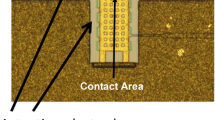
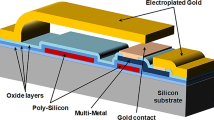
Abstract
This contribution presents an optimization strategy for the mechanical and geometrical characteristics of clamped–clamped dielectric-less RF-MEMS switches in order to enhance their reliability performances both in terms of switch properties control and long-term actuation behavior. The modifications mainly affect the switch membrane, which is made more robust, and the stopping pillar dimensions, while the switch dimensions are practically unaffected. In the case of the proposed ohmic switch, also the mobile contact region was redesigned in order to increase the contact force. Experimental measurements have demonstrated that the optimized version of the capacitive switch investigated shows an improved resistance to high bias voltages (up to 90 V), while the optimized ohmic switch shows a lower, more stable and more reproducible contact resistance. Long-term actuation measurements are analyzed in detail, proposing a model to evaluate the switch lifetime, which was found of the order of few years in the more conservative estimate in the case of capacitive switches. The lifetime estimates are less precise in the case of ohmic switches, mainly because the contact instability sums up with the charging contribution. In spite of the improved switch general properties, lifetime is however not increased with optimization. The most likely explanation is that the optimization strategy was aimed at reducing charge injection and charge non-uniformity, but other effects can be important in lifetime determination.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rebeiz, G. M. (2003). RF-MEMS: Theory design and technology. Hoboken: Wiley.
Daneshmand, M., & Mansour, R. (2007). Redundancy RF MEMS multiport switches and switch matrices. IEEE Journal of MEMS, 16, 296–303.
De Groot, W. A., Webster, J. R., Felnhofer, D., & Gusev, E. P. (2009). Review of device and reliability physics of dielectrics in electrostatically driven MEMS devices. IEEE Transaction on Device and Materials Reliability, 9, 190–202.
Van Spengen, W. M. (2012). Capacitive RF MEMS switch dielectric charging and reliability: A critical review with recommendations. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, 22(074001), 23.
Yuan, X., et al. (2006). Acceleration of dielectric charging in RF MEMS capacitive switches. IEEE Transactions on Device and Materials Reliability, 6(4), 556–563.
Papaioannou, G., et al. (2005). Temperature study of the dielectric polarization effects of capacitive RF MEMS switches. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 53(11), 3467–3473.
Mardivirin, D., Bouyge, D., Crunteanu, A., Pothier, A., & Blondy, P. (2008). Study of residual charging in dielectric less capacitive MEMS switches. Microwave Symposium Digest, 15–20, 33–36.
Grichener, A., & Rebeiz, G. (2010). High-reliability RF-MEMS switched capacitors with digital and analog tuning characteristics. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 58(10), 2692–2701.
Giacomozzi, F., Mulloni, V., Colpo, S., Iannacci, J., Margesin, B., & Faes, A. (2011). A flexible fabrication process for RF-MEMS devices. Romanian Journal of Information Science and Technology, 14(3), 259–268.
Lucibello, A., Marcelli, R., Proietti, E., Bartolucci, G., Mulloni, V., & Margesin, B. (2013). Reliability of RF MEMS capacitive and ohmic switches for space redundancy configurations. in Proc. symposium on design, test, integration and packaging of MEMS/MOEMS (DTIP), April 16–18 2013, pp. 167–172.
Rottenberg, X., De Wolf, I., Nauwelaers, B. K. J. C., De Raedt, W., & Tilmans, H. A. C. (2007). Analytical model of the DC actuation of electrostatic MEMS devices with distributed dielectric charging and nonplanar electrodes. IEEE Journal of MEMS, 16, 1243–1253.
Rottenberg, X., Jansen, H., Fiorini, P., De Raedt, W., & Tilmans, H. A. C. (2002). Novel RF-MEMS capacitive switching structures. in Proc. European microwave conference, Milan, September 24–26 2002, pp. 809–812.
Bartolucci, G., Marcelli, R., Catoni, S., Margesin, B., Giacomozzi, F., Mulloni, V., et al. (2008). An equivalent circuital model for shunt connected coplanar RF MEMS switches. Journal of Applied Physics, 104(8), 84514-1-8.
Solazzi, F., Resta, G., Mulloni, V., Margesin, B., & Farinelli, P. (2011). Influence of beam geometry on the dielectric charging of RF MEMS switches. in Proc. 6th European microwave integrated circuits conference, Manchester, October 10–11 2011, pp. 398–401.
Peng, Z., Yuan, X., Hwang, J. C. M., Forehand, D., & Goldsmith, C. L. (2006). Top vs. bottom charging of the dielectric in RF MEMS capacitive switches. in IEEE APMC, pp. 1535–1538.
Yan, X., Brown, W. L., Li, Y., Papapolymerou, J., Palego, C., Hwang, J. C. M., et al. (2009). Anelastic stress relaxation in gold films and its impact on restoring forces in MEMS devices. Journal of MEMS, 18, 570–576.
Czarnecki, P., Rottenberg, X., Soussan, P., Nolmans, P., Ekkels, P., Muller, P., Tilmans, H. A. C., De Raedt, W., Puers, R., Marchand, L., & De Wolf I. (2008). New insights into charging in capacitive RF MEMS switches. in IEEE proc. 46th annual international reliability physics symposium, Phoenix, pp. 496–505.
Acknowledgments
This work has been partially supported by ESA/ESTEC within the contract ESA ITT AO/1-5288/06/NL/GLC “High Reliability MEMS Redundancy Switch”. The authors are also grateful to FBK-MTLab for technical help during switch fabrication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mulloni, V., Solazzi, F., Resta, G. et al. RF-MEMS switch design optimization for long-term reliability. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 78, 323–332 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-013-0220-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-013-0220-x