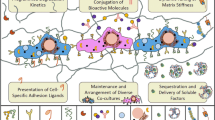
Abstract
In an effort to develop bioactive matrices for regenerative medicine, peptides have been used widely to promote interactions with cells and elicit desired behaviors in vivo. This paper describes strategies that utilize peptide-based molecules as building blocks to create supramolecular nanostructures that emulate not only the architecture but also the chemistry of the extracellular matrix in mammalian biology. After initiating a desired regenerative response in vivo, the innate biodegradability of these systems allow for the natural biological processes to take over in order to promote formation of a new tissue without leaving a trace of the nonnatural components. These bioactive matrices can either bind or mimic growth factors or other protein ligands to elicit a cellular response, promote specific mechano-biological responses, and also guide the migration of cells with programmed directionality. In vivo applications discussed in this review using peptide-based matrices include the regeneration of axons after spinal cord injury, regeneration of bone, and the formation of blood vessels in ischemic muscle as a therapy in peripheral arterial disease and cardiovascular diseases.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abouna, G. M. Organ shortage crisis: problems and possible solutions. Transplant. Proc. 40:34–38, 2008.
Angeloni, N. L., C. W. Bond, Y. Tang, D. A. Harrington, S. Zhang, S. I. Stupp, K. E. McKenna, and C. A. Podlasek. Regeneration of the cavernous nerve by Sonic hedgehog using aligned peptide amphiphile nanofibers. Biomaterials 32:1091–1101, 2011.
Banwell, E. F., E. S. Abelardo, D. J. Adams, M. A. Birchall, A. Corrigan, A. M. Donald, M. Kirkland, L. C. Serpell, M. F. Butler, and D. N. Woolfson. Rational design and application of responsive alpha-helical peptide hydrogels. Nat. Mater. 8:596–600, 2009.
Berndt, P., G. B. Fields, and M. Tirrell. Synthetic lipidation of peptides and amino-acids—monolayer structure and properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 117:9515–9522, 1995.
Berns, E. J., S. Sur, L. Pan, J. E. Goldberger, S. Suresh, S. Zhang, J. A. Kessler, and S. I. Stupp. Aligned neurite outgrowth and directed cell migration in self-assembled monodomain gels. Biomaterials 35:185–195, 2014.
Boekhoven, J., and S. I. Stupp. 25th anniversary article: supramolecular materials for regenerative medicine. Adv. Mater. 26:1642–1659, 2014.
Capila, I., and R. J. Linhardt. Heparin–protein interactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 41:391–412, 2002.
Cheng, T. Y., M. H. Chen, W. H. Chang, M. Y. Huang, and T. W. Wang. Neural stem cells encapsulated in a functionalized self-assembling peptide hydrogel for brain tissue engineering. Biomaterials 34:2005–2016, 2013.
D’Andrea, L. D., G. Iaccarino, R. Fattorusso, D. Sorriento, C. Carannante, D. Capasso, B. Trimarco, and C. Pedone. Targeting angiogenesis: structural characterization and biological properties of a de novo engineered VEGF mimicking peptide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102:14215–14220, 2005.
D’Andrea, L. D., A. Del Gatto, L. De Rosa, A. Romanelli, and C. Pedone. Peptides targeting angiogenesis related growth factor receptors. Curr. Pharm. Des. 15:2414–2429, 2009.
Davis, M. E., J. P. Motion, D. A. Narmoneva, T. Takahashi, D. Hakuno, R. D. Kamm, S. Zhang, and R. T. Lee. Injectable self-assembling peptide nanofibers create intramyocardial microenvironments for endothelial cells. Circulation 111:442–450, 2005.
Demirbag, B., P. Y. Huri, G. T. Kose, A. Buyuksungur, and V. Hasirci. Advanced cell therapies with and without scaffolds. Biotechnol. J. 6:1437–1453, 2011.
Di Lullo, G. A., S. M. Sweeney, J. Korkko, L. Ala-Kokko, and J. D. San Antonio. Mapping the ligand-binding sites and disease-associated mutations on the most abundant protein in the human, type I collagen. J. Biol. Chem. 277:4223–4231, 2002.
Dimmeler, S., S. Ding, T. A. Rando, and A. Trounson. Translational strategies and challenges in regenerative medicine. Nat. Med. 20:814–821, 2014.
Ellis-Behnke, R. G., Y. X. Liang, S. W. You, D. K. Tay, S. Zhang, K. F. So, and G. E. Schneider. Nano neuro knitting: peptide nanofiber scaffold for brain repair and axon regeneration with functional return of vision. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103:5054–5059, 2006.
Fishwick, C. W. G., A. J. Beevers, L. M. Carrick, C. D. Whitehouse, A. Aggeli, and N. Boden. Structures of helical β-tapes and twisted ribbons: the role of side-chain interactions on twist and bend behavior. Nano Lett. 3:1475–1479, 2003.
Folkman, J., and M. Klagsbrun. Angiogenic factors. Science 235:442–447, 1987.
Forbes, S. J., and N. Rosenthal. Preparing the ground for tissue regeneration: from mechanism to therapy. Nat. Med. 20:857–869, 2014.
Gelain, F., D. Silva, A. Caprini, F. Taraballi, A. Natalello, O. Villa, K. T. Nam, R. N. Zuckermann, S. M. Doglia, and A. Vescovi. BMHP1-derived self-assembling peptides: hierarchically assembled structures with self-healing propensity and potential for tissue engineering applications. ACS Nano 5:1845–1859, 2011.
Genove, E., C. Shen, S. Zhang, and C. E. Semino. The effect of functionalized self-assembling peptide scaffolds on human aortic endothelial cell function. Biomaterials 26:3341–3351, 2005.
Giano, M. C., D. J. Pochan, and J. P. Schneider. Controlled biodegradation of self-assembling beta-hairpin peptide hydrogels by proteolysis with matrix metalloproteinase-13. Biomaterials 32:6471–6477, 2011.
Griffith, L. G., and M. A. Swartz. Capturing complex 3D tissue physiology in vitro. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7:211–224, 2006.
Haines-Butterick, L., K. Rajagopal, M. Branco, D. Salick, R. Rughani, M. Pilarz, M. S. Lamm, D. J. Pochan, and J. P. Schneider. Controlling hydrogelation kinetics by peptide design for three-dimensional encapsulation and injectable delivery of cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104:7791–7796, 2007.
Hartgerink, J. D., E. Beniash, and S. I. Stupp. Self-assembly and mineralization of peptide-amphiphile nanofibers. Science 294:1684–1688, 2001.
Hernandez-Gordillo, V., and J. Chmielewski. Mimicking the extracellular matrix with functionalized, metal-assembled collagen peptide scaffolds. Biomaterials 35:7363–7373, 2014.
Horner, P. J., and F. H. Gage. Regenerating the damaged central nervous system. Nature 407:963–970, 2000.
Jung, J. P., A. K. Nagaraj, E. K. Fox, J. S. Rudra, J. M. Devgun, and J. H. Collier. Co-assembling peptides as defined matrices for endothelial cells. Biomaterials 30:2400–2410, 2009.
Khurana, R., M. Simons, J. F. Martin, and I. C. Zachary. Role of angiogenesis in cardiovascular disease: a critical appraisal. Circulation 112:1813–1824, 2005.
Kim, M.-H., M. Park, K. Kang, and I. S. Choi. Neurons on nanometric topographies: insights into neuronal behaviors in vitro. Biomater. Sci. 2:148–155, 2014.
Kong, H. J., and D. J. Mooney. Microenvironmental regulation of biomacromolecular therapies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 6:455–463, 2007.
Kretsinger, J. K., L. A. Haines, B. Ozbas, D. J. Pochan, and J. P. Schneider. Cytocompatibility of self-assembled β-hairpin peptide hydrogel surfaces. Biomaterials 26:5177–5186, 2005.
Kumar, V. A., N. L. Taylor, A. A. Jalan, L. K. Hwang, B. K. Wang, and J. D. Hartgerink. A nanostructured synthetic collagen mimic for hemostasis. Biomacromolecules 15:1484–1490, 2014.
Lee, S. S., B. J. Huang, S. R. Kaltz, S. Sur, C. J. Newcomb, S. R. Stock, R. N. Shah, and S. I. Stupp. Bone regeneration with low dose BMP-2 amplified by biomimetic supramolecular nanofibers within collagen scaffolds. Biomaterials 34:452–459, 2013.
Lee, S. S., E. L. Hsu, M. Mendoza, J. Ghodasra, M. S. Nickoli, A. Ashtekar, M. Polavarapu, J. Babu, R. M. Riaz, J. D. Nicolas, D. Nelson, S. Z. Hashmi, S. R. Kaltz, J. S. Earhart, B. R. Merk, J. S. McKee, S. F. Bairstow, R. N. Shah, W. K. Hsu, and S. I. Stupp. Gel scaffolds of BMP-2-binding peptide amphiphile nanofibers for spinal arthrodesis. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2014. doi:10.1002/adhm.201400129.
Li, A., A. Hokugo, A. Yalom, E. J. Berns, N. Stephanopoulos, M. T. McClendon, L. A. Segovia, I. Spigelman, S. I. Stupp, and R. Jarrahy. A bioengineered peripheral nerve construct using aligned peptide amphiphile nanofibers. Biomaterials 35:8780–8790, 2014.
Lin, Y. D., C. Y. Luo, Y. N. Hu, M. L. Yeh, Y. C. Hsueh, M. Y. Chang, D. C. Tsai, J. N. Wang, M. J. Tang, E. I. Wei, M. L. Springer, and P. C. Hsieh. Instructive nanofiber scaffolds with VEGF create a microenvironment for arteriogenesis and cardiac repair. Sci. Transl. Med. 4:146ra109, 2012.
Lutolf, M. P., P. M. Gilbert, and H. M. Blau. Designing materials to direct stem-cell fate. Nature 462:433–441, 2009.
Mason, J. M., and K. M. Arndt. Coiled coil domains: stability, specificity, and biological implications. ChemBioChem 5:170–176, 2004.
Mata, A., Y. B. Geng, K. J. Henrikson, C. Aparicio, S. R. Stock, R. L. Satcher, and S. I. Stupp. Bone regeneration mediated by biomimetic mineralization of a nanofiber matrix. Biomaterials 31:6004–6012, 2010.
Matson, J. B., R. H. Zha, and S. I. Stupp. Peptide self-assembly for crafting functional biological materials. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 15:225–235, 2011.
Matsuurua, K. Rational design of self-assembled proteins and peptides for nano- and micro-sized architectures. RSC Adv. 4:2942–2953, 2014.
McClendon, M. T., and S. I. Stupp. Tubular hydrogels of circumferentially aligned nanofibers to encapsulate and orient vascular cells. Biomaterials 33:5713–5722, 2012.
Mehrban, N., E. Abelardo, A. Wasmuth, K. L. Hudson, L. M. Mullen, A. R. Thomson, M. A. Birchall, and D. N. Woolfson. Assessing cellular response to functionalized alpha-helical peptide hydrogels. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 3:1387–1391, 2014.
Moyer, T. J., H. G. Cui, and S. I. Stupp. Tuning nanostructure dimensions with supramolecular twisting. J. Phys. Chem. B 117:4604–4610, 2013.
Müller-Mai, C. M., S. I. Stupp, C. Voigt, and U. Gross. Nanoapatite and organoapatite implants in bone: histology and ultrastructure of the interface. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 29:9–18, 1995.
Newcomb, C. J., R. Bitton, Y. S. Velichko, M. L. Snead, and S. I. Stupp. The role of nanoscale architecture in supramolecular templating of biomimetic hydroxyapatite mineralization. Small 8:2195–2202, 2012.
O’Leary, L. E., J. A. Fallas, E. L. Bakota, M. K. Kang, and J. D. Hartgerink. Multi-hierarchical self-assembly of a collagen mimetic peptide from triple helix to nanofibre and hydrogel. Nat. Chem. 3:821–828, 2011.
Palmer, L. C., C. J. Newcomb, S. R. Kaltz, E. D. Spoerke, and S. I. Stupp. Biomimetic systems for hydroxyapatite mineralization inspired by bone and enamel. Chem. Rev. 108:4754–4783, 2008.
Palmgren, B., Y. Jiao, E. Novozhilova, S. I. Stupp, and P. Olivius. Survival, migration and differentiation of mouse tau-GFP embryonic stem cells transplanted into the rat auditory nerve. Exp. Neurol. 235:599–609, 2012.
Pashuck, E. T., and M. M. Stevens. Designing regenerative biomaterial therapies for the clinic. Sci. Transl. Med. 4:160–164, 2012.
Pashuck, E. T., H. G. Cui, and S. I. Stupp. Tuning supramolecular rigidity of peptide fibers through molecular structure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132:6041–6046, 2010.
Pires, M. M., D. E. Przybyla, and J. Chmielewski. A metal-collagen peptide framework for three-dimensional cell culture. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 48:7813–7817, 2009.
Rajangam, K., H. A. Behanna, M. J. Hui, X. Q. Han, J. F. Hulvat, J. W. Lomasney, and S. I. Stupp. Heparin binding nanostructures to promote growth of blood vessels. Nano Lett. 6:2086–2090, 2006.
Reddi, A. H. Role of morphogenetic proteins in skeletal tissue engineering and regeneration. Nat. Biotechnol. 16:247–252, 1998.
Saha, K., A. J. Keung, E. F. Irwin, Y. Li, L. Little, D. V. Schaffer, and K. E. Healy. Substrate modulus directs neural stem cell behavior. Biophys. J. 95:4426–4438, 2008.
Schneider, J. P., D. J. Pochan, B. Ozbas, K. Rajagopal, L. Pakstis, and J. Kretsinger. Responsive hydrogels from the intramolecular folding and self-assembly of a designed peptide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124:15030–15037, 2002.
Semino, C. E., J. R. Merok, G. G. Crane, G. Panagiotakos, and S. Zhang. Functional differentiation of hepatocyte-like spheroid structures from putative liver progenitor cells in three-dimensional peptide scaffolds. Differentiation 71:262–270, 2003.
Silva, G. A., C. Czeisler, K. L. Niece, E. Beniash, D. A. Harrington, J. A. Kessler, and S. I. Stupp. Selective differentiation of neural progenitor cells by high-epitope density nanofibers. Science 303:1352–1355, 2004.
Silver, J., and J. H. Miller. Regeneration beyond the glial scar. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 5:146–156, 2004.
Stendahl, J. C., L. J. Wang, L. W. Chow, D. B. Kaufman, and S. I. Stupp. Growth factor delivery from self-assembling nanofibers to facilitate islet transplantation. Transplantation 86:478–481, 2008.
Stevens, M. M. Biomaterials for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Today 11:18–25, 2008.
Storrie, H., M. O. Guler, S. N. Abu-Amara, T. Volberg, M. Rao, B. Geiger, and S. I. Stupp. Supramolecular crafting of cell adhesion. Biomaterials 28:4608–4618, 2007.
Sur, S., E. T. Pashuck, M. O. Guler, M. Ito, S. I. Stupp, and T. Launey. A hybrid nanofiber matrix to control the survival and maturation of brain neurons. Biomaterials 33:545–555, 2012.
Sur, S., C. J. Newcomb, M. J. Webber, and S. I. Stupp. Tuning supramolecular mechanics to guide neuron development. Biomaterials 34:4749–4757, 2013.
Sur, S., M. O. Guler, M. J. Webber, E. T. Pashuck, M. Ito, S. I. Stupp, and T. Launey. Synergistic regulation of cerebellar Purkinje neuron development by laminin epitopes and collagen on an artificial hybrid matrix construct. Biomater. Sci. 2:903–914, 2014.
Tongers, J., J. G. Roncalli, and D. W. Losordo. Therapeutic angiogenesis for critical limb ischemia: microvascular therapies coming of age. Circulation 118:9–16, 2008.
Tysseling-Mattiace, V. M., V. Sahni, K. L. Niece, D. Birch, C. Czeisler, M. G. Fehlings, S. I. Stupp, and J. A. Kessler. Self-assembling nanofibers inhibit glial scar formation and promote axon elongation after spinal cord injury. J. Neurosci. 28:3814–3823, 2008.
Velichko, Y. S., S. I. Stupp, and M. O. de la Cruz. Molecular simulation study of peptide amphiphile self-assembly. J. Phys. Chem. B 112:2326–2334, 2008.
Webber, M. J., J. Tongers, C. J. Newcomb, K.-T. Marquardt, J. Bauersachs, D. W. Losordo, and S. I. Stupp. Supramolecular nanostructures that mimic VEGF as a strategy for ischemic tissue repair. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 108:13438–13443, 2011.
Webber, M. J., E. J. Berns, and S. I. Stupp. Supramolecular nanofibers of peptide amphiphiles for medicine. Israel J. Chem. 53:530–554, 2013.
White, H. D., and D. P. Chew. Acute myocardial infarction. Lancet 372:570–584, 2008.
Yokoi, H., T. Kinoshita, and S. Zhang. Dynamic reassembly of peptide RADA16 nanofiber scaffold. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102:8414–8419, 2005.
Zhang, S., T. Holmes, C. Lockshin, and A. Rich. Spontaneous assembly of a self-complementary oligopeptide to form a stable macroscopic membrane. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90:3334–3338, 1993.
Zhang, S., M. A. Greenfield, A. Mata, L. C. Palmer, R. Bitton, J. R. Mantei, C. Aparicio, M. O. de la Cruz, and S. I. Stupp. A self-assembly pathway to aligned monodomain gels. Nat. Mater. 9:594–601, 2010.
Acknowledgments
Research performed by the laboratory of the authors described in the review articles was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (NIH): National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (NIDCR) (5R01DE015920–9), Bioengineering Research Partnerships (BRP) (5R01EB003806–09, 5R01HL116577–02), Center of Cancer Nanotechnology Excellence (CCNE) (F5U54CA151880–05), and Project Parent Grant (PPG) (P01HL108795–04), as well as the Dixon Translational Research Grant and the Center for Regenerative Nanomedicine Award at the Simpson Querrey Institute. C.M.R.P. gratefully acknowledges support from a BRP Supplement Award (3R01EB003806–09S1), N.S. from an International Institute for Nanotechnology (IIN) Postdoctoral Fellowship and from a Ruth L. Kirschstein NRSA Postdoctoral Fellowship (5F32NS077728-03), and S.S.L. from a Samsung Scholarship Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Rosemarie Hunziker oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rubert Pérez, C.M., Stephanopoulos, N., Sur, S. et al. The Powerful Functions of Peptide-Based Bioactive Matrices for Regenerative Medicine. Ann Biomed Eng 43, 501–514 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-014-1166-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-014-1166-6