Abstract
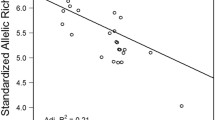
We analysed the pattern of genetic differentiation among six newly established (around 10 generations) sites of the round goby (Neogobius melanostomus) in the southern Baltic Sea by means of nine microsatellite loci and in total 183 individuals. All but one site were within 30 km from each other. We found statistically significant genetic differentiation in ten out of 15 comparisons after Bonferroni correction, and since the species is newly introduced this has happened in less than ten generations. The largest genetic differentiation was found between the two most divergent habitats, while sites with a similar habitat were not significantly differentiated. Estimates of gene flow (Nm) were low and ranged from 1.5 to 5.5. A large proportion of individuals were assigned to one site (Puck), suggesting that this site has acted as a source to the other sites.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams CE, Hamilton DJ, McCarthy I, Wilson AJ, Grant A, Alexander G, Waldron S, Snorasson SS, Ferguson MM, Skúlason S (2006) Does breeding site fidelity drive phenotypic and genetic sub-structuring of a population of Arctic charr? Evol Ecol 20:11–26
Almqvist G (2008) Round goby Neogobius melanstomus in the Baltic Sea—invasion biology in practice. PhD thesis Stockholm University. www.diva-portal.org/su/theses/abstract.xsql?dbid=7450
Begg CB (1994) Publication bias. In: Cooper H, Hedges LV (eds) The handbook of research synthesis. Russel Sage Foundation, New York, pp 399–409
Behrmann-Godel J, Gerlach G (2008) First evidence for postzygotic reproductive isolation between two sites of Eurasian perch (Perca fluviatilis L.) within Lake Constance. Frontier Zool 5:3
Behrmann-Godel J, Gerlach G, Eckmann R (2006) Kin and population recognition in sympatric Lake Constance perch (Perca fluviatilis L.): can assortative shoaling drive population divergence? Behav Ecol Sociobiol 59:461–468
Bergek S, Björklund M (2007) Cryptic barriers to dipsersal within a lake allow genetic divergence of Eurasian perch. Evolution 61:2035–2041
Bergek S, Björklund M (2009) Genetic and morphological divergence reveals local subdivision of perch (Perca fluviatilis L.). Biol J Linn Soc 96:746–758
Björklund M, Bergek S (2009) On the relationship between population divergence and sampling effort: is more always better? Oikos 118:1127–1129
Björklund M, Ruiz I, Senar JC (2010) Genetic differentiation in the urban habitat: the great tits (Parus major) of the parks of Barcelona city. Biol J Linn Soc (in press)
Brown JE, Stepien CA (2008) Ancient divisions, rewcent expansions: phylogeography and population genetics of the round goby Apollonia melanostoma. Mol Ecol 17:2598–2615
Brown JE, Stepien CA (2009) Invasion genetics of the Eurasian round goby in North America: tracing soruces and spread patterns. Mol Ecol 18:64–79
Csilléry K, Johnson T, Beraldi D, Clutton-Brock T, Coltman D, Hansson B, Spong G, Pemberton JM (2006) Performance of marker-based relatedness estimators in natural sites of outbred vertebrates. Genetics 173:2091–2101
Goudet J (2001) FSTAT, a program to estimate and test gene diversities and fixation indices (version 2.9.3). Available from http://www.unil.ch/izea/softwares/fstat.html
Hendry AP, Wenburg JK, Bentzen P, Volk EC, Quinn TP (2000) Rapid evolution of reproductive isolation in the wild: evidence from introduced salmon. Science 290:516–518
Hensler S, Jude D (2007) Diel vertical migration of round goby larvae as a potential mechanism for advective dispersal and ballast water transport. J Great Lakes Res 33:295–302
Jude DJ (1997) Round gobies: cyberfish of the third millenium. Great Lake Res Rev 3:27–34
Karlsson AML, Almqvist G, Skora KE, Appelberg M (2007) Indications of competition between non-indigenous round goby and native flounder in the Baltic Sea. ICES J Mar Sci 64:479–486
Knutsen H, Jorde PE, Andre C, Stenseth NC (2003) Fine-scaled geographic population structuring in a highly mobile marine species: the Atlantic cod. Mol Ecol 12:385–394
Kolar SK, Lodge DM (2001) Progress in invasion biology: predicting invaders. Trends Ecol Evol 16:1233–1236
Kuhner MK (2006) LAMARC 2.0: maximum likelihood and Bayesian estimation of sample parameters. Bioinformatics 22:768–770
Lynch M, Ritland K (1999) Estimation of pairwise relatedness with molecular markers. Genetics 152:1753–1766
Novak SJ (2007) The role of evolution in the invasion process. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:3671–3672
Piry S, Alapetite A, Cornuet J-M, Paetkau D, Baudouin L, Estoup A (2004) GeneClass2: a software for genetic assignment and first-generation migrant detection. J Hered 95:536–539
Rannala B, Mountain JL (1997) Detecting immigration by using multilocus genotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:9197–9201
Raymond M, Rousset F (1997) GENEPOP (version 1.2): population genetics software for exact tests and ecumenicism. J Hered 86:248–249
Rice WR (1989) Analyzing tables of statistical tests. Evolution 43:223–225
Sakai AK, Allendorf FW, Holt JS, Lodge DM, Molofsky J, With KA, Baughman S, Cabin RJ, Cohen JE, Ellstrand NC, McCauley DE, O’Neil P, Parker IM, Thompson JN, Weller SG (2001) The population biology of invasive species. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 32:305–332
Schneider S, Kueffer J-M, Roessli D, Excoffier L (1996) Arlequin, ver. 1.0b5a, University of Geneva
Stone JR, Björklund M (2001) Delrious: a computer program designed to analyse molecular marker data and calculate delta and relatedness estimates with confidence. Mol Ecol Notes 1:209–214
van Oosterhout C, Hutchinson WF, Wills DPM, Shipley P (2004) MICRO-CHECKER: software for identifying and correcting genotyping errors in microsatellite data. Mol Ecol Notes 4:535–538
Vyskocilova M, Ondrackova M, Simkova A, Martin J-F (2007) Isolation and characterization of microsatellites in Neogobius kessleri (Perciformes, Gobiidae) and cross-species amplification within the family Gobidae. Mol Ecol Notes 7:701–704
Waples RS (1998) Separating the wheat from the chaff: patterns of genetic divergence in high gene flow species. J Hered 89:438–450
Waples RS, Gaggiotti O (2006) What is a population? An empirical evaluation of some genetic methods for identifying the number of gene pools and their degree of connectivity. Mol Ecol 15:1419–1439
Whitlock MC (2005) Combining probability from independent tests: the weighted Z-method is superior to Fisher’s approach. J Evol Biol 18:1368–1372
Xu H, Fu Y-X (2004) Estimating effective population size or mutation rate with microsatellites. Genetics 166:555–563
Acknowledgments
MB and the genetic analyses were supported by FORMAS. This study is a part of the Swedish program AquaAliens, funded by Swedish EPA with support from the Swedish Board of Fisheries. We thank Åsa Kestrup, Alma Strandmark Michal Skora and the staff at Hel Marine Station for help, and Atis Minde for samples from Latvia. We also thank Sara Bergek, Niklas Kolm and Mare Löhmus for discussions and comments on the ms, and Reija Dufva for doing the labwork.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Björklund, M., Almqvist, G. Rapid spatial genetic differentiation in an invasive species, the round goby Neogobius melanostomus in the Baltic Sea. Biol Invasions 12, 2609–2618 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-009-9669-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-009-9669-z