to remove Cd by adsorption. Biogenic elemental selenium nanoparticles have been shown to adsorb Zn, Cu and Hg, but these nanoparticles have not been tested for Cd removal. Here we studied the time-dependency and adsorption isotherm of Cd onto biogenic elemental selenium nanoparticles using batch adsorption experiments. We measured ζ-potential values to assess the stability of nanoparticles loaded with Cd. Results show that the maximum Cd adsorption capacity amounts to 176.8 mg of Cd adsorbed per g of biogenic elemental selenium nanoparticles. The ζ-potential of Cd-loaded nanoparticles became less negative from −32.7 to −11.7 mV when exposing nanoparticles to an initial Cd concentration of 92.7 mg L−1. This is the first study that demonstrates the high Cd uptake capacity of biogenic elemental selenium nanoparticles, of 176.8 mg g−1, when compared to that of traditional adsorbents such as carboxyl-functionalized activated carbon, of 13.5 mg g−1. An additional benefit is the easy solid–liquid separation by gravity settling due to coagulation of Cd-loaded biogenic elemental selenium nanoparticles.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benaïssa H, Elouchdi MA (2011) Biosorption of copper (II) ions from synthetic aqueous solutions by drying bed activated sludge. J Hazard Mater 194:69–78
Boyd GE, Adamson AW, Myers LS (1947) The exchange adsorption of ions from aqueous solutions by organic zeolites. II. Kinetics. J Am Chem Soc 69:2836–2848
Cao C, Qu J, Wei F et al (2012) Superb adsorption capacity and mechanism of flowerlike magnesium oxide nanostructures for lead and cadmium ions. Appl Mater Interfaces 4:4283–4287
Dada A, Olalekan AP, Olatunya AM, Dada O (2012) Langmuir, Freundlich, Temkin and Dubinin-Radushkevich isotherms studies of equilibrium sorption of Zn2+ unto phosphoric acid modified rice husk. IOSR J Appl Chem 3:38–45
El-Ramady HR, Domokos-Szabolcsy É, Abdalla NA et al (2014) Selenium and nano-selenium in agroecosystems. Environ Chem Lett 12:495–510
El-Ramady HR, Abdalla N, Alshaal T et al (2015) Giant reed for selenium phytoremediation under changing climate. Environ Chem Lett 13:359–380
Feng Y, Gong J-L, Zeng G-M et al (2010) Adsorption of Cd (II) and Zn (II) from aqueous solutions using magnetic hydroxyapatite nanoparticles as adsorbents. Chem Eng J 162:487–494
Findon A, McKay G, Blair HS (1993) Transport studies for the sorption of copper ions by chitosan. J Environ Sci Heal A 28:173–185
Furusawa T, Smith JM (1973) Fluid-particle and intraparticle mass transport rates in slurries. Ind Eng Chem Fundam 12:197–203
Hamdaoui O, Naffrechoux E (2007) Modeling of adsorption isotherms of phenol and chlorophenols onto granular activated carbon. Part I. Two-parameter models and equations allowing determination of thermodynamic parameters. J Hazard Mater 147:381–394
Haug A, Graham RD, Christophersen OA, Lyons GH (2007) How to use the world’s scarce selenium resources efficiently to increase the selenium concentration in food. Microb Ecol Health Dis 19:209–228
Ho YS (2006) Review of second-order models for adsorption systems. J Hazard Mater 136:681–689
Hua M, Zhang S, Pan B et al (2012) Heavy metal removal from water/wastewater by nanosized metal oxides: a review. J Hazard Mater 211–212:317–331
Jain R, Jordan N, Schild D et al (2015a) Adsorption of zinc by biogenic elemental selenium nanoparticles. Chem Eng J 260:855–863
Jain R, Jordan N, Weiss S et al (2015b) Extracellular polymeric substances govern the surface charge of biogenic elemental selenium nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol 49:1713–1720
Jain R, Dominic D, Jordan N et al (2016) Preferential adsorption of Cu in a multi-metal mixture onto biogenic elemental selenium nanoparticles. Chem Eng J 284:917–925
Johnson NC, Manchester S, Sarin L et al (2008) Mercury vapor release from broken compact fluorescent lamps and in situ capture by new nanomaterial sorbents. Environ Sci Technol 42:5772–5778
Lenz M, Smit M, Binder P et al (2008) Biological alkylation and colloid formation of selenium in methanogenic UASB reactors. J Environ Qual 37:1691–1700
Machida M, Fotoohi B, Amamo Y et al (2012) Cadmium (II) adsorption using functional mesoporous silica and activated carbon. J Hazard Mater 221–222:220–227
Mckay G, Poots VJP (1980) Kinetics and diffusion processes in colour removal from effluent using wood as an adsorbent. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 30:279–292
Meng YT, Zheng YM, Zhang LM, He JZ (2009) Biogenic Mn oxides for effective adsorption of Cd from aquatic environment. Environ Pollut 157:2577–2583
Sen Gupta S, Bhattacharyya KG (2008) Immobilization of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Ni(II) ions on kaolinite and montmorillonite surfaces from aqueous medium. J Environ Manag 87:46–58
Sharma VK, McDonald TJ, Sohn M et al (2014) Biogeochemistry of selenium. A review. Environ Chem Lett 13:49–58
Sheela T, Nayaka YA, Viswanatha R et al (2012) Kinetics and thermodynamics studies on the adsorption of Zn(II), Cd(II) and Hg(II) from aqueous solution using zinc oxide nanoparticles. Powder Technol 217:163–170
Staicu LC, van Hullebusch ED, Lens PNL (2015) Production, recovery and reuse of biogenic elemental selenium. Environ Chem Lett 13:89–96
Tirtom VN, Dinçer A, Becerik S et al (2012) Comparative adsorption of Ni(II) and Cd(II) ions on epichlorohydrin crosslinked chitosan–clay composite beads in aqueous solution. Chem Eng J 197:379–386
Weber WJ, Morris JC (1962) Removal of biologically resistant pollutants from waste waters by adsorption. Adv Water Pollut Res 2:231–266
Acknowledgments
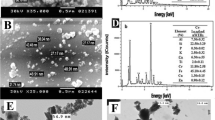
The authors would like to acknowledge Ferdi Battles and Berend Lolkema (UNESCO-IHE, Delft) for ICP-MS and Elfi Christalle (HZDR, Germany) for SEM-EDXS measurements. This research was supported through the Erasmus Mundus Joint Doctorate Environmental Technologies for Contaminated Solids, Soils, and Sediments (ETeCoS3) (FPA n°2010-0009) and Netherlands Fellowship Program for conducting master studies (NFP-MA.12 4689).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jain, R., Dominic, D., Jordan, N. et al. Higher Cd adsorption on biogenic elemental selenium nanoparticles. Environ Chem Lett 14, 381–386 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-016-0560-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-016-0560-8