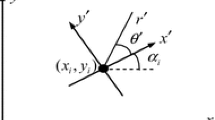
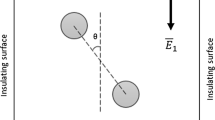
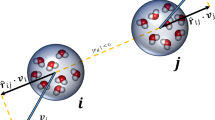
Abstract
Dielectrophoresis (DEP) is one of the most popular techniques for bio-particle manipulation in microfluidic systems. Traditional calculation of dielectrophoretic forces of single particle based on the approximation of equivalent dipole moment (EDM) cannot be directly applied on the dense particle interactions in an electrical field. The Maxwell stress tensor (MST) method is strictly accurate in the theory for dielectrophoretic forces of particle interaction, but the cumbersome and complicated numerical computation greatly limits its practical applications. A novel iterative dipole moment (IDM) method is presented in this work for calculating the dielectrophoretic forces of particle-particle interactions. The accuracy, convergence, and simplicity of the IDM are confirmed by a series of examples of two-particle interaction in a DC/AC electrical field. The results indicate that the IDM is able to calculate the DEP particle interaction forces in good agreement with the MST method. The IDM is a purely analytical operation and does not require complicated numerical computation for solving the differential equations of an electrical field while the particle is moving.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jones, T. B. Electromechanics of Particles, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1995)
Morgan, H. and Green, N. G. AC Electrokinetics: Colloids and Nanoparticles, Research Studies Press, Hertfordshire (2003)
Kang, Y. and Li, D. Electrokinetic motion of particles and cells in microchannels. Microfluidics and Nanofluidics, 6(4), 431–460 (2009)
Pohl, H. A. Dielectrophoresis: the Behavior of Neutral Matter in Nonuniform Electric Fields, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1978)
Aubry, N. and Singh, P. Control of electrostatic particle-particle interactions in dielectrophoresis. Europhysics Letters, 74(4), 623–629 (2006)
Kumar, S. and Hesketh, P. J. Interpretation of ac dielectrophoretic behavior of tin oxide nanobelts using Maxwell stress tensor approach modeling. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 161(1), 1198–1208 (2012)
Kang, K. H. and Li, D. Dielectric force and relative motion between two spherical particles in electrophoresis. Langmuir, 22(4), 1602–1608 (2006)
House, D. L., Luo, H., and Chang, S. Numerical study on dielectrophoretic chaining of two ellipsoidal particles. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 374(1), 141–149 (2012)
Ai, Y., Beskok, A., Gauthier, D. T., Joo, S. W., and Qian, S. DC electrokinetic transport of cylindrical cells in straight microchannels. Biomicrofluidics, 3(4), 044110 (2009)
Ai, Y., Joo, S.W., Jiang, Y., Xuan, X., and Qian, S. Transient electrophoretic motion of a charged particle through a converging-diverging microchannel: effect of direct current-dielectrophoretic force. Electrophoresis, 30(14), 2499–2506 (2009)
Ai, Y., Park, S., Zhu, J., Xuan, X., Beskok, A., and Qian, S. DC electrokinetic particle transport in an L-shaped microchannel. Langmuir, 26(4), 2937–2944 (2009)
Ai, Y. and Qian, S. DC dielectrophoretic particle-particle interactions and their relative motions. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 346(2), 448–454 (2010)
Xie, C., Chen, B., Ng, C. O., Zhou, X., and Wu, J. Numerical study of interactive motion of dielectrophoretic particles. European Journal of Mechanics, B: Fluids, 49, 208–216 (2015)
Kang, S. and Maniyeri, R. Dielectrophoretic motions of multiple particles and their analogy with the magnetophoretic counterparts. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 26(11), 3503–3513 (2012)
Hossan, M. R., Dillon, R., Roy, A. K., and Dutta, P. Modeling and simulation of dielectrophoretic particle-particle interactions and assembly. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 394, 619–629 (2013)
Kang, S. Two-dimensional dipolophoretic motion of a pair of ideally polarizable particles under a uniform electric field. European Journal of Mechanics, B: Fluids, 41, 66–80 (2013)
Kurgan, E. Stress calculation in two-dimensional DC dielectrophoresis. Przeglad Elektrotechniczny, 87, 107–110 (2011)
Kurgan, E. Comparison of different force calculation methods in DC dielectrophoresis. Przeglad Elektrotechniczny, 88, 11–14 (2012)
Washizu, M. and Jones, T. Multipolar dielectrophoretic force calculation. Journal of Electrostatics, 33(2), 187–198 (1994)
Washizu, M. and Jones, T. B. Dielectrophoretic interaction of two spherical particles calculated by equivalent multipole-moment method. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 32(2), 233–242 (1996)
La Magna, A., Camarda, M., Deretzis, I., Fisicaro, G., and Coffa, S. Coupled Monte Carlo-Poisson method for the simulation of particle-particle effects in dielectrophoretic devices. Applied Physics Letters, 100(13), 134104 (2012)
Lee, D. H., Yu, C., Papazoglou, E., Farouk, B., and Noh, H. M. Dielectrophoretic particle-particle interaction under AC electrohydrodynamic flow conditions. Electrophoresis, 32(17), 2298–2306 (2011)
Ai, Y., Zeng, Z., and Qian, S. Direct numerical simulation of AC dielectrophoretic particle-particle interactive motions. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 417, 72–79 (2014)
Moncada-Hernandez, H., Nagler, E., and Minerick, A. R. Theoretical and experimental examination of particle-particle interaction effects on induced dipole moments and dielectrophoretic responses of multiple particle chains. Electrophoresis, 35, 1803–1813 (2014)
Wang, X., Wang, X. B., and Gascoyne, P. R. General expressions for dielectrophoretic force and electrorotational torque derived using the Maxwell stress tensor method. Journal of Electrostatics, 39(4), 277–295 (1997)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11172111)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, L., Xie, C., Chen, B. et al. Iterative dipole moment method for calculating dielectrophoretic forces of particle-particle electric field interactions. Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. Ed. 36, 1499–1512 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-015-1998-7
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-015-1998-7
Keywords
- dielectrophoresis (DEP)
- equivalent dipole moment (EDM)
- particle interaction
- Maxwell stress tensor (MST)
- iterative dipole moment (IDM)