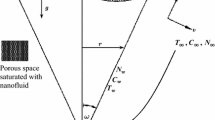
Abstract
Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) bioconvection of an incompressible electrically conducting nanofluid near a vertical wavy surface saturated porous medium containing both nanoparticle and gyrotactic microorganisms is investigated. The nanofluid is represented by a model that includes both Brownian motion and thermophoresis effects. A suitable set of non-dimensional variables are used to transform the governing boundary layer equations into a dimensionless form. The resulting nonlinear system is mapped to the vertical flat plate domain, and a non-similar solution is used to the obtained equations. The obtained non-similar system is then solved numerically using the fourth-order Runge-Kutta method. The influence of various physical parameters on the local Nusselt number, the local Sherwood number, the local density number of the motile microorganisms, the dimensionless velocity, the dimensionless temperature, and the rescaled density of motile microorganisms is studied. It is found that the local Nusselt number, the local Sherwood number, and the local density number of the motile microorganisms decrease by increasing either the Grashof number or the magnetic field parameter.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ã:
-
amplitude of wavy surface
- A :
-
microorganisms concentration difference parameter
- C :
-
nanoparticle volume fraction
- D :
-
Brownian diffusion coefficient
- D t :
-
thermophoretic diffusion coefficient
- D n :
-
diffusivity of microorganisms
- f :
-
dimensionless stream function
- g :
-
acceleration due to gravity
- Gr:
-
Grashofnumber
- k :
-
thermal conductivity
- K :
-
permeability of porous medium
- \(\bar K\) :
-
material parameter
- L :
-
characteristic length of wavy surface
- Le b :
-
bioconvectionLewisnumber
- Le :
-
Lewis number
- M n :
-
magnetic field parameter
- N :
-
rescaled density of motile microorganisms
- N b :
-
Brownian motion parameter
- N r :
-
buoyancy ratio
- N t :
-
thermophoresis parameter
- N nx :
-
local density number of motile microorganisms
- N ux :
-
local Nusselt number
- P :
-
pressure
- Pe b :
-
bioconvection Péclet number
- qm :
-
surface mass flux
- qn:
-
surface motile microorganisms flux
- qw:
-
surface heat flux
- Ra :
-
Rayleigh number
- Ra b :
-
bioconvection Rayleigh number
- Sh x :
-
local Sherwood number
- T :
-
temperature
- W :
-
constant maximum cell swimming speed
- (u, v):
-
velocity components of fluid
- (x, y):
-
coordinate axes
- α :
-
thermal diffusivity of porous media
- φ :
-
dimensionless nanoparticle volume fraction
- β :
-
volumetric expansion coefficient
- θ :
-
dimensionless temperature
- (ξ, η):
-
non-similarity variables
- (ρc)p:
-
effective heat capacity of nanoparticle material
- (ρc)f:
-
heat capacity of fluid
- ρf:
-
density of fluid
- ρp:
-
nanoparticle mass density
- j :
-
ratio between effective heat capacity of nanoparticle material and heat capacity of fluid
- μ :
-
dynamic viscosity
- γ :
-
average volume of microorganisms
- σ :
-
wavy surface
- ψ :
-
stream function
- w :
-
condition at surface
- f :
-
fluid
- ∞:
-
condition in free stream
References
Aziz, A., Khan, W. A., and Pop, I. Free convection boundary layer flow past a horizontal flat plate embedded in porous medium filled by nanofluid containing gyrotactic microorganisms. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 56, 48–57 (2012)
Nield, D. A. and Bejan, A. Convection in Porous Media, 3rd ed., Springer, New York (2006)
Pop, I. and Ingham, D. B. Convective Heat Transfer: Mathematical and Computational Modeling of Viscous Fluids and Porous Media, Pergamon, Oxford (2001)
Ingham, D. B. and Pop, I. Transport Phenomena in Porous Media III, Elsevier, Oxford (2005)
Vafai, K. Handbook of Porous Media, 2nd ed., Taylor & Francis, New York (2005)
Vafai, K. Porous Media: Applications in Biological Systems and Biotechnology, CRC Press, Boca Raton (2010)
Vadasz, P. Emerging Topics in Heat and Mass Transfer in Porous Media, Springer, New York (2008)
Cheng, C, Y. Natural convection heat transfer from an inclined wavy plate in a bidisperse porous medium. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 43, 69–74 (2013)
Chang, T. Laminar film condensation on a horizontal wavy plate embedded in a porous medium. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 47, 35–42 (2008)
Elshehawey, E. F., Elbarbary, E. M. E., and Elgazery, N. S. Effect of inclined magnetic field on magneto fluid flow through a porous medium between two inclined wavy porous plates (numerical study). Applied Mathematics and Computation, 135, 85–103 (2003)
Cheng, C. Y. Non-Darcy natural convection heat and mass transfer from a vertical wavy surface in saturated porous media. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 182, 1488–1500 (2006)
Mahdy, A. MHD non-Darcian free convection from a vertical wavy surface embedded in porous media in the presence of Soret and Dufour effect. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 36, 1067–1074 (2009)
Mahdi, R. A., Mohammed, H. A., Munisamy, K. M., and Saeid, N. H. Review of convection heat transfer and fluid flow in porous media with nanofluid. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 41, 715–734 (2015)
Khan, W. A., Makinde, O. D., and Khan, Z. H. MHD boundary layer flow of a nanofluid containing gyrotactic microorganisms past a vertical plate with Navier slip. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 74, 285–291 (2014)
Xu, H. and Pop, I. Mixed convection flow of a nanofluid over a stretching surface with uniform free stream in the presence of both nanoparticle and gyrotactic microorganisms. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 75, 610–623 (2014)
Kuznetsov, A. V. The onset of nanofluid bioconvection in a suspension containing both nanoparticles and gyrotactic microorganisms. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 37, 1421–1425 (2010)
Xu, H. and Pop, I. Fully developed mixed convection flow in a horizontal channel filled by a nanofluid containing both nanoparticles and gyrotactic microorganisms. European Journal of Mechanics-B/Fluids, 46, 37–45 (2014)
Kuznetsov, A. V. and Nield, D. A. The Cheng-Minkowycz problem for natural convective boundary layer flow in a porous medium saturated by a nanofluid a revised model. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 65, 682–685 (2013)
Mahdy, A. Natural convection boundary layer flow due to gyrotactic microorganisms about a vertical cone in porous media saturated by a nanofluid. Journal of the Brazilian Society of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering, 38, 67–76 (2015)
Akbar, N. S. Bioconvection peristaltic flow in an asymmetric channel filled by nanofluid containing gyrotactic microorganism: bio nano engineering model. International Journal of Numerical Methods for Heat and Fluid Flow, 25, 214–224 (2015)
Raees, A., Xu, H., Sun, Q., and Pop, I. Mixed convection in gravity-driven nano-liquid film containing both nanoparticles and gyrotactic microorganisms. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 36(2), 163–178 (2015) DOI 10.1007/s10483-015-1901-7
Khan, W. A. and Makinde, O. D. MHD nanofluid bioconvection due to gyrotactic microorganisms over a convectively heat stretching sheet. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 81, 118–124 (2014)
Sheremet, M. A. and Pop, I. Thermo-bioconvection in a square porous cavity filled by oxytactic microorganisms. Transport in Porous Media, 103, 191–205 (2014)
Uddin, M. J., Khan, W. A., and Ismail, A. I. M. Free convective flow of non-Newtonian nanofluids in porous media with gyrotactic microorganism. Journal of Thermophysics and Heat Transfer, 27, 326–333 (2013)
Mutuku, W. N. and Makinde, O. D. Hydromagnetic bioconvection of nanofluid over a permeable vertical plate due to gyrotactic microorganisms. Computers and Fluids, 95, 88–97 (2014)
Hillesdon, A. J. and Pedley, T. J. Bioconvection in suspensions of oxytactic bacteria: linear theory. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 324, 223–259 (1996)
Hill, N. A., Pedley, T. J., and Kessler, J. O. Growth of bioconvection patterns in a suspension of gyrotactic microorganisms in a layer of finite depth. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 208, 509–543 (1989)
Kuznetsov, A. V. Non-oscillatory and oscillatory nanofluid bio-thermal convection in a horizontal layer of finite depth. European Journal of Mechanics-B/Fluids, 30, 156–165 (2011)
Makinde, O. D. Computational modeling of MHD unsteady flow and heat transfer over a flat plate with Navier slip and Newtonian heating. Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 29, 159–166 (2012)
Mahdy, A. and Ahmed, S. E. Laminar free convection over a vertical wavy surface embedded in a porous medium saturated with a nanofluid. Transport in Porous Media, 91, 423–435 (2012)
Ergun, S. Fluid flow through packed columns. Chemical Engineering Progress, 48, 89–94 (1952)
Mahdy, A. and Ahmed, S. E. Thermosolutal Marangoni boundary layer magnetohydrodynamic flow with the Soret and Dufour effects past a vertical flat plate. Engineering Science and Technology, an International Journal, 18, 24–31 (2015)
Nield, D. A. and Kuznetsov, A. V. The Cheng-Minkowycz problem for natural convective boundary-layer flow in a porous medium saturated by a nanofluid. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 52, 5792–5795 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmed, S.E., Mahdy, A. Laminar MHD natural convection of nanofluid containing gyrotactic microorganisms over vertical wavy surface saturated non-Darcian porous media. Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. Ed. 37, 471–484 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-016-2044-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-016-2044-9