Abstract
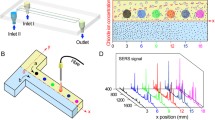
In order to obtain a better understanding of the physical and chemical processes within micromixers or microreactors and to optimize these devices it is necessary to monitor the concentrations within the microchannels. To get chemical information, laser Raman spectroscopy can be used. This method is very selective for individual chemical compounds, allows a spatial resolution of 10 μm within fluids and a quantitative analysis. We examined the hydrolysis of the acetal 2,2-dimethoxypropane to acetone and methanol in the presence of hydrogen ions as catalyst. This reaction can be used to characterize micromixers. The aim of this work is the in situ monitoring of concentrations of acetal and its products, acetone and methanol, during the hydrolysis of acetal within a T-shaped micromixer with a channel width of 0.4 mm and a channel depth of 0.2 mm. In these experiments a continuous-wave argon ion laser was used as an excitation source. The laser radiation was coupled into a microscope and into the micromixer covered with a quartz plate. A special microscope objective was used. It allows the correction of optical aberrations resulting from quartz plates up to a thickness of 2 mm. Concentration profiles of acetal, methanol, and acetone were measured across the width of the microchannel.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramowitz M, Stegun IA (1972) Handbook of mathematical functions with formulas, graphs, and mathematical tables. NBS, New York, Dover
Antes J, Boskovic D, Krause H, Löbbecke S, Lutz N, Türcke T, Schweikert W (2003) Analysis and improvement of strong exothermic nitrations in microreactors. Trans Inst Chem Eng 81(Part A):760–765
Baldyga J, Bourne JR, Walker B (1998) Non-isothermal micromixing in turbulent liquids: theory and experiment. Can J Chem Eng 76:641–649
Bohn L, Braune S, Kotthaus M, Kraut M, Pöchlauer P, Vorbach M, Wenka A, Schubert K (2006) Large-scale application of microreaction technology within commercial chemical production of DSM. In: 9th International conference on microreaction technology, 6–8 September 2006, Potsdam
Bothe D, Stemich C, Warnecke HJ (2006) Fluid mixing in a T-shaped micro-mixer. Chem Eng Sci 61(9):2950–2958
Chan KLA, Gulati S, Edel JB, de Mello AJ, Kazarian SG (2009) Chemical imaging of microfluidic flows using ATR-FTIR spectroscopy. Lab Chip 9:2909–2913
Dennison DB, Gettys GA, Kubler DG, Shepard D (1976) Kinetic salt effects on the hydrolysis of benzaldehyde dimethyl acetal. J Org Chem 41(13):2344–2348
Fletcher PD, Haswell SJ (2003) Monitoring of chemical reactions within microreactors using an inverted Raman microscopic spectrometer. Electrophoresis 24:3239–3245
Floyd TM, Schmidt MA, Jensen KF (2005) Silicon micromixers with infrared detection for studies of liquid-phase reactions. Ind Eng Chem Res 44:2351–2358
Hessel V, Hardt S, Löwe H (2004) Chemical micro process engineering: fundamentals, modelling and reactions. Wiley, Weinheim
Hessel V, Löwe H, Schönfeld F (2005) Micromixers: a review on passive and active mixing principles. Chem Eng Sci 60(8–9):2479–2501
Hessel V, Renken A, Schouten JC, Yoshida J (2009) Micro process engineering: a comprehensive handbook. Wiley, Weinheim
Hinsmann P, Frank J, Svasek P, Harasek M, Lendl B (2001) Design, simulation and application of a new micromixing device for time resolved infrared spectroscopy of chemical reactions in solution. Lab Chip 1:16–21
Hoffmann M, Schlüter M, Räbiger N (2006) Experimental investigation of liquid-liquid mixing in T-shaped micro-mixers using μ-LIF and μ-PIV. Chem Eng Sci 61:2968–2976
Johnson BK, Prud’homme RK (2003) Chemical processing and micromixing in confined impinging jets. AIChE J 49(9):2264–2282
Kamholz AE, Weigl BH, Finlayson BA, Yager P (1999) Quantitative analysis of molecular interaction in a microfluidic channel: the T-sensor. Anal Chem 71(23):5340–5346
Kazarian SG, Chan KLA (2006) Applications of ATR-FTIR spectroscopic imaging to biomedical samples. Biochim Biophys Acta 1758:858–867
Keoschkerjan R, Richter M, Boskovic D, Schnürer F, Löbbecke S (2004) Novel multifunctional microreaction unit for chemical engineering. Chem Eng J 101:469–475
Lindenberg C, Schöll J, Vicum L, Mazzotti M, Brozio J (2008) Experimental characterization and multi-scale modeling of mixing in static mixers. Chem Eng Sci 63:4135–4149
Löbbecke S, Ferstl W, Panic S, Türcke T (2005) Concepts for modularization and automation of microreaction technology. Chem Eng Technol 28(4):484–493
Müller A, Cominos V, Hessel V, Horn B, Schürer J, Ziogas A, Jähnisch K, Hillmann V, Großer V, Jam KA, Bazzanella A, Rinke G, Kraut M (2005) Fluidic bus system for chemical process engineering in the laboratory and for small-scale production. Chem Eng J 107:205–214
Nguyen NT, Wu Z (2005) Micromixers–a review. J Micromech Microeng 15:R1–R16
Park T, Lee M, Choo J, Kim YS, Lee EK, Kim DJ, Lee SH (2004) Analysis of passive mixing behavior in a Poly(dimethylsiloxane) microfluidic channel using confocal fluorescence and Raman microscopy. Appl Spectrosc 58:1172–1179
Rinke G, Kraut M, Grosser V, Hillmann V, Müller A, Horn B, Jähnisch K, Bazzanella A (2003) Modular micro process engineering and applications. In: 7th International Conference on Microreaction technology (IMRET 7), Lausanne, CH, 7–10 September 2003, Frankfurt, Proceedings, DECHEMA, 2003, 339–341
Rinke G, Kerschbaum S, Wenka A, Holpe H (2006) Micro process engineering for industrial production of biodiesel. In: 9th International conference on microreaction technology, 6–8 September 2006, Potsdam
Salmon JB, Ajdari A, Tabeling P, Servant L, Talaga D, Joanicot M (2005) In situ Raman imaging of interdiffusion in a microchannel. Appl Phys Lett 86:094106
Santos RG, Figueiredo JR (2007) Laminar elliptic flow in the entrance region of tubes. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 29(3):233–239, Rio de Janeiro July/Sept. 2007
Schubert K, Brandner J, Fichtner M, Linder G, Schygulla U, Wenka A (2001) Microstructure devices for applications in thermal and chemical process engineering. Microscale Thermophys Eng 5:17–39
Steinfeldt N, Bentrup U, Jähnisch K (2010) Reaction mechanism and in situ ATR spectroscopic studies of the 1-Decene ozonolysis in micro- and semibatch reactors. Ind Eng Chem Res 49:72–80
Strehle KR, Cialla D, Rösch P, Henkel T, Köhler M, Popp J (2007) A reproducible surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy approch. Online SERS measurements in a segmented microfluidic system. Anal Chem 79(4):1542–1547
Taylor RA, Penney WR, Vo HX (2005) Scale-up methods for fast competitive chemical reactions in pipeline mixers. Ind Eng Chem Res 44:6095–6102
Urakawa A, Trachsel F, von Rohr PR, Baiker A (2008) On-chip Raman analysis of heterogeneous catalytic reaction in supercritical CO2: phase behaviour monitoring and activity profiling. Analyst 133:1352–1354
Vilkner T, Janasek D, Manz A (2004) Micro total analysis systems. Recent developments. Anal Chem 76:3373–3386
Walker BM (1996) Einfluss der Temperatur auf die Selektivität rasch ablaufender Reaktionen. PhD Thesis, ETH Zürich (in German)
Watts P, Wiles C (2007) Recent advances in synthetic micro reaction technology. Chem Commun 5:443–467
Wirth T (2008) Microreactors in organic synthesis and catalysis. Wiley, Weinheim
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rinke, G., Ewinger, A., Kerschbaum, S. et al. In situ Raman spectroscopy to monitor the hydrolysis of acetal in microreactors. Microfluid Nanofluid 10, 145–153 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-010-0654-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-010-0654-8