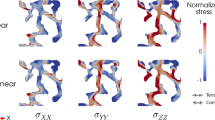
Abstract
Mechanical ventilation is not only a life saving treatment but can also cause negative side effects. One of the main complications is inflammation caused by overstretching of the alveolar tissue. Previously, studies investigated either global strains or looked into which states lead to inflammatory reactions in cell cultures. However, the connection between the global deformation, of a tissue strip or the whole organ, and the strains reaching the single cells lining the alveolar walls is unknown and respective studies are still missing. The main reason for this is most likely the complex, sponge-like alveolar geometry, whose three-dimensional details have been unknown until recently. Utilizing synchrotron-based X-ray tomographic microscopy, we were able to generate real and detailed three-dimensional alveolar geometries on which we have performed finite-element simulations. This allowed us to determine, for the first time, a three-dimensional strain state within the alveolar wall. Briefly, precision-cut lung slices, prepared from isolated rat lungs, were scanned and segmented to provide a three-dimensional geometry. This was then discretized using newly developed tetrahedral elements. The main conclusions of this study are that the local strain in the alveolar wall can reach a multiple of the value of the global strain, for our simulations up to four times as high and that thin structures obviously cause hotspots that are especially at risk of overstretching.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brewer, K., H. Sakai, A. M. Alencar, A. Majumdar, S. P. Arold, K. R. Lutchen, E. P. Ingenito, and B. Suki. Lung and alveolar wall elastic and hysteretic behavior in rats: effects of in vivo elastase treatment. J. Appl. Physiol. 95(5):1926–1936, 2003.
Cavalcante, F. S., S. Ito, H. Sakai, A. M. Alencar, M. P. Almeida, I. S. Andrade, A. Majumdar, E. P. Ingenito, and B. Suki. Mechanical interactions between collagen and proteoglycans: implications for the stability of lung tissue. J. Appl. Physiol. 98(2):672–679, 2005.
Chandel, N. S., and J. I. Sznajder. Stretching the lung and programmed cell death. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 279(6):1003–1004, 2000.
Comerford, A., C. Förster, and W. A. Wall. Structured tree impedance outflow boundary conditions for 3D lung simulations. J. Biomech. Eng. 132(8):081002, 2010.
Copland, I. B., and M. Post. Stretch-activated signaling pathways responsible for early response gene expression in fetal lung epithelial cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 210(1):133–143, 2007.
Dassow, C., L. Wiechert, C. Martin, S. Schumann, G. Müller-Newen, O. Pack, J. Guttmann, W. A. Wall, and S. Uhlig. Biaxial distension of precision-cut lung slices. J. Appl. Physiol. 108:713–721, 2010.
Denny, E., and R. C. Schroter. A model of non-uniform lung parenchyma distortion. J. Biomech. 39(4):652–663, 2006.
DiRocco, J. D., L. A. Pavone, D. E. Carney, Ch. J. Lutz, L. A. Gatto, S. K. Landas, and G. F. Nieman. Dynamic alveolar mechanics in four models of lung injury. Intensive Care Med 32(1):140–148, 2006.
Dos Santos, C. C., and A. S. Slutsky. Invited review: mechanisms of ventilator-induced lung injury: a perspective. J. Appl. Physiol. 89(4):1645–1655, 2000.
Dos Santos, C. C., and A. S. Slutsky. The contribution of biophysical lung injury to the development of biotrauma. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 68:585–618, 2006.
Gee, M. W., C. R. Dohrmann, S. W. Key, and W. A. Wall. A uniform nodal strain tetrahedron with isochoric stabilization. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 78(4):429–443, 2009.
Gefen, A., D. Elad, and R. J. Shiner. Analysis of stress distribution in the alveolar septa of normal and simulated emphysematic lungs. J. Biomech. 32(9):891–897, 1999.
Hintermüller, C., F. Marone, A. Isenegger, and M. Stampanoni. Image processing pipeline for synchrotron-radiation-based tomographic microscopy. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 17(4):550–559, 2010.
Holzapfel, G. A. Nonlinear Solid Mechanics: A Continuum Approach for Engineering. New York: Wiley, 2001.
Karakaplan, A. D., M. P. Bieniek, and R. Skalak. A mathematical model of lung parenchyma. J. Biomech. Eng. 102(2):124–136, 1980.
Kowe, R., R. C. Schroter, F. L. Matthews, and D. Hitchings. Analysis of elastic and surface tension effects in the lung alveolus using finite element methods. J. Biomech. 19(7):541–549, 1986.
Maksym, G. N., J. J. Fredberg, and J. H. T. Bates. Force heterogeneity in a two-dimensional network model of lung tissue elasticity. J. Appl. Physiol. 85:1223–1229, 1998.
Martin, C., S. Uhlig, and V. Ullrich. Videomicroscopy of methacholine-induced contraction of individual airways in precision-cut lung slices. Eur. Respir. J. 9(12):2479–2487, 1996.
Ning, Q., and X. Wang. Response of alveolar type ii epithelial cells to mechanical stretch and lipopolysaccharide. Respiration 74(5):579–585, 2007.
Perlman, C. E., and J. Bhattacharya. Alveolar expansion imaged by optical sectioning microscopy. J. Appl. Physiol. 103:1037–1044, 2007.
Rausch, S. M. K., C. Martin, P. B. Bornemann, S. Uhlig, and W. A. Wall. Material model of lung parenchyma based on living precision-cut lung slice testing. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. 4:583–592, 2011.
Schittny, J. C., and P. H. Burri. Development and Growth of the Lung. Fishman’s Pulmonary Diseases and Disorders. New-York: McGraw-Hill, 2008.
Schittny, J. C., S. I. Mund, and M. Stampanoni. Evidence and structural mechanism for late lung alveolarization. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 294(2):246–254, 2008.
Sobin, S. S., Y. C. Fung, and H. M. Tremer. Collagen and elastin fibers in human pulmonary alveolar walls. J. Appl. Physiol. 64(4):1659–1675, 1988.
Stampanoni, M., A. Groso, A. Isenegger, G. Mikuljan, Q. Chen, A. Bertrand, S. Henein, R. Betemps, U. Frommherz, P. Böhler, D. Meister, M. Lange, and R. Abela. Trends in synchrotron-based tomographic imaging: the SLS experience. In: Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE) Conference Series, 2006.
Suki, B., and J. H. T. Bates. Extracellular matrix mechanics in lung parenchymal diseases. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 163:33–43, 2008.
The Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Network. Ventilation with lower tidal volumes as compared with traditional tidal volumes for acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 342(18):1301–1308, 2000.
Toshima, M., Y. Ohtani, and O. Ohtani. Three-dimensional architecture of elastin and collagen fiber networks in the human and rat lung. Arch. Histol. Cytol. 67(1):31–40, 2004.
Tschanz, S. A., A. N. Makanya, B. Haenni, and P. H. Burri Effects of neonatal high-dose short-term glucocorticoid treatment on the lung: a morphologic and morphometric study in the rat. Pediatr. Res. 53(1):72–80, 2003.
Vlahakis, N. E., M. A. Schroeder, A. H. Limper, and R. D. Hubmayr. Stretch induces cytokine release by alveolar epithelial cells in vitro. Am. J. Physiol. 277(1):167–173, 1999.
Wall, W. A., and M. Gee. Baci: A Parallel Multiphysics Simulation Environment. Technical Report, Institute for Computational Mechanics, TUM, 2010.
Wall, W. A., L. Wiechert, A. Comerford, and S. Rausch. Towards a comprehensive computational model for the respiratory system. Int. J. Numer. Methods Biomed. Eng. 26(7):807–827, 2010.
Wiechert, L., and W. A. Wall. A nested dynamic multi-scale approach for 3D problems accounting for micro-scale multi-physics. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 199(21–22):1342–1351, 2010.
Wiechert, L., R. Metzke, and W. A. Wall. Modeling the mechanical behavior of lung tissue at the micro-level. J. Eng. Mech. 135(5):434–438, 2009.
Wilson, T. A., and H. Bachofen. A model for mechanical structure of the alveolar duct. J. Appl. Physiol. 52:1064–1070, 1982.
Yuan, H., E. P. Ingenito, and B. Suki. Dynamic properties of lung parenchyma: mechanical contributions of fiber network and interstitial cells. J. Appl. Physiol. 83(5):1420–1431, 1997 (discussion 1418–9).
Yuan, H., S. Kononov, F. S. Cavalcante, K. R. Lutchen, E. P. Ingenito, and B. Suki. Effects of collagenase and elastase on the mechanical properties of lung tissue strips. J. Appl. Physiol. 89(1):3–14, 2000.
Acknowledgments
Support by the German Science Foundation/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft DFG and the TUM Graduate School is gratefully acknowledged. We also gratefully acknowledge the help of Christian Martin and Stefan Uhlig for providing us with the PCLSs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Associate Editor Kerry Hourigan oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rausch, S.M.K., Haberthür, D., Stampanoni, M. et al. Local Strain Distribution in Real Three-Dimensional Alveolar Geometries. Ann Biomed Eng 39, 2835–2843 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-011-0328-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-011-0328-z