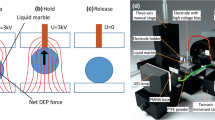
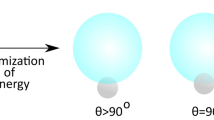
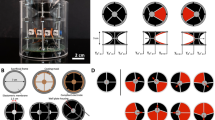
Abstract
A liquid marble is a liquid droplet coated with hydrophobic powder which enables the marble to be manipulated like a soft solid. Recently, liquid marbles have been used in applications such as microbioreactors for three-dimensional cell cultures and could be a new platform for digital microfluidics. Despite its potential significance, there is a lack of a systematic, thorough review and discussion on the manipulation schemes for liquid marbles. This paper presents past and recent manipulation schemes for liquid marbles. This paper discusses the major working principles, their advantages and drawbacks. Finally, the paper concludes with recent applications and the challenges of this research area.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arbatan T, Al-Abboodi A et al (2012a) Tumor inside a pearl drop. Adv Healthc Mater 1(4):467–469
Arbatan T, Li L et al (2012b) Liquid marbles as micro-bioreactors for rapid blood typing. Adv Healthc Mater 1(1):80–83
Aussillous P, Quere D (2001) Liquid marbles. Nature 411(6840):924–927
Aussillous P, Quere D (2004) Shapes of rolling liquid drops. J Fluid Mech 512:133–151
Aussillous P, Quere D (2006) Properties of liquid marbles. Proc R Soc A Math Phys Eng Sci 462(2067):973–999
Barthlott W, Neinhuis C (1997) Purity of the sacred lotus, or escape from contamination in biological surfaces. Planta 202(1):1–8
Bhosale PS, Panchagnula MV (2010) On synthesizing solid polyelectrolyte microspheres from evaporating liquid marbles. Langmuir 26(13):10745–10749
Bhosale PS, Panchagnula MV et al (2008) Mechanically robust nanoparticle stabilized transparent liquid marbles. Appl Phys Lett 93(3):034109
Bormashenko E (2011) Liquid marbles: properties and applications. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 16(4):266–271
Bormashenko E (2012) New insights into liquid marbles. Soft Matter 8(43):11018–11021
Bormashenko E, Musin A (2009) Revealing of water surface pollution with liquid marbles. Appl Surf Sci 255(12):6429–6431
Bormashenko E, Pogreb R et al (2008) New investigations on ferrofluidics: ferrofluidic marbles and magnetic-field-driven drops on superhydrophobic surfaces. Langmuir 24(21):12119–12122
Bormashenko E, Bormashenko Y et al (2009a) Water rolling and floating upon water: marbles supported by a water/marble interface. J Colloid Interface Sci 333(1):419–421
Bormashenko E, Bormashenko Y et al (2009b) On the mechanism of floating and sliding of liquid marbles. ChemPhysChem 10(4):654–656
Bormashenko E, Pogreb R et al (2009c) Shape, vibrations, and effective surface tension of water marbles. Langmuir 25(4):1893–1896
Bormashenko E, Balter R et al. (2010a) Micropump based on liquid marbles. Appl Phys Lett 97(9):091908
Bormashenko E, Bormashenko Y et al (2010b) Janus droplets: liquid marbles coated with dielectric/semiconductor particles. Langmuir 27(1):7–10
Bormashenko E, Pogreb R et al (2010c) Interfacial and conductive properties of liquid marbles coated with carbon black. Powder Technol 203(3):529–533
Bormashenko E, Pogreb R et al (2012a) Stable water and glycerol marbles immersed in organic liquids: from liquid marbles to Pickering-like emulsions. J Colloid Interface Sci 366(1):196–199
Bormashenko E, Pogreb R et al (2012b) Electrically deformable liquid marbles. J Adhes Sci Technol 25(12):1371–1377
Bormashenko E, Pogreb R et al. (2012c) Composite non-stick droplets and their actuation with electric field. Appl Phys Lett 100(15):151601
Braun H-G, Cardoso AZ (2012) Self-assembly of Fmoc-diphenylalanine inside liquid marbles. Colloids Surf B 97:43–50
Cengiz U, Erbil HY (2013) The lifetime of floating liquid marbles: the influence of particle size and effective surface tension. Soft Matter 9(37):8980–8991
Chin JM, Reithofer MR et al (2013) Supergluing MOF liquid marbles. Chem Commun 49(5):493–495
Dalbe M-J, Cosic D et al. (2011) Aggregation of frictional particles due to capillary attraction. Phys Rev E 83(5):051403
Dandan M, Erbil HY (2009) Evaporation rate of graphite liquid marbles: comparison with water droplets. Langmuir 25(14):8362–8367
Doganci MD, Sesli BU et al (2011) Liquid marbles stabilized by graphite particles from aqueous surfactant solutions. Colloids Surf A 384(1–3):417–426
Dorvee JR, Derfus AM et al (2004) Manipulation of liquid droplets using amphiphilic, magnetic one-dimensional photonic crystal chaperones. Nat Mater 3(12):896–899
Dupin D, Armes SP et al (2009) Stimulus-responsive liquid marbles. J Am Chem Soc 131(15):5386–5387
Erbil HY, McHale G et al (2002) Drop evaporation on solid surfaces: constant contact angle mode. Langmuir 18(7):2636–2641
Eshtiaghi N, Hapgood KP (2012) A quantitative framework for the formation of liquid marbles and hollow granules from hydrophobic powders. Powder Technol 223:65–76
Eshtiaghi N, Arhatari B et al (2009) Producing hollow granules from hydrophobic powders in high-shear mixer granulators. Adv Powder Technol 20(6):558–566
Eshtiaghi N, Liu JJS et al (2010) Formation of hollow granules from liquid marbles: small scale experiments. Powder Technol 197(3):184–195
Finn R (1986) Equilibrium capillary surfaces. Springer, New York
Fujii S, Murakami R (2008) Smart particles as foam and liquid marble stabilizers. KONA Powder Particle J 26:153–166
Fujii S, Kameyama S et al (2010) pH-responsive liquid marbles stabilized with poly(2-vinylpyridine) particles. Soft Matter 6(3):635–640
Fujii S, Suzaki M et al (2011) Liquid marbles prepared from pH-responsive sterically stabilized latex particles. Langmuir 27(13):8067–8074
Fujishige S, Kubota K et al (1989) Phase transition of aqueous solutions of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) and poly(N-isopropylmethacrylamide). Journal Phys Chem 93(8):3311–3313
Gao L, McCarthy TJ (2007) Ionic Liquid Marbles. Langmuir 23(21):10445–10447
Guan Y, Meng X et al (2014) Hollow microsphere with mesoporous shell by pickering emulsion polymerization as a potential colloidal collector for organic contaminants in water. Langmuir 30(13):3681–3686
Hashmi A, Strauss A et al (2012) Freezing of a liquid marble. Langmuir 28(28):10324–10328
Inoue M, Fujii S et al (2011) pH-responsive disruption of ‘liquid marbles’ prepared from water and poly(6-(acrylamido) hexanoic acid)-grafted silica particles. Polym J 43(9):778–784
Kralchevsky PA, Nagayama K (2000) Capillary interactions between particles bound to interfaces, liquid films and biomembranes. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 85(2–3):145–192
Laborie B, Lachaussee F et al (2013) How coatings with hydrophobic particles may change the drying of water droplets: incompressible surface versus porous media effects. Soft Matter 9(19):4822–4830
Lee DG, Kim HY (2008) Impact of a superhydrophobic sphere onto water. Langmuir 24(1):142–145
Mahadevan L, Pomeau Y (1999) Rolling droplets. Phys Fluids 11(9):2449–2453
Matsukuma D, Watanabe H et al (2013) Preparation of poly(lactic-acid)-particle stabilized liquid marble and the improvement of its stability by uniform shell formation through solvent vapor exposure. RSC Adv 3(21):7862–7866
McEleney P, Walker GM et al (2009) Liquid marble formation using hydrophobic powders. Chem Eng J 147(2–3):373–382
McHale G, Shirtcliffe NJ et al. (2007) Self-organization of hydrophobic soil and granular surfaces. Appl Phys Lett 90(5):054110
McHale G, Newton MI (2011) Liquid marbles: principles and applications. Soft Matter 7(12):5473–5481
Mele E, Bayer IS et al (2014) Biomimetic approach for liquid encapsulation with nanofibrillar cloaks. Langmuir 30(10):2896–2902
Miao YE, Lee HK et al (2014) Catalytic liquid marbles: Ag nanowire-based miniature reactors for highly efficient degradation of methylene blue. Chem Commun (Camb) 50(44):5923–5926
Nakai K, Fujii S et al (2013) Ultraviolet-light-responsive Liquid Marbles. Chem Lett 42(6):586–588
Newton MI, Herbertson DL et al (2007) Electrowetting of liquid marbles. J Phys D Appl Phys 40(1):20–24
Nguyen NT (2012) Micro-magnetofluidics: interactions between magnetism and fluid flow on the microscale. Microfluid Nanofluid 12(1–4):1–16
Nguyen NT (2013) Deformation of ferrofluid marbles in the presence of a permanent magnet. Langmuir 29(45):13982–13989
Ogawa S, Watanabe H et al (2014) Liquid marbles supported by monodisperse poly(methylsilsesquioxane) particles. Langmuir 30(30):9071–9075
Pike N, Richard D et al (2002) How aphids lose their marbles. Proc R Soc B Biol Sci 269(1497):1211–1215
Planchette C, Biance AL et al. (2013) Coalescence of armored interface under impact. Phys Fluids 25:042104
Richard D, Quere D (1999) Viscous drops rolling on a tilted non-wettable solid. Europhys Lett 48(3):286–291
Sarvi F, Jain K et al (2014) Cardiogenesis of embryonic stem cells with liquid marble micro-bioreactor. Adv Healthc Mater 4(1):77–86
Singh P, Joseph DD (2005) Fluid dynamics of floating particles. J Fluid Mech 530:31–80
Sivan V, Tang S-Y et al (2013) Liquid metal marbles. Adv Funct Mater 23(2):144–152
Tan TTY, Ahsan A et al (2014) Photoresponsive liquid marbles and dry water. Langmuir 30(12):3448–3454
Tian J, Arbatan T et al (2010a) Liquid marble for gas sensing. Chem Commun 46(26):4734–4736
Tian J, Arbatan T et al (2010b) Porous liquid marble shell offers possibilities for gas detection and gas reactions. Chem Eng J 165(1):347–353
Tian J, Fu N et al (2013) Respirable liquid marble for the cultivation of microorganisms. Colloids Surf B 106:187–190
Tosun A, Erbil HY (2009) Evaporation rate of PTFE liquid marbles. Appl Surf Sci 256(5):1278–1283
Ueno K, Hamasaki S et al (2014) Microcapsules fabricated from liquid marbles stabilized with latex particles. Langmuir 30(11):3051–3059
Vallet M, Berge B et al (1996) Electrowetting of water and aqueous solutions on poly(ethylene terephthalate) insulating films. Polymer 37(12):2465–2470
Vassileva ND, van den Ende D et al (2005) capillary forces between spherical particles floating at a liquid–liquid interface. Langmuir 21(24):11190–11200
Whitby CP, Bian X et al (2012) Spontaneous liquid marble formation on packed porous beds. Soft Matter 8(44):11336–11342
Whitby CP, Bian X et al (2013) Rolling, penetration and evaporation of alcohol–water drops on coarse and fine hydrophobic powders. Colloids Surf A 436:639–646
Wu H, Watanabe H et al (2013) Robust liquid marbles stabilized with surface-modified halloysite nanotubes. Langmuir 29(48):14971–14975
Xue Y, Wang H et al (2010) Magnetic liquid marbles: a “precise” miniature reactor. Adv Mater 22(43):4814–4818
Yan C, Li M et al (2011) Progress in Liquid Marbles. Prog Chem 23(4):649–656
Yang Z, Halvorsen E et al (2012) Power generation from conductive droplet sliding on electret film. Appl Phys Lett 100(21):213905
Yusa S-I, Morihara M et al (2014) Thermo-responsive liquid marbles. Polym J 46(3):145–148
Zang D, Chen Z et al (2013) Effect of particle hydrophobicity on the properties of liquid water marbles. Soft Matter 9(20):5067
Zang D, Lin K et al (2014) Tunable shape transformation of freezing liquid water marbles. Soft Matter 10(9):1309–1314
Zeng H, Zhao Y (2010) Dynamic behavior of a liquid marble based accelerometer. Appl Phys Lett 96(11):114104
Zhang L, Cha D et al (2012) Remotely controllable liquid marbles. Adv Mater 24(35):4756–4760
Zhao Y, Fang J et al (2010) magnetic liquid marbles: manipulation of liquid droplets using highly hydrophobic Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Adv Mater 22(6):707–710
Zhao Y, Xu ZG et al (2012) Magnetic liquid marbles, their manipulation and application in optical probing. Microfluid Nanofluid 13(4):555–564
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ooi, C.H., Nguyen, NT. Manipulation of liquid marbles. Microfluid Nanofluid 19, 483–495 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-015-1595-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-015-1595-z