Abstract
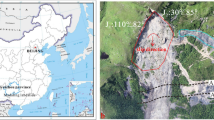
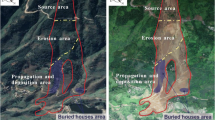
Based on field geological survey and unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) photography, this paper studied the inherent causes, intrinsic mechanisms, and kinematic characteristics of a catastrophic landslide of dissolved and fractured rock slope in a mountainous area of Southwestern China. The discrete element method (DEM) model of representative volume element of fractured rock mass considering karst existence was developed with its micromechanical parameters calibrated from laboratory element tests. The coupled finite difference and discrete element methods (FDM-DEM) were then employed to simulate deformation and failure evolution and collapse development of the rock slope with both internal and externally triggering factors properly addressed. The kinematic characteristics of mobile collapse debris flow were analyzed, and the numerical simulation results were validated by laboratory physical model test. The results show that the internal causes were mainly manifested in slope structure, lithology combination, karst, and fracture development, among which the unfavorable interaction disintegrated rock masses. The primary external cause was the staged underground coal-mining operations underneath the collapsed body, which led to large cracks appearing at the back edges of the slope. The maximum velocity of mobile collapse debris was about 65 m/s with the maximum travel distance of more than 600 m. Numerical simulation results matched well with both field forensic investigation and laboratory physical model test results. The findings would help further understand the deformation and failure process of fractured rock slope subject to underground mining and provide technical reference for accurate assessment and proper mitigation of similar landslide disasters.























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aydan Ö, Kawamoto T (1992) The stability of slopes and underground openings against flexural toppling and their stabilisation. Rock Mech Rock Eng 25:143–165. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01019709
Barla M, Piovano G, Grasselli G (2012) Rock slide simulation with the combined finite-discrete element method. Int J Geomech 12(6):711–721. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)gm.1943-5622.0000204
Carnec C, Delacourt C (2000) Three years of mining subsidence monitored by SAR interferometry, near Gardanne, France. J Appl Geophys 43(1):43–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-9851(99)00032-4
Cheng XT, Huang BL (2018) Application of FEM/DEM method in the numerical analysis of failure process of the typical columnar dangerous rock mass. Hydrogeol Eng Geol 45(04):137–141. (in Chinese)
Crosta GB, Imposimato S, Roddeman DG (2003) Numerical modelling of large landslides stability and runout. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 3(6):523–538. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-3-523-2003
Cui KFE, Zhou GGD, Jing L, Chen X, Song D (2020) Generalized friction and dilatancy laws for immersed granular flows consisting of large and small particles. Phys Fluids 32(11):113312. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0024762
Cundall PA, Strack ODL (1979) A discrete numerical model for granular assemblies. Geotechnique 29(1):47–65. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.1979.29.1.47
Deng YY, Chen CX, Xia KZ, Yang KY, Sun CY, Zheng XW (2018) Investigation on the characteristics of overlying strata caving in the Chengchao Iron Mine, China. Environ Earth Sci 77(10):362. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7553-9
Ewy RT, Hood M (1984) Surface strain over longwall coal mines: its relation to the subsidence trough curvature and to surface topography. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 21(3):155–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(84)91533-X
Fan XM, Juang CH, Wasowski J, Huang RQ, Xu Q, Scaringi G, van Westen CJ, Havenith HB (2018) What we have learned from the 2008 Wenchuan Earthquake and its aftermath: A decade of research and challenges. Eng Geol 241:25–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.05.004
Guo S, Xu P, Zheng Z, Gao Y (2015) Estimation of flow velocity for a debris flow via the two-phase fluid model. Nonlinear Process Geophys 22(1):109–116. https://doi.org/10.5194/npg-22-109-2015
Han Z, Chen GQ, Li YG, Wang W, Zhang H (2015) Exploring the velocity distribution of debris flows: An iteration algorithm based approach for complex cross-sections. Geomorphology 241:72–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2015.03.043
Han Z, Chen GQ, Li YR, Xu L, Zheng L, Zhang YB (2014) A new approach for analyzing the velocity distribution of debris flows at typical cross-sections. Nat Hazards 74(3):2053–2070. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-014-1276-3
Huang RQ (2009) Some catastrophic landslides since the twentieth century in the southwest of china. Landslides 6(1):69–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-009-0142-y
Huang H, Lecampion B, Detournay E (2013) Discrete element modeling of tool-rock interaction I: rock cutting. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 37(13):1913–1929. https://doi.org/10.1002/nag.2113
Huo YM, Song XM, Zhu DF (2020) Numerical investigation of top-coal migration in the first coal-drawing process by an FDM–DEM coupling method. Energies 13:5493. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13205493
Jiao YY, Wang ZH, Wang XZ, Adoko AC, Yang ZX (2013) Stability assessment of an ancient landslide crossed by two coal mine tunnels. Eng Geol 159:36–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2013.03.021
Kim JG (2020) Measurement of surface subsidence and ground collapse caused by underground mining in the Boleo Copper District, Mexico. J Sustain Min 19:2. https://doi.org/10.46873/2300-3960.1011
Li H, Ju NP, Zheng D, Peng HM (2013) Study on the mechanism of pull crack toppling collapse in shangyangshui River Basin, Guizhou. J Eng Geol 21(2):289–296. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2013.02.015 (in Chinese)
Li MG, Yu HT, Wang JH, Xia XH, Chen JJ (2015) A multiscale coupling approach between discrete element method and finite difference method for dynamic analysis. Int J Numer Methods Eng 102(1):1–21. https://doi.org/10.1002/nme.4771
Li WL, Zhao B, Xu Q, Yang F, Fu H, Dai C, Wu XX (2020) Deformation characteristics and failure mechanism of a reactivated landslide in Leidashi, Sichuan, China, on August 6, 2019: an emergency investigation report. Landslides 17(6):1405–1413. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-020-01367-w
Lin CX, Tu FB, Ling DS, Hu CB (2018) FEM-DEM coupled modeling of cone penetration tests in lunar soil. J Cent South Univ 25:392–405. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-018-3745-4
Lin F, Feng L, Sun C, Zhang WS, Zeng H (2015) Study on the formation mechanism of strong karst controlled collapse. J Eng Geol 23(03):408–414. (in Chinese)
Ma GT, Hu XW, Yin YP, Luo G, Pan YX (2018) Failure mechanisms and development of catastrophic rockslides triggered by precipitation and open-pit mining in Emei, Sichuan, China. Landslides 15:1401–1414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-018-0981-5
Ma YF, Huang HY (2018) DEM analysis of failure mechanisms in the intact Brazilian test. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 102:109–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2017.11.010
Muñoz-Salinas E, Manea VC, Palacios D, Castillo-Rodriguez M (2007) Estimation of lahar flow velocity on Popocatépetl volcano (Mexico). Geomorphology 92(1–2):91–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2007.02.011
Ning YB, Tang HM, Zhang BH et al (2020) Investigation of the rock similar material proportion based on orthogonal design and its application in base friction physical model tests. Rock Soil Mech 41(6):2009–2020 ((in Chinese))
Okura Y, Kitahara H, Sammori T, Kawanami A (2000) Effects of rockfall volume on runout distance. Eng Geol 58(2):109–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-7952(00)00049-1
[Online] Available: China National Meteorological Data Center[DB/OL]. http://www.nmic.cn/dataService/cdcindex/datacode/A.0012.0001/show_value/normal.html. Accessed 8 Oct 2021
Parise M, Lollino P (2011) A preliminary analysis of failure mechanisms in karst and man-made underground caves in Southern Italy. Geomorphology 134(1–2):132–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2011.06.008
Pawe S (2021) Simulation possibilites of the post-mining goafs impact on the deformations induced by next underground mining operations with use of the cellular automata method. Geotech Geol Eng 39(8):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-020-01595-w
Potyondy DO, Cundall PA (2004) A bonded-particle model for rock. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 41(8):1329–1364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2004.09.011
Prochaska AB, Santi PM, Higgins JD, Cannon SH (2008) A study of methods to estimate debris flow velocity. Landslides 5(4):431–444. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-008-0137-0
Rahman MA, Konagai K (2017) Substantiation of debris flow velocity from super-elevation: a numerical approach. Landslides 14(2):633–647. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-016-0725-3
Rahman MA, Konagai K (2018) A hands-on approach to estimate debris flow velocity for rational mitigation of debris hazard. Can Geotech J 55(7):941–955. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2017-0211
Shao S (2012) FEM-DEM analysis of soil rock mixture slope stability. Dalian University of Technology. (in Chinese)
Shi C, Yang WK, Yang JK, Chen X (2019) Calibration of micro-scaled mechanical parameters of granite based on a bonded-particle model with 2D particle flow code. Granul Matter 21(2). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-019-0889-3
Sun YK, Yao BK (1983) Study on the collapse mechanism of Yanchihe phosphorus mine. Hydrogeol Eng Geol (1):5–11. (in Chinese)
Tan X, Feng L, Hu Z, Abbas SM (2021a) The equivalent shear strength properties of the composite soil reinforced by stone columns: an FDM-DEM-coupled numerical evaluation. Environ Earth Sci 80(4):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09412-0
Tan B, Yang T, Qin HY Liu Q (2021b) Laboratory study on the stability of large-size graded crushed stone under cyclic rotating axial compression. Materials 14:1584. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14071584
Wang G (2014) Failure mechanism of steep layered rock slope: A case study of Jiguanling landslide. Shanghai Jiaotong University. (in Chinese)
Wang XM, Xiao YJ, Shi WB, Ren JJ, Chang ZX, Li H (2021) Research on meso-scale deformation and failure mechanism of fractured rock mass subject to biaxial compression. Arab J Geosci 14(14). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07769-x
Wang YC, Ju NP, Zhao JJ, Xiang XQ (2013) Analysis on formation mechanism of landslide over goaf in gently inclined coal seam. J Eng Geol 21(01):61–68. (in Chinese)
Wang Z, Yan E, Yin X, Zhang X, Tang R (2014) Study on collapse mechanism of layered anti dip rock slope: a case study of honglianchi iron mine slope in Hefeng, Hubei Province. Zhongnan Daxue Xuebao (Ziran Kexue Ban)/J Cent South Univ (Science and Technology) 45(7):2295–2302.
Wei JB, Zhao Z, Xu C, Wen Q (2019) Numerical investigation of landslide kinetics for the recent Mabian landslide (Sichuan, China). Landslides 16(11):2287–2298. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-019-01237-0
Wei ZA, Shen LY, Chen YL, Zhu B (2012) Back analysis of rockfall trajectory and its parameters. Adv Mat Res 402:828–834. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.402.828
Wong RHC, Chiu M (2001) A study on failure mechanism of block-flexural toppling by physical modelling testing. DC Rocks 2001, The 38th U.S. Symposium on Rock Mechanics (USRMS). https://onepetro.org/ARMAUSRMS/proceedings/ARMA01/All-ARMA01/ARMA-01-0989/117021
Xiao P, Li DY, Zhao GY, Zhu QQ, Liu HX, Zhang CS (2020) Mechanical properties and failure behavior of rock with different flaw inclinations under coupled static and dynamic loads. J Cent South Univ 27(10):2945–2958. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4520-x
Xiong SZ, Shi WB, Wang XM (2020) Damge and failure characteristic of karst fractured rock mass under uniaxal compression. J Eng Geol 1–13[2021–06–28]. https://doi.org/10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2020-158 (in Chinese)
Xu Q, Fan XM, Dong XJ (2012) Characteristics and formation mechanism of a catastrophic rainfall-induced rock avalanche-mud flow in Sichuan, China, 2010. Landslides 9(1):143-154. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-011-0278-4
Yang HQ, Lan YF, Lu L, Zhou XP (2015) A quasi-three-dimensional spring-deformable-block model for runout analysis of rapid landslide motion. Eng Geol 185:20–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.11.016
Yang JH, Yu X, Yang Y, Yang ZQ (2018) Physical simulation and theoretical evolution for ground fissures triggered by underground coal mining. PLoS One 13(3):e0192886. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0192886
Yu JY, Xue XK, Chen CF, Chen RP, He KY, Li F (2021) Three-dimensional reconstruction and disaster identification of highway slope based on UAV tilt photography. China Journal of Highway and Transport 1–13. (in Chinese)
Yu XX (2020) Study on deformation and failure mechanism of gentle anti dip mining slope in karst mountainous area. Guizhou University. (in Chinese)
Zhang M, Wu LZ, Zhang JC, Li LP (2019) The 2009 Jiweishan rock avalanche, Wulong, China: deposit characteristics and implications for its fragmentation. Landslides 16(5):893–906. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-019-01142-6
Zheng D, Frost JD, Huang RQ, Liu FZ (2015) Failure process and modes of rockfall induced by underground mining: A case study of Kaiyang Phosphorite Mine rockfalls. Eng Geol 197:145–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.08.011
Zheng G, Xu Q, Ju YZ, Li WL, Zhou XP, Peng SQ (2018) Study on collapse characteristics and genetic mechanism of pusha village, Zhangjiawan Town, Nayong County, Guizhou Province on August 28, 2017. J Eng Geol 26(1):223–240. https://doi.org/10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2018.01.023 (in Chinese)
Zhou Q, Xu WJ, Lubbe R (2021) Multi-scale mechanics of sand based on FEM-DEM coupling method. Powder Technol 380:394–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2020.11.006
Zhu YG, Gong J, Nie ZH (2020) Shear behaviours of cohesionless mixed soils using the DEM: The influence of coarse particle shape. Particuology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.partic.2020.07.002
Zuo ZX (2009) Study on stability evaluation and control technology of high and steep slope in the process of open pit to underground mining. Central South University. (in Chinese)
Funding
This research work presented herein was jointly funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51878673, 52178443, U1734208, U1934209 & 42067046), the National Key R&D program of China (Grant No. 2019YFC1904704), the Key R&D Program of China Academy of Railway Sciences Corporation Limited (Grant No. 2019YJ026), the Open Foundation of MOE Key Laboratory of Engineering Structures of Heavy Haul Railway (Central South University) (Grant No. 2021JZZ01 & 2021JZZ02), and the Science and Technology Planning Project of Guizhou Province of China (Grants No. QKHJC-ZK[2021]228).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Xiao, Y., Shi, W. et al. Forensic analysis and numerical simulation of a catastrophic landslide of dissolved and fractured rock slope subject to underground mining. Landslides 19, 1045–1067 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-021-01842-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-021-01842-y