Abstract
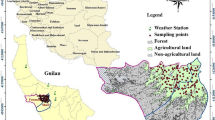
In this study, the clustering method was applied to improve the usage of effective rainfall (ER) for irrigating rice paddy in the region managed by the TaoYuan Irrigation Association (TIA) of Taiwan. A total of 16 rainfall stations and rainfall data from 1981 to 2000 were used. A traditional area-weighted method (Thiessen polygons method) and an optimal clustering model of ER were evaluated and compared. The optimal clustering model of ER comprised self-organizing map (SOM), k-means (KM), and fuzzy c-means (FCM) clustering algorithms. To obtain optimal clustering data of ER, the clustering groups from two to five of SOM, KM, and FCM algorithms were determined using root-mean-squared-error. The results show that three algorithms with group numbers from two to five are adopted for the monthly optimal clustering model in different months. However, for the annual optimal model, 12 sub-models are assessed and then compared. The results show that the SOM clustering with groups three was the optimal model for annual ER. The optimal clustering model of ER provides a new procedure step in preparation of the irrigation scheduling for the TIA, and the amount irrigation water waste can be reduced from 770.1 to 22.3 mm/year. The planned ER using the optimal clustering model significantly improves the irrigation water use efficient in agricultural water management.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adnan S, Khan AH (2009) Effective rainfall for irrigated agriculture plains of Pakistan. Pak J Meteorol 6(11):61–72
Bezdek JC (1981) Pattern recognition with fuzzy objective function algorithms. Plenum, New York
Bezdek JC, Ehrlich R, Full W (1984) FCM: the fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm. Comput Geosci 10(2–3):191–203
Brassel KE, Reif D (1979) A procedure to generate Thiessen polygons. Geogr Anal 11(3):289–303
Brouwer C, Heibloem M (1986) Irrigation water needs. Irrigation Water Management Training Manual 3, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome
Chang FJ, Chang LC (2007) Neural network, 1st edn. Tunghua, Taipei
Chang FJ, Chiang YM, Cheng WG (2013) Self-organizing radial basis neural network for predicting typhoon-induced losses to rice. Paddy Water Environ 11:369–380
Chen S (1979) Estimation of effective rainfall. J Chin Agric Eng 25(1):44–47
Chen S (1989) Research on effective rainfall for water management in Taoyuan of Taiwan. Dissertation, Hokkaido University
Chen FW, Chen S, Tsai SM (2003) A study on deep ponding cultivation to estimate effective rainfall in Paddy Fields. Proceedings of the 2003 conference on agricultural engineering, Kaohsiung, p. 701–712
Chen FW, Chen S, Tsai SM, Huang ST (2005) Comparison with irrigation associations for calculation method of effective rainfall in Taiwan. Proceedings of the 2005 conference on agricultural engineering, Miaoli
Chen LH, Hong YT, Hsu CW (2011) A study on regional drought frequency analysis using self-organizing map and l-moments. J Taiwan Agric Eng 57(2):57–77
Chin LD (1965) Study on the effective rainfall. J Chin Agric Eng 11(4):17–27
Chiu SL (1994) Fuzzy model identification based on cluster estimation. J Intell Fuzzy syst 12:267–278
Chow VT (1964) Handbook of applied hydrology. McGraw Hill Book Co, New York
Chung S-O, Rodríguez-Díaz JA, Weatherhead EK, Knox JW (2011) Climate change impacts on water for irrigating paddy rice in South Korea. Irrig Drain 60:263–273
Cuenca RH (1989) Irrigation system design: an engineering approach. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey
Dastane NG (1974) Effective rainfall in irrigated agriculture. FAO irrigation and drainage paper NO.25, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome
Dhandapani KR (1980) Effective rainfall in the estimation of irrigation requirement of transplanted rice. Oryza 17(1):1–5
Hall MJ, Minns AW (1999) The classification of hydrological homogeneous regions. Hydrol Sci J 44(5):693–704
Hayes GI, Buell JH (1955) Water and our forests: trees also need water at the right time and place. Yearbook of Agriculture. USDA, p 219–228
Hershfield DM (1964) Effective rainfall and irrigation water requirement. Proceedings of the ASCE. J Irrig Drain Div 90:33–37
Horikawa N, Hayase Y (2006) Irrigation system operations and effective rainfall: case study on low land paddy irrigation area. Tech Rep Nat Inst Rural Eng 204:175–183
Hsu KC, Li ST (2010) Clustering spatial-temporal precipitation data using wavelet transform and self-organizing map neural network. Adv Water Resour 33:190–200
Hu CP, Qin XL (2008) Spatial classification and prediction based on fuzzy c-means. J Comput Res Dev 45(7):1183–1188
IRRI (1981) Irrigation and water management, International Rice Research Institute Report for 1980. Los Banos
Jackson A (1992) Deciding how much to plant during a drought. Drought Tips 92-43, UC Department of Land, Air and Water Resource
Jensen ME, Burman RD, Allen RG (1990) Evapotranspiration and irrigation water requirements. ASCE-Manuals and Reports on Engineering Practice 70, New York
Kim SJ, Kwon HJ, Jung IK, Park GA (2003) A comparative study on grid-based storm runoff prediction using Thiessen and spatially distributed rainfall. Paddy Water Environ 1:149–155
Kohonen T (1995) Self-organizing maps. Springer, New York
Kuo SF, Ho SS, Liu CW (2006) Estimation irrigation water requirements with derived crop coefficients for upland and paddy crops in ChiaNan irrigation association, Taiwan. Agric Water Manage 82:433–451
Kwedlo W (2011) A clustering method combining differential evolution with the K-means algorithm. Pattern Recogn Lett 32(12):1613–1621
Li DZ (1956) Estimation of effective rainfall for paddy irrigation. J Chin Agric Eng 1(8):98–99
Li PH (2009) An investigation of artificial neural networks on regional classification and estimation of evaporation in Taiwan. Dissertation, National Taiwan University
Lin GF, Chen LH (2006) Identification of homogeneous regions for regional frequency. J Hydrol 324:1–9
Lin GF, Wu MC (2007) A SOM-based approach to estimating design hyetographs of ungauged sites. J Hydrol 339:216–226
Lin GF, Chen LH, Kao SC (2005) Development of regional design hyetographs. Hydro Process 19(4):937–946
Liu ZD, Duan AW, Xiao JF, Liu ZG (2007) Research progress on calculation methods of effective rainfall in growing period on dry crop. J Irrig Drain 26(3):27–30
Lo AH (1962) The estimate and operation of water source for irrigation. J Taiwan Water Conserv 9(12):12–21
MOAF, Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry, Republic of Korea (2000) Agricultural water supply survey report. 566 Seoul
Mohan S, Simhadrirao B, Arumugam N (1996) Comparative study of effective rainfall estimation methods for lowland rice. Water Resour Manag 10:35–44
Obreza TA, Pitts DJ (2002) Effective rainfall in poorly drained microirrigated citrus orchards. Soil Sci Soc Am J 66(1):212–221
Ogrosky HO, Mockus V (1964) Hydrology of agricultural lands. Sec 21 in handbook of hydrology. McGraw Hill Book Co, New York, p 1–79
Panigrahi B, Sharma SD, Behera BP (1992) Irrigation water requirement models of some major crops. Water Resour Manag 6:69–77
Patwardhan AS, Nieber JL, Johns EL (1990) Effective rainfall estimation methods. J Irrig Drain Eng 116(2):182–193
Rahman MM, Islam MO, Hasanuzzaman M (2008) Study of effective rainfall for irrigated agriculture in south-eastern part of Bangladesh. World J Agric Sci 4(4):453–457
Ramos MC (2001) Divisive and hierarchical clustering techniques to analyse variability of rainfall distribution patterns in a Mediterranean region. Atmos Res 57:123–138
Ren M, Wang B, Liang Q, Fu G (2010) Classified real-time flood forecasting by coupling fuzzy clustering and neural network. Int J Sediment Res 25:134–148
Ross TJ (1995) Fuzzy logic with engineering applications. McGraw-Hill, New York
Ruspini EH (1970) Numerical methods for fuzzy clustering. Inf Sci 2(3):319–350
Satyanarayana P, Srinivas VV (2011) Regionalization of precipitation in data sparse areas using large scale atmospheric variables: a fuzzy clustering approach. J Hydrol 405:462–473
Smith MA (1992) Computer programme for irrigation planning and management. FAO Irrig Drain Paper 46:49–62
Stamm GG (1967) Problems and procedures in determining water supply requirements for irrigation projects. Chap. 40 in irrigation of agricultural lands by Hagan et al. Wisconsin, Amer Soc Agron Agronomy II
Tekwa IJ, Bwade EK (2011) Estimation of irrigation water requirement of maize (zea-mays) using pan evaporation method in Maiduguri, Northeastern Nigeria. Agric Eng Int CIGR J 13(1):1–5
Tsai SM, Chen S, Wang HY (2005) A study on the practical model of planned effective rainfall for paddy fields in Taiwan. J Mar Sci Technol 13(2):73–82
Tsao YS (1966) Effective rainfall in irrigation of upland crops. J Chin Agric Eng 12(1):33–41
Tsao YS (1969) A study on calculation of effective rainfall in upland crop irrigation by using of computer and the effective rainfall in Huolung area. J Chin Agric Eng 15(1):19–35
Tsao YS (1972) A study on the calculation and estimation of effective rainfall on paddy field by using electronic computer. J Taiwan Water Conserv 19(2):7–29
USDA, the United States Department of Agriculture (1967) Irrigation water requirements. Technical Release 21. USDA Soil Conservation Service, Washington DC
Van Hulle MM (2011) Self-organizing maps. In: Rozenberg G, Baeck T, Kok J (eds) Handbook of natural computing: theory, experiments, and applications. Springer, Berlin, pp 1–45
Vesanto J, Alhoniemi E (2000) Clustering of the self-organizing map. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 11(3):586–600
Water Conservancy Bureau of Taiwan (WCB) (1982) Manual for working stations of irrigation associations, pp 109–117
Wei W, Chen L, Fu B, Huang Z, Wu D (2007) The effect of land uses and rainfall regimes on runoff and soil erosion in the semi-arid loess hilly area, China. J Hydrol 335:247–258
Yager RR, Filev DP (1994) Approximate clustering via the mountain method. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 24(8):1279–1284
Yomota A, Ndegwa GM (1995) Water use for upland irrigation in a humid region of Japan. Agric Water Manag 28:185–200
Zahraie B, Roozbahani A (2011) SST clustering for winter precipitation prediction in southeast of Iran: comparison between modified k-means and genetic algorithm-based clustering methods. Expert Syst Appl 38:5919–5929
Zhang J, Hall MJ (2004) Regional flood frequency analysis for the Gan-Ming River basin in China. J Hydrol 296:98–117
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, FW., Liu, CW. & Chang, FJ. Improvement of the agricultural effective rainfall for irrigating rice using the optimal clustering model of rainfall station network. Paddy Water Environ 12, 393–406 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-013-0395-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-013-0395-x