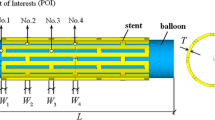
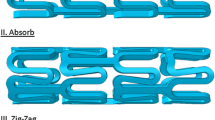
Abstract
In recent years, advances in computing power and computational methods have made it possible to perform detailed simulations of the coronary artery stenting procedure and of related virtual tests of performance (including fatigue resistance, corrosion and haemodynamic disturbance). Simultaneously, there has been a growth in systematic computational optimisation studies, largely exploiting the suitability of surrogate modelling methods to time-consuming simulations. To date, systematic optimisation has focussed on stent shape optimisation and has re-affirmed the complexity of the multi-disciplinary, multi-objective problem at hand. Also, surrogate modelling has predominantly involved the method of Kriging. Interestingly, though, optimisation tools, particularly those associated with Kriging, haven’t been used as efficiently as they could have been. This has especially been the case with the way that Kriging predictor functions have been updated during the search for optimal designs. Nonetheless, the potential for future, carefully posed, optimisation strategies has been suitably demonstrated, as described in this review.




Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
ACCF/AHA/SCAI: American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association/Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions.
DACE: Design and analysis of computer experiments.
References
Amirjani, A., M. Yousefi, and M. Cheshmaroo. Parametrical optimization of stent design; a numerical-based approach. Comput. Mat. Sci. 90:210–220, 2014.
Atherton, M. A., and R. A. Bates. Robust optimization of cardiovascular stents: a comparison of methods. Eng. Optimiz. 36(2):207–217, 2004.
Auricchio, F., M. Di Loreto, and E. Sacco. Finite element analysis of a stenotic artery revascularisation through a stent insertion. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 4:249–263, 2001.
Azaouzi, M., N. Lebaal, A. Makradi, and S. Belouettar. Optimization based simulation of self-expanding Nitinol stent. Mater. Des. 50:917–928, 2013.
Blouza, A., L. Dumas and I. M’Baye. Multiobjective optimization of a stent in a fluid-structure context. Proceedings of the 2008 GECCO Conference Companion on Genetic and Evolutionary Computation, pp. 2055–2060, 2008.
Booker, A. J., J. E. Dennis, P. D. Frank, D. B. Serafini, and V. Torczon. A rigorous framework for optimization of expensive functions by surrogates. Struct. Optim. 17:1–13, 1999.
Bozsak, F., D. Gonzalez-Rodriguez, Z. Sternberger, P. Belitz, T. Bewley, J-M. Chomaz, and A. I. Barakat. Optimization of drug delivery by drug-eluting stents. PLoS One 10(6):e0130182, 2015. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0130182.
Caixeta, A., P. Genereux, G. Dangas, and R. Mehran. In-stent restenosis in the drug-eluting stent era. In: Chapter 28 in Oxford Textbook of Interventional Cardiology, edited by S. Redwood, N. Curzen, and M. Thomas. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2010.
Clune, R., D. Kelliher, J. C. Robinson, and J. S. Campbell. NURBS modeling and structural shape optimization of cardiovascular stents. Struct. Multidisc. Optim. 50:159–168, 2014.
Conway, C., F. Sharif, J. McGarry, and P. McHugh. A computational test-bed to assess coronary stent implantation mechanics using a population-specific approach. Cardiovasc. Eng. Technol. 3(4):374–387, 2012.
De Beule, M., S. Van Cauter, P. Mortier, D. Van Loo, R. Van Impe, and P. Verdonck. Virtual optimization of self-expandable braided wire stents. Med. Eng. Phys. 31:448–453, 2009.
Deb, K., and R. B. Agrawal. A fast and elitist multi-objective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 6(2):182–197, 2002.
Deb, K., M. Mohan and S. Mishra. A fast multiobjective evolutionary algorithm for finding well-spread pareto-optimal solutions. KanGAL Report Number 2003002, 2003.
Dumoulin, C., and B. Cochelin. Mechanical behaviour modelling of balloon-expandable stents. J. Biomech. 33:1461–1470, 2000.
Etave, F., G. Finet, M. Boivin, J. Boyer, G. Rioufol, and G. Thollet. Mechanical properties of coronary stents determined by using finite element analysis. J. Biomech. 34:1065–1075, 2001.
FDA. Non-clinical engineering tests and recommended labeling for intravascular stents and associated delivery systems. http://www.fda.gov/medicaldevices/deviceregulationandguidance/guidancedocuments/ucm071863.htm. 2010. Accessed 1st April 2015.
Forrester, A. I. J., A. Sóbester, and A. J. Keane. Engineering Design via Surrogate Modelling: A Practical Guide. Chichester: Wiley, 2008.
Gijsen, F., F. Migliavacca, S. Schievano, L. Socci, L. Petrini, A. Thury, J. Wentzel, A. van der Steen, P. Serruys, and G. Dubini. Simulation of stent deployment in a realistic human coronary artery. BioMed. Eng. OnLine 7:23, 2008.
Grogan, J. A., S. B. Leen, and P. E. McHugh. Optimizing the design of a bioabsorbable metal stent using computer simulation methods. Biomaterials 34(33):8049–8060, 2013.
Gundert, T. J., A. L. Marsden, W. Yang, and J. F. LaDisa, Jr. Optimization of cardiovascular stent design using computational fluid dynamics. J. Biomech. Eng. 134:011002-1–011002-8, 2012.
Harewood, F., R. Thornton and P. Sharp. Step change in design: exploring sixty stent design variations overnight. www.altairproductdesign.com, 2011.
Harold, J. G., T. A. Bass, T. M. Bashore, et al. ACCF/AHA/SCAI, Update of the clinical competence statement on coronary artery interventional procedures. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 128:436–472, 2013.
He, Y., N. Duraiswamy, A. O. Frank, and J. E. Moore, Jr. Blood flow in stented arteries: a parametric comparison of strut design patterns in three dimensions. ASME J. Biomech. Eng. 127:637–647, 2005.
Johnson, P. M., J. Patel, M. Yeung, and P. Kaul. Intra-coronary imaging modalities. Curr. Treat. Options Cardiovasc. Med. 16:304, 2014.
Jones, D. R. A taxonomy of global optimization methods based on response surfaces. J. Glob. Optim. 21(4):345–383, 2001.
Krige, D. G. A statistical approach to some basic mine valuation problems on the Wit-watersrand. J. Chem. Metall. Miner. Soc. SA 52(6):119–139, 1951.
Levine, G. N., E. R. Bates, J. C. Blankenship, et al. ACCF/AHA/SCAI guideline for percutaneous coronary intervention: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 58:e44–e122, 2011.
Li, H., T. Qiu, B. Zhu, J. Wu, and X. Wang. Design optimization of coronary stent based on finite element models. Sci. World J. 2013:630243, 2013.
Li, N., H. Zhang, and H. Ouyang. Shape optimization of coronary artery stent based on a parametric model. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 45:468–475, 2009.
Lophaven, S., H. Nielsen and J. Søndergaard. DACE—A MATLAB Kriging Toolbox Version 2.0, Technical University of Denmark, Copenhagen, Technical Report IMM-TR-2002-12, 2002.
Martin, D., and F. J. Boyle. Computational structural modelling of coronary stent deployment: a review. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 14(4):331–348, 2011.
Migliavacca, F., L. Petrini, M. Colombo, F. Auricchio, and R. Pietrabissa. Mechanical behavior of coronary stents investigated through the finite element method. J. Biomech. 35:803–811, 2002.
Morice, M.-C., P. Serruys, J. Sousa, J. Fajadet, E. Ban Hayashi, M. Perin, A. Colombo, G. Schuler, P. Barragan, G. Guagliumi, et al. The RAVEL Study Group. A randomized comparison of a sirolimus-eluting stent with a standard stent for coronary revascularization. N. Engl. J. Med. 346:1773–1780, 2002.
Morlacchi, S., and F. Migliavacca. Modeling stented coronary arteries: where we are, where to go? Ann. Biomed. Eng. 41(7):1428–1444, 2013.
Morris, M. D., and T. J. Mitchell. Exploratory designs for computational experiments. J. Stat. Plan. Inference 43:381–402, 1995.
Moses, J., M. Leon, J. Popma, P. Fitzgerald, D. Holmes, C. O’Shaughnessy, R. Caputo, D. Kereiakes, D. Williams, P. Teirstein, et al. The SIRIUS Investigators. Sirolimus-eluting stents versus standard stents in patients with stenosis in a native coronary artery. N. Engl. J. Med. 349:1315–1323, 2003.
Murphy, J., and F. J. Boyle. Predicting neointimal hyperplasia in stented arteries using time-dependant computational fluid dynamics: a review. Comput. Biol. Med. 40:408–418, 2010.
Pant, S., N. W. Bressloff, and G. Limbert. Geometry parameterization and multidisciplinary constrained optimisation of coronary stents. Biomech. Model Mechanobiol. 11(1):61–82, 2012.
Pant, S., G. Limbert, N. Curzen, and N. W. Bressloff. Multi-objective design optimisation of coronary stents. Biomaterials 32:7755–7773, 2011.
Rogers, C., D. Y. Tseng, J. C. Squere, and E. R. Edelman. Balloon-artery interactions during stent placement. A finite element analysis approach to pressure, compliance, and stent design as contributors to vascular injury. Circ. Res. 84:378–383, 1999.
Srinivas, K., T. Nakayama, M. Ohta, S. Obayashi, and T. Yamaguchi. Studies on design optimization of coronary stents. ASME J. Med. Devices 2(1):011004, 2008.
Statnikov, R., and J. Matusov. Multicriteria Analysis in Engineering: Using the PSI Method with MOVI 1.0. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publications, 2002.
Stoeckel, D., C. Bonsignore, and S. Duda. A survey of stent designs. Minim. Invasive Ther. Allied Technol. 11(4):137–147, 2002.
Timmins, L. H., M. R. Moreno, C. A. Meyer, J. C. Criscione, A. Rachev, and J. E. Moore, Jr. Stented artery biomechanics and device design optimization. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 45(5):505–513, 2007.
Wang, W.-Q., D.-K. Liang, D.-Z. Liang, and M. Qi. Analysis of the transient expansion behavior and design optimization of coronary stents by finite element method. J. Biomech. 29:21–32, 2006.
Wu, W., L. Petrini, D. Gastaldi, T. Villa, M. Vedani, E. Lesma, B. Previtali, and F. Migliavacca. Finite element shape optimization for biodegradable magnesium alloy stents. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 38(9):2829–2840, 2010.
Wu, W., D. Z. Yang, Y. Y. Huang, M. Qi, and W. Q. Wang. Topology optimization of a novel stent platform with drug reservoirs. Med. Eng. Phys. 30(9):1177–1185, 2008.
Yoon, H.-J., and S.-H. Hur. Optimization of stent deployment by intravascular ultrasound. Korean J. Int. Med. 27:30–38, 2012.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Medtronic Inc. (Minnesota, USA) for their unrestricted support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Peter E. McHugh oversaw the review of this article.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bressloff, N.W., Ragkousis, G. & Curzen, N. Design Optimisation of Coronary Artery Stent Systems. Ann Biomed Eng 44, 357–367 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-015-1373-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-015-1373-9