Abstract
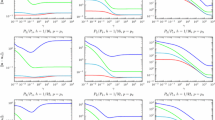
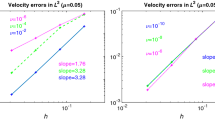
Standard error analysis for grad-div stabilization of inf-sup stable conforming pairs of finite element spaces predicts that the stabilization parameter should be optimally chosen to be \(\mathcal O(1)\). This paper revisits this choice for the Stokes equations on the basis of minimizing the \(H^{1}(\Omega )\) error of the velocity and the \(L^{2}(\Omega )\) error of the pressure. It turns out, by applying a refined error analysis, that the optimal parameter choice is more subtle than known so far in the literature. It depends on the used norm, the solution, the family of finite element spaces, and the type of mesh. In particular, the approximation property of the pointwise divergence-free subspace plays a key role. With such an optimal approximation property and with an appropriate choice of the stabilization parameter, estimates for the \(H^{1}(\Omega )\) error of the velocity are obtained that do not directly depend on the viscosity and the pressure. The minimization of the \(L^{2}(\Omega )\) error of the pressure requires in many cases smaller stabilization parameters than the minimization of the \(H^{1}(\Omega )\) velocity error. Altogether, depending on the situation, the optimal stabilization parameter could range from being very small to very large. The analytic results are supported by numerical examples. Applying the analysis to the MINI element leads to proposals for the stabilization parameter which seem to be new.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold, D., Brezzi, F., Fortin, M.: A stable finite element for the Stokes equations. Calcolo 21(4), 337–344 (1984)
Arnold, D., Qin, J.: Quadratic velocity/linear pressure Stokes elements. In: Vichnevetsky, R., Knight, D., Richter, G. (eds.) Advances in Computer Methods for Partial Differential Equations VII, pp. 28–34. IMACS (1992)
Braack, M., Burman, E., John, V., Lube, G.: Stabilized finite element methods for the generalized Oseen problem. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 196(4-6), 853–866 (2007)
Brenner, S., Scott, L.R.: The Mathematical Theory of Finite Element Methods. Springer-Verlag, New York (1994)
Bychenkov, Y., Chizonkov, E.V.: Optimization of one three-parameter method of solving an algebraic system of Stokes type. Russ. J. Numer. Anal. Math. Model. 14, 429–440 (1999)
Case, M., Ervin, V., Linke, A., Rebholz, L.: A connection between Scott-Vogelius elements and grad-div stabilization. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 49(4), 1461–1481 (2011)
Dorok, O., Grambow, W., Tobiska, L.: Aspects of finite element discretizations for solving the Boussinesq approximation of the Navier-Stokes equations. Notes on numerical fluid mechanics; numerical methods for the Navier-Stokes equations. In: Hebeker, F.-K., Rannacher, R., Wittum, G. (eds.) Proceedings of the International Workshop held at Heidelberg, October 1993, vol. 47, pp. 50–61. (1994)
Franca, L., Hughes, T.: Two classes of mixed finite element methods. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 69(1), 89–129 (1988)
Franca, L.P., Oliveira, S.P.: Pressure bubbles stabilization features in the Stokes problem. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 192(16-18), 1929–1937 (2003)
freeFEM.org. freeFEM. http://www.freefem.org/
Galvin, K., Linke, A., Rebholz, L., Wilson, N.: Stabilizing poor mass conservation in incompressible flow problems with large irrotational forcing and application to thermal convection. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 237, 166–176 (2012)
Gelhard, T., Lube, G., Olshanskii, M., Starcke, J.: Stabilized finite element schemes with LBB-stable elements for incompressible flows. J. Comput. Math. 177, 243–267 (2005)
Glowinski, R., Le Tallec, P.: Augmented Lagrangian and operator splitting methods in nonlinear mechanics. SIAM, Studies in Applied Mathematics, Philadelphia (1989)
Heister, T., Rapin, G.: Efficient augmented Lagrangian-type preconditioner for the Oseen problem using grad-div stabilization. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids. 71, 118–134 (2013)
John, V., Kindl, A.: Numerical studies of finite element variational multiscale methods for turbulent flow simulations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 199(13-16), 841–852 (2010)
John, V., Matthies, G.: MooNMD - a program package based on mapped finite element methods. Comput. Vis. Sci. 6(2–3), 163–170 (2004)
Layton, W.: An Introduction to the Numerical Analysis of Viscous Incompressible Flows, SIAM (2008)
Layton, W., Manica, C., Neda, M., Olshanskii, M.A., Rebholz, L.: On the accuracy of the rotation form in simulations of the Navier-Stokes equations. J. Comput. Phys. 228(9), 3433–3447 (2009)
Linke, A., Rebholz, L., Wilson, N.: On the convergence rate of grad-div stabilized Taylor-Hood to Scott-Vogelius solutions for incompressible flow problems. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 381, 612–626 (2011)
Lube, G., Olshanskii, M.: Stable finite element calculations of incompressible flows using the rotation form of convection. IMA J. Num. Anal. 22, 437–461 (2002)
Lube, G., Rapin, G.: Residual-based stabilized higher-order FEM for a generalized Oseen problem. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 16(7), 949–966 (2006)
Manica, C., Neda, M., Olshanskii, M.A., Rebholz, L.: Enabling accuracy of Navier-Stokes-alpha through deconvolution and enhanced stability. M2AN: Math. Model. Numer. Anal. 45, 277–308 (2011)
Olshanskii, M.A.: A low order Galerkin finite element method for the Navier-Stokes equations of steady incompressible flow: a stabilization issue and iterative methods. Comput. Meth. Appl. Mech. Eng. 191, 5515–5536 (2002)
Olshanskii, M.A., Lube, G., Heister, T., Lowe, J.: Grad-div stabilization and subgrid pressure models for the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations. Comput. Meth. Appl. Mech. Eng. 198(49-52), 3975–3988 (2009)
Olshanskii, M.A., Reusken, A.: Grad-div stabilization for the Stokes equations. Math. Comp. 73, 1699–1718 (2004)
Pierre, R.: Simple C 0 approximations for the computation of incompressible flows. Comput. Methods Appl, Mech. Eng. 68(2), 205–227 (1988)
Qin, J.: On the convergence of some low order mixed finite elements for incompressible fluids. Pennsylvania State University, PhD thesis (1994)
Roos, H.-G., Stynes, M., Tobiska, L.: Numerical methods for singularly perturbed differential equations. Convection-diffusion and flow problems. In: Springer Series in Computational Mathematics, vol. 24. Springer-Verlag, Berlin (1996)
Roos, H.-G., Stynes, M., Tobiska, L. Numerical methods for singularly perturbed differential equations. Convection-diffusion and flow problems. In: Springer Series in Computational Mathematics, vol. 24, 2nd edn. Springer-Verlag, Berlin (2008)
Tobiska, L., Verfürth, R.: Analysis of a streamline diffusion finite element method for the Stokes and Navier-Stokes equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 33, 107–127 (1996)
Zhang, S.: A new family of stable mixed finite elements for the 3d Stokes equations. Math. Comput. 74(250), 543–554 (2005)
Zhang, S.: On the P1 Powell-Sabin divergence-free finite element for the Stokes equations. J. Comput. Math. 26(3), 456–470 (2008)
Zhang, S.: Bases for C0-P1 divergence-free elements and for C1-P2 finite elements on union jack grids. Submitted (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Communicated by: M. Stynes
A. Linke supported by the DFG Research Center MATHEON, project D27. L. G. Rebholz partially supported by NSF grant DMS1112593.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jenkins, E.W., John, V., Linke, A. et al. On the parameter choice in grad-div stabilization for the Stokes equations. Adv Comput Math 40, 491–516 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10444-013-9316-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10444-013-9316-1
Keywords
- Incompressible Stokes equations
- Mixed finite elements
- Grad-div stabilization
- Error estimates
- Pointwise divergence-free subspace