Abstract
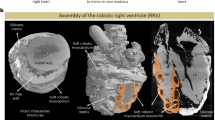
We introduce an implantable intracardiac soft robotic right ventricular ejection device (RVED) for dynamic approximation of the right ventricular (RV) free wall and the interventricular septum (IVS) in synchrony with the cardiac cycle to augment blood ejection in right heart failure (RHF). The RVED is designed for safe and effective intracardiac operation and consists of an anchoring system deployed across the IVS, an RV free wall anchor, and a pneumatic artificial muscle linear actuator that spans the RV chamber between the two anchors. Using a ventricular simulator and a custom controller, we characterized ventricular volume ejection, linear approximation against different loads and the effect of varying device actuation periods on volume ejection. The RVED was then tested in vivo in adult pigs (n = 5). First, we successfully deployed the device into the beating heart under 3D echocardiography guidance (n = 4). Next, we performed a feasibility study to evaluate the device’s ability to augment RV ejection in an experimental model of RHF (n = 1). RVED actuation augmented RV ejection during RHF; while further chronic animal studies will provide details about the efficacy of this support device. These results demonstrate successful design and implementation of the RVED and its deployment into the beating heart. This soft robotic ejection device has potential to serve as a rapidly deployable system for mechanical circulatory assistance in RHF.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, M. B., J. Goldstein, C. Milano, L. D. Morris, R. L. Kormos, J. Bhama, N. K. Kapur, A. Bansal, J. Garcia, J. N. Baker, S. Silvestry, W. L. Holman, P. S. Douglas, and W. O’Neill. Benefits of a novel percutaneous ventricular assist device for right heart failure: the prospective RECOVER RIGHT study of the Impella RP device. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 34:1549–1560, 2015.
Anderson, M. B., and M. O’Brien. Use of the impella 2.5 microaxial pump for right ventricular support after insertion of heartmate II left ventricular assist device. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 95:e109–e110, 2013.
Anderson, R. H., J. Yanni, M. R. Boyett, N. J. Chandler, and H. Dobrzynski. The anatomy of the cardiac conduction system. Clin. Anat. 22:99–113, 2009.
Auger, D. A., X. Zhong, and F. H. Epstein. Mapping right ventricular myocardial mechanics using 3D cine DENSE cardiovascular magnetic resonance. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 14:1, 2012.
Bramos, D., N. Tsirikos, G. Kottis, C. Pamboucas, V. Kostopoulou, C. Trika, I. Ikonomidis, and S. Toumanidis. The acute effect of an echo-contrast agent on right ventricular dimensions and contractility in pigs. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 51:86–91, 2008.
Buckberg, G. D., and Restore Group. The ventricular septum: the lion of right ventricular function, and its impact on right ventricular restoration. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 29:S272–S278, 2006.
Chou, C. P., and B. Hannaford. Static and dynamic characteristics of McKibben pneumatic artificial muscles. IEEE. Int. Conf. Robot. Autom. 1:281–286, 1994.
Chou, C. P., and B. Hannaford. Measurement and modeling of McKibben pneumatic artificial muscles. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 12:90–102, 1996.
Geva, T., A. J. Powell, E. C. Crawford, T. Chung, and S. D. Colan. Evaluation of regional differences in right ventricular systolic function by acoustic quantification echocardiography and cine magnetic resonance imaging. Circulation 98:339–345, 1998.
Haddad, F., R. Doyle, D. J. Murphy, and S. A. Hunt. Right ventricular function in cardiovascular disease, part II: pathophysiology, clinical importance, and management of right ventricular failure. Circulation 117:1717–1731, 2008.
Hsu, D. T., and G. D. Pearson. Heart failure in children part I: history, etiology, and pathophysiology. Circ Heart Fail. 2:63–70, 2009.
Hsu, P., J. Parker, C. Egger, R. Autschbach, T. Schmitz-Rode, and U. Steinseifer. Mechanical circulatory support for right heart failure: current technology and future outlook. Artif. Organs 36:332–347, 2012.
James, T. N., and G. E. Burch. Blood supply of the human interventricular septum. Circulation 17:391–396, 1958.
Lai, W. W., K. Gauvreau, E. S. Rivera, and S. Saleeb. Accuracy of guideline recommendations for two-dimensional quantification of the right ventricle by echocardiography. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 24:691–698, 2008.
Larose, E., P. Ganz, H. G. Reynolds, S. Dorbala, M. F. Di Carli, K. A. Brown, and R. Y. Kwong. Right ventricular dysfunction assessed by cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging predicts poor prognosis late after myocardial infarction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 49:855–862, 2007.
Leclair J., M. Doumit, and G. McAllister. Analytical stiffness modeling and experimental validation for a pneumatic artificial muscle. ASME, 2014.
Markel, T. A., G. M. Wairiuko, T. Lahm, P. R. Crisostomo, M. Wang, C. M. Herring, and D. R. Meldrum. The right heart and its distinct mechanisms of development, function, and failure. J. Surg. Res. 146:304–313, 2008.
Meyer, P., G. S. Filippatos, M. I. Ahmed, A. E. Iskandrian, V. Bittner, G. J. Perry, M. White, I. B. Aban, M. Mujib, L. J. Dell’Italia, and A. Ahmed. Effects of right ventricular ejection fraction on outcomes in chronic systolic heart failure. Circulation 121:252–258, 2010.
Obiajulu S. C., and E. T. Roche. Soft pneumatic artificial muscles with low threshold pressures for a cardiac compression device. ASME, 2013.
Park, E., N. Mehandru, and T. L. Beltran. An intraventricular soft robotic pulsatile assist device for right ventricular heart failure. J. Med. Dev. 8:020908, 2014.
Roche E. T., and M. A. Horvath. Design and fabrication of a soft robotic direct cardiac compression device. ASME, 2015.
Roche, E. T., M. A. Horvath, I. Wamala, A. Alazmani, S.-E. Song, W. Whyte, Z. Machaidze, C. J. Payne, J. C. Weaver, G. Fishbein, J. Kuebler, N. V. Vasilyev, D. J. Mooney, F. A. Pigula, and C. J. Walsh. Soft robotic sleeve supports heart function. Sci. Transl. Med. 9:3925, 2017.
Roche, E. T., R. Wohlfarth, J. T. B. Overvelde, N. V. Vasilyev, F. A. Pigula, D. J. Mooney, K. Bertoldi, and C. J. Walsh. A bioinspired soft actuated material. Adv. Mater. 26:1200–1206, 2014.
Stone, G. W., E. M. Ohman, and M. F. Miller. Contemporary utilization and outcomes of intra-aortic balloon counterpulsation in acute myocardial infarction: the benchmark registry. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 41:1940–1945, 2003.
Vasilyev, N. V., J. F. Martinez, and F. P. Freudenthal. Three-dimensional echo and videocardioscopy-guided atrial septal defect closure. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 82:1322–1326, 2006.
van de Veerdonk, M. C., T. Kind, J. T. Marcus, G.-J. Mauritz, M. W. Heymans, H.-J. Bogaard, A. Boonstra, K. M. J. Marques, N. Westerhof, and A. Vonk-Noordegraaf. Progressive right ventricular dysfunction in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension responding to therapy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 58:2511–2519, 2011.
Voelkel N. F., R. A. Quaife, L. A. Leinwand, R. J. Barst, M. D. McGoon, D. R. Meldrum, J. Dupuis, C. S. Long, L. J. Rubin, F. W. Smart, Y. J. Suzuki, M. Gladwin, E. M. Denholm, D. B. Gail, and L. National heart and blood institute working group on cellular and molecular mechanisms of right heart failure. Right ventricular function and failure: report of a National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute working group on cellular and molecular mechanisms of right heart failure, 2006.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the NIH/NHLBI NCAI Boston Biomedical Innovation Center Pilot Grant (NVV), the DoD CDMRP Discovery Award W81XWH-15-1-0248 (NVV), the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering and the Harvard Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor K. A. Athanasiou oversaw the review of this article.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (MP4 5063 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horvath, M.A., Wamala, I., Rytkin, E. et al. An Intracardiac Soft Robotic Device for Augmentation of Blood Ejection from the Failing Right Ventricle. Ann Biomed Eng 45, 2222–2233 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-017-1855-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-017-1855-z