Abstract
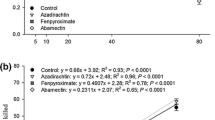
The coconut mite, Aceria guerreronis Keifer, is a major pest of coconut palm in the world. The control of this pest species is done through acaricide applications at short time intervals. However, the predators of this pest may also be affected by acaricides. Among the predators of A. guerreronis, Neoseiulus baraki (Athias-Henriot) has potential for biological control. The objective of this study was to assess the effect of acaricides on the survival and behavior of N. baraki. The survivorship of N. baraki was recorded in surface-impregnated arenas. Choice and no-choice behavioral bioassays were carried out using a video tracking system to assess the walking behavior of the predator under acaricide exposure. Although all acaricides negatively affected the survival of N. baraki, chlorfenapyr and azadirachtin caused lower effect than the other acaricides. No significant differences in walking behavior were observed under exposure to fenpyroximate, chlorfenapyr and chlorpyrifos on fully-contaminated arenas. Azadirachtin and chlorpyrifos caused repellence. Irritability was observed for all acaricides, except for abamectin. Chlorfenapyr was the most suitable product for managing the coconut mite because of its low effect on survival and behavior of N. baraki.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aratchige NS, Sabelis MW, Lesna I (2007) Plant structural changes due to herbivory: do changes in Aceria-infested coconut fruits allow predatory mites to move under the perianth? Exp Appl Acarol 43:97–107
Aygun D, Doganay Z, Altintop L, Guven H, Onar M, Deniz T, Sunter T (2002) Serum acetylcholinesterase and prognosis of acute organophosphate poisoning. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol 40:903–910
Chen TY, French JV, Liu T-X, DaGraca JV (2003) Residual toxicities of pesticides to the predaceous mite Galendromus helveolus (Acari: Phytoseiidae) on Texas citrus. Subtrop Plant Sci 55:40–45
Cordeiro EMG, Corrêa AS, Venzon M, Guedes RNC (2010) Insecticide survival and behavioral avoidance in the lacewings Chrysoperla externa and Ceraeochrysa cubana. Chemosphere 81:1352–1357
Davidson G (1953) Experiments on the effect of residual insecticides in houses against Anopheles gambiae and Anopheles funestus. Bull Entomol Res 44:231–254
Domingos CA, Melo JWS, Gondim MGC Jr, Moraes GJ, Hanna R, Lawson-Balagbo LM, Schausberger P (2010) Diet-dependent life history, feeding preference and thermal requirements of the predatory mite, Neoseiulus baraki (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Exp Appl Acarol 50:201–215
Duso C, Malagnini V, Pozzebon A, Castagnoli M, Liguori M, Simoni S (2008) Comparative toxicity of botanical and reduced-risk insecticides to Mediterranean populations of Tetranychus urticae and Phytoseiulus persimilis (Acari Tetranychidae, Phytoseiidae). Biol Control 47:16–21
Fernando LCP, Waidyarathne KP, Perera KFG, De Silva PHPR (2010) Evidence for suppressing coconut mite, Aceria guerreronis by inundative release of the predatory mite, Neoseiulus baraki. Biol Control 53:108–111
Guedes RNC, Campbell JF, Arthur FH, Opit GP, Zhu KY, Throne JE (2008) Acute lethal and behavioral sublethal responses of two stored-product psocids to surface insecticides. Pest Manag Sci 64:1314–1322
Hamedi N, Fathipour Y, Saber M (2010a) Sublethal effects of abamectin on the biological performance of the predatory mite, Phytoseius plumifer (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Exp Appl Acarol 53:29–40
Hamedi N, Fathipour Y, Saber M (2010b) Sublethal effects of fenpyroximate on life table parameters of the predatory mite Phytoseius plumifer. Biocontrol 55:271–278
Haynes K (1988) Sublethal effects of neurotoxic insecticides on insect behavior. Ann Rev Entomol 33:149–168
Hernandez RF (1977) Combate quimico del eriofiídeo del cocotero Aceria (Eriophyes) guerreronis (K) em la costa de Guerrero. Agric Tec Mex 4:23–28
Hibbard BE, Bjostad LB (1989) Corn semiochemicals and their effects on insecticide efficacy and insecticide repellency toward western corn rootworm larvae (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). J Econ Entomol 82:773–781
Hunt DA, Tracy MF (1998) Pyrrole insecticide: a new class of agriculturally important insecticides functioning as uncouplers of oxidative phosphorylation. In: Ishaaya I, Degheele D (eds) Insecticides with novel modes of action. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 138–151
IRAC (2009) Method N°4. Insecticide Resistance Action Committee
Jallow MFA, Hoy CW (2005) Phenotypic variation in adult behavioral response and offspring fitness in Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) in response to permethrin. J Econ Entomol 98:2195–2202
Jansson RK, Dybes RA (1998) Avermectins: biochemical mode of action, biological activity and agricultural importance. In: Ishaava I, Degheele D (eds) Insecticides with novel modes of action, mechanism and application. Springer-Verlag, New York, pp 152–167
Julia JF, Mariau D (1979) Nouvelles recherches em Coted’Ivoire sur Eriophyes guerreronis K., acarien ravageur dês noix du cocotier. Oleagineux 34:181–187
Kim SS, Yoo SS (2002) Comparative toxicity of some acaricides to the predatory mite, Phytoseiulus persimilis and the two spotted spider mite, Tetranychus urticae. Biocontrol 47:563–573
Kongmee M, Prabaripai A, Akratanakul P, Bangs MJ, Chareonviriyaphap T (2004) Behavioral responses of Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) exposed to deltamethrin and possible implications for disease control. J Med Entomol 41:1055–1063
Kumar PS, Singh SP (2000) Hirsutella thompsonii. The best biological control option for the management of the coconut mite in India. Indian Coconut J 31:11–15
Lawson-Balagbo LM, Gondim MGC Jr, Moraes GJ, Hanna R, Schausberger P (2007a) Life history of the predatory mites Neoseiulus paspalivorus and Proctolaelaps bickleyi, candidates for biological control of Aceria guerreronis. Exp Appl Acarol 43:49–61
Lawson-Balagbo LM, Gondim MGC Jr, Moraes GJ, Hanna R, Schausberger P (2007b) Refuge use by the coconut mite Aceria guerreronis: fine scale distribution and association with other mites under the perianth. Biol Control 43:102–110
Lawson-Balagbo LM, Gondim MGC Jr, Moraes GJ, Hanna R, Schausberger P (2008) Exploration of the acarine fauna on coconut palm in Brazil with emphasis on Aceria guerreronis (Acari: Eriophyidae) and its natural enemies. Bull Entomol Res 98:83–96
Levot GW, Sales N (1998) Protection from restrike provided by flystrike dressings. Aust J Exp Agric 38:551–554
Lima DB (2012) Seletividade e resposta comportamental a acaricidas em Neoseiulus baraki (Athias-Henriot) (Acari: Phytoseiidae). MSc. dissertation, Universidade Federal Rural de Pernambuco, Brasil
Lima DB, Melo JWS, Gondim MGC Jr, De Moraes GJ (2012) Limitations of Neoseiulus baraki and Proctolaelaps bickleyi as control agents of Aceria guerreronis. Exp Appl Acarol 56:233–246
Mansour FA, Ascher KPS, Abo-Moch F (1997) Effects of neemgard on phytophagous and predacious mites and on Spiders. Phytoparasitica 25:333–336
Mariau D, Tchibozo HM (1973) Essais de lutte chimique contre Aceria guerreronis (Keifer). Oleagineux 28:133–135
Massa R, Blevins S, Chao SL (2008) Role of acetylcholinesterase and glutathione S-transferase following exposure to nicosulfuron and diazinon in Helicoverpa zea. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 71:230–235
Melo JWS, Lima DB, Pallini A, Oliveira JEM, Gondim MCG Jr (2011) Olfactory response of predatory mites to vegetative and reproductive parts of coconut palm infested by Aceria guerreronis. Exp Appl Acarol 55:191–202
Melo JWS, Domingos CA, Pallini A, Oliveira JEM, Gondim MGC Jr (2012) Removal of bunches or spikelets is not effective for the control of Aceria guerreronis. HortScience 47:626–630
Monteiro VB, Lima DB, Gondim MGC Jr, Siqueira HAA (2012) Residual bioassay to assess the toxicity of acaricides against Aceria guerreronis (Acari: Eriophyidae) under laboratory conditions. J Econ Entomol 105:1419–1425
Moore D, Alexander L (1987) Aspects of migration and colonization of the coconut palm by the coconut mite, Eriophyes guerreronis (Keifer) (Acari: Eriophyidae). Bull Entomol Res 77:641–650
Moore D, Howard FW (1996) Coconuts. In: Lindquist EE, Sabelis MW, Bruin J (eds) Eriophyoid mites: their biology, natural enemies and control. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 561–570
Moraes GJ, Zacarias MS (2002) Use of predatory mites for control of eriophyid mites. In: Fernando LCP, Moraes GJ, Wickramananda IR (eds) Proceedings of the international workshop on coconut mite (Aceria guerreronis). Coconut Research Institute, Sri Lanka, pp 78–88
Nair CPR (2002) Status of eriophyid mite Aceria guerreronis Keifer in India. In: Fernando LCP, Moraes GJ, Wickramananda IR (eds) Proceedings of the International Workshop on Coconut Mite (Aceria guerreronis). Coconut Research Institute, Sri Lanka, pp 9–12
Pothikasikorn J, Overgaard H, Ketavan C, Visetson S, Bangs MJ, Chareonviriyaphap T (2007) Behavioral responses of malaria vectors, Anopheles minimus Complex, to three classes of agrochemicals in Thailand. J Med Entomol 44:1032–1039
Ramaraju K, Natarajan K, Babu PCS, Palanisamy S, Rabindra RJ (2002) Studies on coconut eriophyid mite, Aceria guerreronis Keifer in Tamil Nadu, India. In: Fernando LCP, Moraes GJ, Wickramananda IR (eds) Proceedings of the International Workshop on Coconut Mite (Aceria guerreronis). Coconut Research Institute, Sri Lanka, pp 13–31
Roberts DR, Chareonviriyaphap T, Harlan HH, Hshieh P (1997) Methods for testing and analyzing excito repellency responses of malaria vectors to insecticides. J Am Mosq Contr Assoc 13:13–17
Robertson JL, Preisler HK (1992) Pesticide bioassays with arthropods. CRC Press, Inc., Boca Raton, FL
SAS Institute Inc (2008) SAS/STAT user’s guide. SAS Institute, Cary, NC
Seguni Z (2002) Incidence, distribution and economic importance of the coconut eriophyid mite, Aceria guerreronis Keifer in Tanzanian coconut based cropping systems. In: Fernando LCP, Moraes GJ, Wickramananda IR (eds) Proceedings of the International Workshop on Coconut Mite (Aceria guerreronis). Coconut Research Institute, Sri Lanka, pp 54–57
Singh K, Singh DK (2000) Toxicity to the snail Limnaea acuminata of plant-derived molluscicides in combination with synergists. Pest Manag Sci 56:889–898
Soderlund DM, Bloomquist JR (1989) Neurotoxic actions of pyrethroid insecticides. Annu Rev Entomol 34:77–96
Wang C, Scharf ME, Bennett GW (2004) Behavioral and physiological resistance of the German cockroach to gel baits (Blattodea: Blattellidae). J Econ Entomol 97:2067–2072
Yu SJ (2008) The mode of action of insecticides. In: Yu SJ (ed) The toxicology and biochemistry of insecticides. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 115–142
Zhai J, Robinson WH (1992) Measuring cypermethrin resistance in the German cockroach (Orthoptera: Blattellidae). J Econ Entomol 85:348–351
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Brazilian Federal Agency for the Support and Evaluation of Graduate Education (Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Ensino Superior- CAPES) for the graduate student stipend allocated to the first author. The authors would also like to thank the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico- CNPq) and CAPES for financially supporting this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lima, D.B., Melo, J.W.S., Guedes, R.N.C. et al. Survival and behavioural response to acaricides of the coconut mite predator Neoseiulus baraki . Exp Appl Acarol 60, 381–393 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-012-9644-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-012-9644-8