Abstract
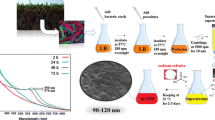
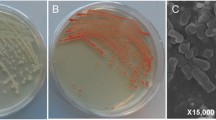
The potential of the environment to yield organisms that can produce functional bionanominerals is demonstrated by selenium-tolerant, aerobic bacteria isolated from a seleniferous rhizosphere soil. An isolate, NS3, was identified as a Bacillus species (EU573774.1) based on morphological and 16S rRNA characterization. This strain reduced Se(IV) under aerobic conditions to produce amorphous α Se(0) nanospheres. A room-temperature washing treatment was then employed to remove the biomass and resulted in the production of clusters of hexagonal Se(0) nano-rods. The Se(0) nanominerals were analyzed using electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction techniques. This Bacillus isolate has the potential to be used both in the neutralizing of toxic Se(IV) anions in the environment and in the environmentally friendly manufacture of nanomaterials.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Corb BW, Wei WD, Averbach BL (1982) Atomic models of amorphous selenium. J Non-Cryst Solids 53:29–42
Cui D, Gao H (2003) Advance and prospects of bionanomaterials. Biotechnol Prog 19:683–692
Focht DD (1994) Microbiological procedures for biodegradation research. In: Weaver RW, Angle JS, Bottomley PS (eds) Methods of soil analysis, part 2. Microbiological and biochemical properties. Soil Science Society of America, Madison, WI, pp 407–426
Gates B, Yin Y, Xia Y (2000) A solution phase approach to synthesis of uniform nanowires of crystalline selenium with lateral dimensions in the range of 10–30 nm. J Am Chem Soc 122:12582–12583
Gates B, Mayers B, Cattle B, Xia Y (2002a) Synthesis and characterization of uniform nanowires of trigonal selenium. Adv Funct Mater 12:219–227
Gates B, Mayers B, Grossman A, Xia Y (2002b) A sonochemical approach to the synthesis of crystalline selenium nanowires in solutions and on solid supports. Adv Mater 14:1749–1752
Kasap SO, Yannacopoulos S (1989) Kinetics of structural relaxations in the glassy semiconductor amorphous selenium. J Mat Res 4:893–905
Krieg NR, Holt JG, Murray RGE (1984) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, vols 1 and 2. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore
Mayers B, Gates B, Yin Y, Xia Y (2001) Large scale synthesis of monodisperse nanorods of Se/Te alloys through a homogeneous nucleation and solution growth. Adv Mater 13:1380–1384
Miyata T, Kitamura M, Sunagawa I (1978) Theoretical and experimental morphology of monoclinic selenium. Mineral J 9:482–509
Oremland RS, Herbal MJ, Blum JS, Langely S, Beveridge TJ, Ajayan PM, Sutto T, Ellis AV (2004) Structural and spectral features of selenium nanospheres produced by Se-respiring bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:52–60
Pearce CI, Coker VS, Charnock JM, Pattrick RAD, Mosselmans JFW, Law N, Beveridge TJ, Lloyd JR (2008) Microbial manufacture of calcogenide-based nanoparticles via reduction of selenite using Veillonella atypica: an in situ EXAFS study. Nanotechnology. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/19/15/155603
Peled A, Hadziioannou E (1991) Thermal characterization of amorphous selenium films obtained by low-temperature photodeposition. J Mater Sci 26:1769–1774
Ren L, Zhang H, Tan P, Chen Y, Zhang Z, Chang Y, Xu J, Yang F, Yu D (2004) Hexagonal Se nanospheres synthesized via vapor-phase growth. J Phys Chem B 108:4627–4630
Takahashi H, Fujikawa T, Konishi T (2006) XAFS study of nanocrystalline selenium embedded in amorphous matrix. eJ Surf Sci Nanotechnol 4:213–218
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Thomson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, positions-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Zhang X, Xie Y, Xu F, Liu X, Zhang S, Tian X (2003) Room temperature rapid growth of monocrystalline selenium nanowires in a polymer buffer system. Solid State Sci 5:525–527
Zhou B, Zhu JJ (2006) A general route for the rapid synthesis of one-dimensional nanostructured single-crystal Te, Se and Se–Te alloys directly from Te or/and Se powders. Nanotechnology 17:1763–1769
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the Chris Boothman, Alastair Bewsher and Steve Caldwell of Williamson Centre for Molecular Environmental Sciences, for facilitating Molecular, ion chromatography and ESEM analysis. NTP acknowledges Erasmus-Mundus Programme for funding MESPOM Visiting Scholarship for carrying out research work at University of Manchester, United Kingdom and Defence Research and Development Organization, India for research grant and fellowship to Ms. Sharma.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tejo Prakash, N., Sharma, N., Prakash, R. et al. Aerobic microbial manufacture of nanoscale selenium: exploiting nature’s bio-nanomineralization potential. Biotechnol Lett 31, 1857–1862 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-009-0096-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-009-0096-0