Abstract
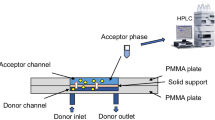
Microfluidic extraction based on a co-laminar flow of aqueous two-phase system is used to separate bovine serum albumin (BSA). Mass transfer between the continuous two-phase flows is demonstrated by the extraction of BSA in a microfluidic device. The protein concentrations of the BSA samples were determined using the Bradford method. Polyethylene glycol 4000 and ammonium sulfate ((NH4)2SO4) served as model aqueous two-phase solutions. The appropriate flow rates of the aqueous two phases were thus determined. We can flexibly control the mass transfer area and time by simply adjusting the flow rate. It takes only 3.6 s for three extraction cycles in a coaxial microfluidic device to achieve a BSA recovery yield of 71.1 %, which is superior to the traditional beaker aqueous two-phase extraction process. In this study, co-laminar flow-based continuous microextraction is demonstrated and its mass transfer is analyzed by solving the diffusion model, based on a large specific interfacial area and surface renewal.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albertsson PÅ (1960) Partition of cell particles and macromolecules: distribution and fractionation of cells, viruses, microsomes, proteins, nucleic acids, and antigen-antibody complexes in aqueous polymer two-phase systems. J. Wiley, New York
Alves J, Chumpitaz LDA, da Silva LHM, Franco TT, Meirelles AJA (2000) Partitioning of whey proteins, bovine serum albumin and porcine insulin in aqueous two-phase systems. J Chromatogr B 743(1–2):235–239. doi:10.1016/s0378-4347(00)00111-0
Benavides J, Mena JA, Cisneros-Ruiz M, Ramirez OT, Palomares LA, Rito-Palomares M (2006) Rotavirus-like particles primary recovery from insect cells in aqueous two-phase systems. J Chromatogr B 842(1):48–57. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2006.05.006
Benavides J, Aguilar O, Lapizco-Encinas BH, Rito-Palomares M (2008) Extraction and purification of bioproducts and nanoparticles using aqueous two-phase systems strategies. Chem Eng Technol 31(6):838–845. doi:10.1002/ceat.200800068
Burns JR, Ramshaw C (1999) Development of a microreactor for chemical production. Chem Eng Res Des 77(A3):206–211. doi:10.1205/026387699526106
Chu LY, Utada AS, Shah RK, Kim JW, Weitz DA (2007) Controllable monodisperse multiple emulsions. Angew Chem Int Ed 46(47):8970–8974. doi:10.1002/anie.200701358
Cisneros M, Benavides J, Brenes CH, Rito-Palomares M (2004) Recovery in aqueous two-phase systems of lutein produced by the green microalga Chlorella protothecoides. J Chromatogr B 807(1):105–110. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2004.01.009
Harris DP, Andrews AT, Wright G, Pyle DL, Asenjo JA (1997) The application of aqueous two-phase systems to the purification of pharmaceutical proteins from transgenic sheep milk. Bioseparation 7(1):31–37. doi:10.1023/a:1007908703773
Huh YS, Jeong CM, Chang HN, Lee SY, Hong WH, Park TJ (2010) Rapid separation of bacteriorhodopsin using a laminar-flow extraction system in a microfluidic device. Biomicrofluidics 4(1). doi: 10.1063/1.3298608
Kumar A, Kamihira M, Galaev IY, Mattiasson B, Iijima S (2001) Type-specific separation of animal cells in aqueous two-phase systems using antibody conjugates with temperature-sensitive polymers. Biotechnol Bioeng 75(5):570–580. doi:10.1002/bit.10080
Lan WJ, Li SW, Lu YC, Xu JH, Luo GS (2009) Controllable preparation of microscale tubes with multiphase co-laminar flow in a double co-axial microdevice. Lab Chip 9(22):3282–3288. doi:10.1039/b913247c
Lee EZ, Huh YS, Jun YS, Won HJ, Hong YK, Park TJ, Lee SY, Hong WH (2008) Removal of bovine serum albumin using solid-phase extraction with in situ polymerized stationary phase in a microfluidic device. J Chromatogr A 1187(1–2):11–17. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2009.01.084
Lu YC, Xia Y, Luo GS (2011) Phase separation of parallel laminar flow for aqueous two phase systems in branched microchannel. Microfluid Nanofluid 10(5):1079–1086. doi:10.1007/s10404-010-0736-7
McGovern S, Harish G, Pai CS, Mansfield W, Taylor JA, Pau S, Besser RS (2009) Investigation of multiphase hydrogenation in a catalyst-trap microreactor. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 84(3):382–390. doi:10.1002/jctb.2051
Meagher RJ, Light YK, Singh AK (2008) Rapid, continuous purification of proteins in a microfluidic device using genetically-engineered partition tags. Lab Chip 8(4):527–532. doi:10.1039/b716462a
Mokhtarani B, Karimzadeh R, Amini MH, Manesh SD (2008) Partitioning of ciprofloxacin in aqueous two-phase system of poly(ethylene glycol) and sodium sulphate. Biochem Eng J 38(2):241–247. doi:10.1016/j.bej.2007.07.009
Nam KH, Chang WJ, Hong H, Lim SM, Kim DI, Koo YM (2005) Continuous-flow fractionation of animal cells in microfluidic device using aqueous two-phase extraction. Biomed Microdevices 7(3):189–195. doi:10.1007/s10544-005-3025-6
Ribeiro SC, Monteiro GA, Cabral JMS, Prazeres DMF (2002) Isolation of plasmid DNA from cell lysates by aqueous two-phase systems. Biotechnol Bioeng 78(4):376–384. doi:10.1002/bit.10227
Rito-Palomares M, Lyddiatt A (2000) Practical implementation of aqueous two-phase processes for protein recovery from yeast. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 75(7):632–638. doi:10.1002/1097-4660(200007)75:7<632:aid-jctb248>3.0.co;2-7
Silvério SC, Moreira S, Milagres AMF, Macedo EA, Teixeira JA, Mussatto SI (2012) Interference of some aqueous two-phase system phase-forming components in protein determination by the Bradford method. Anal Biochem 421(2):719–724. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2011.12.020
Song YS, Choi YH, Kim DH (2007) Microextraction in a tetrabutylammonium bromide/ammonium sulfate aqueous two-phase system and electrohydrodynamic generation of a micro-droplet. J Chromatogr A 1162(2):180–186. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2007.06.032
SooHoo JR, Walker GM (2009) Microfluidic aqueous two phase system for leukocyte concentration from whole blood. Biomed Microdevices 11(2):323–329. doi:10.1007/s10544-008-9238-8
Trindade IP, Diogo MM, Prazeres DMF, Marcos JC (2005) Purification of plasmid DNA vectors by aqueous two-phase extraction and hydrophobic interaction chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1082(2):176–184. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2005.05.079
Tsukamoto M, Taira S, Yamamura S, Morita Y, Nagatani N, Takamura Y, Tamiya E (2009) Cell separation by an aqueous two-phase system in a microfluidic device. Analyst 134(10):1994–1998. doi:10.1039/b909597g
Utada AS, Lorenceau E, Link DR, Kaplan PD, Stone HA, Weitz DA (2005) Monodisperse double emulsions generated from a microcapillary device. Science 308(5721):537–541. doi:10.1126/science.1109164
Yamada M, Kasim V, Nakashima M, Edahiro J, Seki M (2004) Continuous cell partitioning using an aqueous two-phase flow system in microfluidic devices. Biotechnol Bioeng 88(4):489–494. doi:10.1002/bit.20276
Zhao YC, Chen GW, Yuan Q (2007) Liquid-liquid two-phase mass transfer in the T-junction microchannels. AIChE J 53(12):3042–3053. doi:10.1002/aic.11333
Zijlstra GM, Michielsen MJF, deGooijer CD, vanderPol LA, Tramper J (1996) Hybridoma and CHO cell partitioning in aqueous two-phase systems. Biotechnol Prog 12(3):363–370. doi:10.1021/bp960017e
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21106115) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (SWJTU12CX049, SWJTU11ZT25). Tao Meng thanks the China Scholarship Council (201208510015). The authors thank Prof. Liang-Yin Chu (Sichuan University) for his enthusiastic support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Yushi Huang and Tao Meng have contributed equally to the work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Y., Meng, T., Guo, T. et al. Aqueous two-phase extraction for bovine serum albumin (BSA) with co-laminar flow in a simple coaxial capillary microfluidic device. Microfluid Nanofluid 16, 483–491 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-013-1245-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-013-1245-2