Abstract
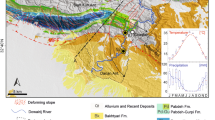
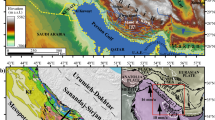
The Siwanli landslide is located in the middle section of the Dadu River in the eastern part of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau in a complex regional geological environment. Strong erosion of the river valley has caused numerous rockfalls and slides on both sides of the valley since the Late Pleistocene. A large number of landslide deposits provide the opportunity for examination of the sedimentary and erosional environment along the Dadu River. Identifying the spatial and temporal characteristics of the large, ancient landslides in the Dadu River valley can help improve understanding of the formation mechanism and evolutionary process of ancient and recurrent landslides. In this paper, the formation mechanism of the ancient, complex, and multistage Siwanli landslide is discussed, as well as an important link between river erosion and the formation and evolution of the landslide. In the first stage, the initial landslide blocked the Dadu River, forming a barrier lake, and multistage landslide dam breaches occurred. The entire landslide dam experienced creep deformation, and local minor multistage sliding occurred at the front and middle parts of the initial landslide. Subsequently, a large landslide formed at the scarp of the initial landslide.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen CR, Luo Z, Qian H, Wen X, Zhou H, Huang W (1991) Field study of a highly active fault zone: the Xianshuihe fault of southwestern China. Geol Soc Am Bull 103:1178–1199
Chai HJ, Liu HC, Zhang ZY (1995) The catalog of Chinese landslide dam events. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation 6(4):1–9 in Chinese
Chai HJ, Liu HC, Zhang ZY, ZW X (2000) The distribution, causes and effects of damming landslides in China. Journal of Chengdu Institute of Technology 27:302–307 in Chinese
Chen J, Dai FC, Yao X (2008) Holocene debris-flow deposits and their implications on climate in the upper Jinsha River valley, China. Geomorphology 93:493–500
Costa JE, Schuster RL (1988) The formation and failure of natural dams. Geol Soc Am Bull 100:1054–1068
Costa JE, Schuster RL (1991) Documented historical landslide dams from around the world. US Geological Survey Open-File Report 91-239:486
Dai FC, Lee CF, Deng JH, Tham LG (2005) The 1786 earthquake triggered landslide dam and subsequent dam-break flood on the Dadu River, southwestern China. Geomorphology 65:205–221
Deng JH, Chen F, Yin H, Gao MZ, Meng YL, Huang RT (2007) Geological origin and stability evaluation of the Siwancun landslide in Luding County. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 26(10):1945–1950
Evans SG, Hermanns R, Strom A., Scarascia-Mugnozza G (Eds) (2011) Natural and artificial rock slide dams. Springer (Series: Lecture Notes in Earth Sciences).
Huang RQ, Xu Q (2008) Catastrophic landslide in China. Science Publishing House, Beijing, China (in Chinese).
Keefer DK (1984) Landslides caused by earthquakes. Geol Soc Am Bull 95:406–421
Keefer DK (1994) The importance of earthquake-induced landslides to long-term slope erosion and slope-failure hazards in seismically active regions. Geomorphology 10:265–284
Korup O (2002) Recent research on landslide dams—a literature review with special attention to New Zealand. Prog Phys Geogr 26:206–235
Korup O, Montgomery DR (2008) Tibetan plateau river incision inhibited by glacial stabilization of the Tsangpo gorge. Nature 455:786–789
Phartiyal B, Sharma A, Srivastava P (2009) Chronology of relict lake deposits in the Spiti River, NW Trans Himalaya: implications to Late Pleistocenee Holocene climate-tectonic perturbations. Geomorphology 108:264–272
Wang XM, Pei XY (1987) The 1786 Kangding-Luding earthquake. Earthquake Research in Sichuan 1–51. (Supplement Issue, in Chinese).
Wang XM, Pei XY (1998) Major active faults and earthquake-induced cracks in Kangding-Luding area. Earthquake Research in Sichuan 1-2:46–56 in Chinese
Weidinger JT (2006) Landslide dams in the high mountains of India, Nepal and China - stability and life span of their dammed lakes. Italian Journal of Engineering Geology and Environment 1:67–80 special issue
Zhang YS, Zhao XT, Lan HX, Xiong TY (2011) A Pleistocene landslide-dammed lake, Jinsha River, Yunnan, China. Quat Int 233(1):72–80
Zhao Y, Xu M, Guo J, Zhang Q, Zhao HM, Kang XB, Xia Q (2014) Accumulation characteristics, mechanism, and identification of an ancient translational landslide in China. Landslides:1–12
Acknowledgments
We thank constructive suggestions from Dr. van Asch TWJ. We thank the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (No. 2013CB733202), investigation and evaluation of slope geological disasters in the thick valleys of Southwest China (No. 12120113010500), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 41272332 and 41672282). The second author thanks the Innovative Team of the Chengdu University of Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, H., Wu, L.Z., Huang, R.Q. et al. Formation of the Siwanli ancient landslide in the Dadu River, China. Landslides 14, 385–394 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-016-0756-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-016-0756-9