Abstract
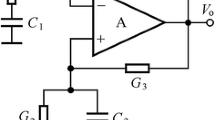
A new approach in the systematic synthesis of current conveyor based active RC canonic oscillators is given. The synthesis procedure is based on the generalized systematic synthesis framework using admittance matrix expansion. The resulting derived oscillators include many novel oscillators, using various types of current conveyors and inverting current conveyors. The oscillators considered in this paper uses the minimum number of passive elements namely two capacitors and three resistors necessary to have independent control on the condition of oscillation and on the frequency of oscillation. The generated oscillators employ two grounded capacitors and have the advantage of their ability to absorb parasitic element effects. Three classes are considered in this paper, class I oscillators have a common node between one of the capacitors and one of the two grounded resistors. Class II oscillators have a common node between one of the capacitors and the floating resistor. Class III has all three resistors being grounded and one of them shares a node with one of the capacitors. It should be noted that this is the first paper in the literature to use nodal admittance matrix expansion in the generation of current conveyor oscillators. Spice simulation results are included to support the theory. The proposed method can be generalized to other active devices.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhattacharyya, B. B., Sundaramurthy, M., & Swamy, M. N. S. (1981). Systematic generation of canonic sinusoidal RC active oscillators. IEE Proceedings, 128(3), 114–126.
Boutin, N. (1984). On the identification and design of single amplifier single resistance controlled oscillators. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems, 31(12), 1046–1049.
Bhushan, M., & Newcomb, R. W. (1967). Grounding of capacitors in integrated circuits. Electronics Letters, 3, 148–149.
Bhattacharyya, B. B., Sundaramurthy, M., & Swamy, M. N. S. (1980). Realization of tunable RC-active oscillators using grounded capacitors and voltage amplifiers. International Journal of Circuit Theory and Applications, 8(5), 355–371.
Horng, H. W., Chang, C. W., & Lee, M. H. (1997). Single element controlledsinusoidal oscillators using CCIIs. International Journal of Electronic Healthcare, 83(6), 831–836.
Gupta, S. S., & Senani, R. (2006). New single resistance controlled oscillator configurations using unity gain cells. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 46, 111–119.
Tao, Y., & Fidler, J. K. (2000). Electronically tunable dual-OTA second-order sinusoidal oscillators/filters with non-interacting controls: A systematic synthesis approach. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I, 47(2), 117–129.
Linares-Barranco, B., Rodriguez-Vazquez, A., Sanchez-Sinencio, E., & Huertas, J. L. (1992). Generation, design and tuning of OTA-C high frequency sinusoidal oscillators. IEE Proceedings, 139(5), 557–568.
Senani, R., Tripathi, M. P., Bhaskar, D. R., & Banerjee, A. K. (1990). Systematic generation of OTA-C sinusoidal oscillators. Electronics Letters, 26(18), 1457–1459.
Senani, R., & Gupta, S. S. (1997). Synthesis of single-resistance-controlled oscillators using CFOAs: Simple state variable approach. IEE Proceeding on Circuits, Devices and Systems, 144(2), 104–106.
Sedra, A. S., & Smith, K. C. (1970). A second generation current conveyor and its applications. IEEE Transactions Circuit Theory, CT-17(1), 132–134.
Soliman, A. M. (1975). Simple sinusoidal active RC oscillators. International Journal of Electronics, 39(4), 455–458.
Svoboda, J. A. (1989). Current conveyors operational amplifiers and nullors. IEE Proceeding on Circuits, Devices and Systems, 136(6), 317–322.
Soliman, A. M. (1998). New grounded capacitor current mode oscillators using single output CCIIs. Journal of Circuits Systems and Computers, 8(3), 363–378.
Martinez, P. A., Celma, S., & Gutierrez, I. (1995). Wien type oscillators using CCII+, Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing 7, 139–147–315.
Celma, S., Martinez, P. A., & Carlosena, A. (1994). Approach to the synthesis of canonic RC-active oscillators using CCII. IEE Proceeding on Circuits, Devices and Systems, 141(6), 493–497.
Martınez, P. A., Sabadell, J., Aldea, C., & Celma, S. (1999). Variable frequency sinusoidal oscillators based on CCII+. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I, 46(11), 1386–1390.
Soliman, A. M. (2000). Current feedback operational amplifier based oscillators. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 23(1), 45–55.
Soliman, A. M. (1999). Synthesis of grounded capacitor and grounded resistor oscillators. Journal of Franklin Institute, 336(4), 735–746.
Soliman, A. M. (1998). Current mode CCII oscillators using grounded capacitors and resistors. International Journal of Circuit Theory and Applications, 26(5), 431–438.
Haigh, D. G., Clarke, T. J. W., & Radmore, P. M. (2006). Symbolic framework for linear active circuits based on port equivalence using limit variables. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I, Regarding Papers, 53(9), 2011–2024.
Haigh, D. G. (2006). A method of transformation from symbolic transfer function to active-RC circuit by admittance matrix expansion. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems. I, Regarding Papers, 53(12), 2715–2728.
Haigh, D. G., Tan, F. Q., & Papavassiliou, C. (2005). Systematic synthesis of active-RC circuit building-blocks. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 43(3), 297–315.
Haigh, D. G., & Radmore, P. M. (2006). Admittance matrix models for the nullor using limit variables and their application to circuit design. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems. I, Regarding Papers, 53(10), 2214–2223.
Carlin, H. J. (1964). Singular network elements. IEEE Transactions on Circuits Theory, 11(1), 67–72.
Awad, I. A., & Soliman, A. M. (1999). Inverting second generation current conveyors: The missing building blocks, CMOS realizations and applications. International Journal of Electronic Healthcare, 86(4), 413–432.
Awad, I. A., & Soliman, A. M. (2002). On the voltage mirrors and the current mirrors. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 32(1), 79–81.
Awad, I. A., & Soliman, A. M. (2000). A new approach to obtain alternative active building blocks realizations based on their ideal representations. Frequenz, 54(4), 290–299.
Saad, R. A., & Soliman, A. M. (2008). Generation, modeling, and analysis of CCII−. Based gyrators using the generalized symbolic framework for linear active circuits. International Journal of Circuit Theory and Applications, 36(3), 289–309.
Saad, R. A., & Soliman, A. M. (2008). Use of mirror elements in the active device synthesis by admittance matrix expansion. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I, 55(10), 2726–2735.
Saad, R. A., & Soliman, A. M. (2008). A new approach for using the pathological mirror elements in the ideal representation of active devices, International Journal of Circuit Theory and applications. doi:10.1002/cta.534.
Elwan, H. O., & Soliman, A. M. (1997). Novel CMOS differential voltage current conveyor and its applications. IEE Proceedings-Circuits, Devices and Systems, 144(3), 195–200.
Chiu, W., Liu, S. I., Tsao, H. W., & Chen, J. J. (1996). CMOS differential difference current conveyors and their applications. IEE Proceedings-Circuits, Devices and Systems, 143(2), 91–96.
Elwan, H. O., Mahmoud, S. A., & Soliman, A. M. (1995). Voltage controlled square law grounded MOS resistor. Electronic Engineering, 67, 34–38.
Mahmoud, S. A., Elwan, H. O., & Soliman, A. M. (1997). Grounded MOS resistor. Electronic Engineering, 69, 22–24.
Soliman, A. M. (1996). Linear transconductor-multiplier using matched pair of MOS transistors and a current conveyor. Frequenz, 50, 292–293.
Wang, Z. (1990). Current controlled linear MOS earthed and floating resistors and their applications. IEE Proceedings-Circuits, Devices and Systems, 137, 479–481.
Sakurai, S., & Ismail, M. (1992). CMOS square-law programmable floating resistor independent of the threshold voltage. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits Systems CAS-II, 39, 565–574.
Elwan, H. O., Mahmoud, S. A., & Soliman, A. M. (1996). CMOS voltage- controlled floating resistor. International Journal of Electronics, 81, 571–576.
Soliman, A. M., & Elwakil, A. S. (1999). Wien oscillators using current conveyors. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 25, 45–55.
Maneechukate, T., Koseeyaporn, J., Wardkein, P., & Koseeyaporn, P. (2008). Wide band amplitude control of the second order oscillator circuit. AEU—International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 62(9), 666–673.
Acknowledgments
The author thanks the reviewers for the useful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soliman, A.M. Generation of current conveyor based oscillators using nodal admittance matrix expansion. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 65, 43–59 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-009-9432-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-009-9432-5