Abstract
In May 2012, two seismic events hit the Emilia-Romagna Region, in Northern Italy. The earthquakes caused collapses and damage to traditional vernacular building heritage, highlighting its seismic high vulnerability. The paper presents a wide collection of damage and collapses observed in the aftermath field inspections on 22 historical vernacular buildings. It was noted that few recurring structural typologies are present in the area hit by earthquake and buildings of the same typology show similar damage mechanisms. Then, with the main goal to identify the most typical damage affecting similar structures, the building stock has been subdivided in different categories based on building plan distribution and intended use. The principal collapse causes, based both on in-field observations and analyses, performed on local and global finite element models, can be ascribed to poor connections between orthogonal walls, lack of effective connections between floor elements and walls, excessive flexibility of floor diaphragms and high slenderness of vertical elements. The outcomes in the present paper allow identifying the vernacular building typologies most vulnerable to earthquake and can help to plan the future retrofitting strategies for vernacular heritage.

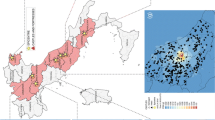
Source ITACA (2018)















Similar content being viewed by others
References
ANTC (Aggiornamento delle Norme Tecniche per le Costruzioni) Italian Building Code. Ministerial Decree 17/01/2018 (in Italian)
Barros R, Rodrigues H, Varum H, Costa A, Correia M (2018) Seismic analysis of a Portuguese vernacular building. J Archit Eng 24(1):05017010
Belleri A, Brunesi E, Nascimbene R, Pagani M, Riva P (2014) Seismic performance of precast industrial facilities following major earthquakes in the Italian territory. J Perform Constr Facil 29(5):04014135
Bovo M, Savoia M (2018) Numerical simulation of seismic-induced failure of a precast structure during the Emilia earthquake. J Perform Constr Facil 32(1):04017119
Bovo M, Savoia M (2019) Evaluation of force fluctuations induced by vertical seismic component on reinforced concrete precast structures. Eng Struct 178:70–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2018.10.018
Cardoso R, Lopes M, Bento R (2005) Seismic evaluation of old masonry buildings. Part I: method description and application to a case-study. Eng Struct 27:2024–2035
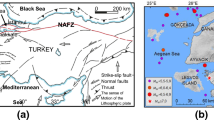
Carydis P, Castiglioni C, Lekkas E, Kostaki I, Lebesis N, Drei A (2012) The Emilia Romagna, May 2012 earthquake sequence. The influence of the vertical earthquake component and related geoscientific and engineering aspects. Ing Sismica 29(2–3):31–58
Cattari S, Abbati SD, Ferretti D, Lagomarsino S, Ottonelli D, Tralli A (2012) The seismic behaviour of ancient masonry buildings after the earthquake in Emilia (Italy) on May 20th and 29th, 2012. Ing Sismica 29(2–3):87–119
Cattari S, Degli Abbati S, Ferretti D, Lagomarsino S, Ottonelli D, Tralli A (2013) Damage assessment of fortresses after the 2012 Emilia earthquake (Italy). Bull Earthq Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10518-013-9520-x
Ferretti F, Ferracuti B, Mazzotti C, Savoia M (2019) Destructive and minor destructive tests on masonry buildings: experimental results and comparison between shear failure criteria. Constr Build Mater 199:12–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.11.246
Foppoli D (2016) Inspections and NDT for the characterization of historical buildings after seismic events: 2012 Emilia earthquake. In: Proceedings of 10th international conference on structural analysis of historical constructions—SAHC 2016, Leuven, Belgium, September 13–15
Galli E, Savoia M, Colla C, Ferretti D (2015) Mechanical and mineralogical characterization of mortar in masonry buildings damaged by the 20–29th May earthquake in Emilia. Key Eng Mater 624:379–386
Gallipoli MR, Chiauzzi L, Stabile TA, Mucciarelli M, Masi A, Lizza C et al (2014) The role of site effects in the comparison between code provisions and the near field strong motion of the Emilia 2012 earthquakes. Bull Earthq Eng 12:2211–2230. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10518-014-9628-7)
Ghersi A, Rossi P (2001) Influence of bi-directional ground motions on the inelastic response of one-storey in-plan irregular structures. Eng Struct 23(6):579–591
Grimaz S, Malisan P (2014) Near field domain effects and their consideration in the international and Italian seismic codes. Boll Di Geofis Teor Ed Appl 55:717–738. https://doi.org/10.4430/bgta0130
http://www.regione.emilia-romagna.it/terremoto. Last accessed 1 Oct 2018
IESN (Italian Experimental Seismic Network). http://www.iesn.it. Accessed 1 Oct 2018
INGV (Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia). http://shakemap.rm.ingv.it/shake/index.html. Accessed 1 Nov 2018
ISTAT (Italian National Institute for Statistics) (2011) 15° Censimento generale della popolazione. ISTAT, Roma (in Italian)
ITACA (ITalian ACcelerometric Archive) version 2.0. http://itaca.mi.ingv.it. Accessed 1 Oct 2018
Lagomarsino S (2006) On the vulnerability assessment of monumental buildings. Bull Earthq Eng 4(4):445–463
Lagomarsino S (2012) Damage assessment of churches after L’Aquila earthquake (2009). Bull Earthq Eng 10:73–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10518-011-9307-x
Li S, Xie L (2007) Progress and trend on near-field problems in civil engineering. Acta Seismol Sin 20:105–114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11589-007-0105-0
Liossatou E, Fardis MN (2015) Residual displacements of RC structures as SDOF systems. Earthq Eng Struct Dyn 44(5):713–734
Lucchini A, Monti G, Kunnath S (2009) Seismic behavior of single-story asymmetric-plan buildings under uniaxial excitation. Earthq Eng Struct Dyn 38:1053–1070
Maino E, Benni S, Torreggiani D, Barbaresi A, Tassinari P (2016) A quantitative physiognomic analysis of contemporary farm buildings to improve awareness in rural planning. Trans ASABE 59(2):509–519
Marastoni D, Benedetti A, Pelà L, Pignagnoli G (2017) Torque penetrometric test for the in situ characterisation of historical mortars: fracture mechanics interpretation and experimental validation. Constr Build Mater 157:509–520
Mavroeidis GP, Dong G, Papageorgiou AS (2004) Near-fault ground motions, and the response of elastic and inelastic single-degree-of-freedom (SDOF) systems. Earthq Eng Struct Dyn 33:1023–1049
Meli R, Peña F (2004) On elastic models for evaluation of the seismic vulnerability of masonry churches. In: Structural analysis of historical constructions. (SAHC) 2004; Balkema, Leiden, pp 1121–1131
Milani G (2013) Lesson learned after the Emilia-Romagna, Italy, 20–29 May 2012 earthquakes: a limit analysis insight on three masonry churches. Eng Fail Anal 34:761–778
Minghini F, Ongaretto E, Ligabue V, Savoia M, Tullini N (2016) Observational failure analysis of precast buildings after the 2012 Emilia earthquakes. Earthq Struct 11(2):327–346
Mistler M, Butenweg C, Meskouris K (2006) Modelling methods of historic masonry buildings under seismic excitation. J Seismol 10:497–510
Ortega J, Vasconcelos G, Rodrigues H, Correia M, Lourenco PB (2017) Traditional earthquake resistant techniques for vernacular architecture and local seismic cultures: a literature review. J Cult Herit 27:181–196
Ortega J, Vasconcelos G, Rodrigues H, Correia M (2018a) Assessment of the influence of horizontal diaphragms on the seismic performance of vernacular buildings. Bull Earthq Eng 16:3871–3904. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10518-018-0318-8
Ortega J, Vasconcelos G, Rodrigues H, Correia M (2018b) Assessment of the efficiency of traditional earthquake resistant techniques for vernacular architecture. Eng Struct 173:1–27
Ortolani M (1953) La casa rurale nella pianura emiliana. Centro di studi per la geografia etnologica, Florence
Parisi F, Augenti N (2013) Earthquake damages to cultural heritage constructions and simplified assessment of artworks. Eng Fail Anal 34:735–760
Paul G (2005) Somerville Engineering characterization of near fault ground motions URS Corporation, Pasadena, CA, USA. 2005 NZSEE conference
Penna A, Morandi P, Rota M, Manzini CF, da Porto F, Magenes G (2013) Performance of masonry buildings during the Emilia 2012 earthquake. Bull Earthq Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10518-013-9496-6
Perus I, Fajfar P (2005) On the inelastic torsional response of single-storey structures under bi-axial excitation. Earthq Eng Struct Dyn 34(8):931–941
Priolo E, Romanelli M, Barnaba C, Mucciarelli M, Laurenzano G, Dall’Olio L et al (2012) The Ferrara thrust earthquakes of May–June 2012: preliminary site response analysis at the sites of the OGS temporary network. Ann Geophys 2012(55):591–597
Ramos LF, Lourenco PB (2004) Modeling and vulnerability of historical city centers in seismic areas: a case study in Lisbon. Eng Struct 26:1295–1310
Reddy JN (2006) Theory and analysis of elastic plates and shells, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton (First Published 2006)
Ricciardi A (2013) I distretti industriali italiani: recenti tendenze evolutive. Sinergie 91:21–58
Roca P, Cervera M, Gariup G, Pelà L (2010) Structural analysis of Masonry historical constructions. Classical and advanced approaches. Arch Comput Methods Eng 17:299–325
Shrestha B (2009) Vertical ground motions and its effect on engineering structures: a state-of-the-art review. In: Proceeding int seminar hazard management sustain developemnt, Kathmandu, Nepal; 29–30 November 2009. http://dx.doi.org/10.13140/2.1.2863.6165
Sorrentino L, Liberatore L, Liberatore D, Masiani R (2013) The behaviour of vernacular buildings in the2012 Emilia earthquakes. Bull Earthq Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10518-013-9455-2
Tomazevic M (2000) Earthquake—resistant design of masonry buildings. Imperial College Press, London
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bovo, M., Barbaresi, A., Torreggiani, D. et al. Collapse and damage to vernacular buildings induced by 2012 Emilia earthquakes. Bull Earthquake Eng 18, 1049–1080 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10518-019-00737-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10518-019-00737-7