Abstract
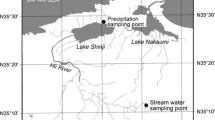
Atmospheric bulk depositions of soluble reactive phosphorus (SRP), soluble unreactive phosphorus (SUP), particulate inorganic phosphorus (PIP), particulate organic phosphorus (POP), total phosphorus (TP) and some other dissolved and particulate components were monitored for 3 years in Ashiu, Central Japan. The mean bulk depositions of SRP, SUP, PIP, POP, TP, dissolved components (Na, Mg, nss-Ca, K, V, Mo, nss-SO4) and particulate components (Al, Fe, Ti, Ca, Mg, Mn, Ba, Sr, Zn) were 175, 76, 136, 397, 783, 156,000, 10,900, 7450, 5470, 10.3, 1.52, 40,100, 13,200, 3590, 2630, 576, 624, 42.3, 30.2, 17.4, 8.2 μmol m−2 year−1, respectively. The value for TP deposition was in the lower range of previous literature. The low P deposition probably reflected the method applied to reduce the contribution of local particles, including (1) placement of samplers off the ground surface, (2) installation of multiple samplers, and (3) rejection of contaminated samples. Al data suggested that 15 ± 5% of TP was brought by lithogenic dust from East Eurasia. Nss-SO4 and Mo data and air-mass backward trajectories suggested that 39 ± 4% of TP was derived from coal combustion in China. It was speculated that the rest (47 ± 6%) of the TP deposition might be predominantly attributed to the contribution of local biogenic particles. Net atmospheric TP input (lithogenic dust and fossil fuel combustion) was almost equal to the TP outflow from Japanese forests on granitic soils.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Ahn R.T. James (1999) ArticleTitleOutlier detection in phosphorus dry deposition rates measured in South Florida Atmos. Environ. 33 5123–5131 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S1352-2310(99)00165-X
M.R. Alcock A.J. Morton (1985) ArticleTitleNutrient content of throughfall and stem-flow in woodland recently established on heathland J. Ecol. 73 625–632
S.E. Allen A. Carlisle E.J. White C.C. Evans (1968) ArticleTitleThe plant nutrient content of rainwater J. Ecol. 56 497–504
G. Bergametti E. Remoudaki R. Losno E. Steiner B. Chatenet P. Buat-Menard (1992) ArticleTitleSource transport and deposition of atmospheric phosphorus over the Northwestern Mediterranean J. Atmos. Chem. 14 501–513 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00115254
M.M. Brinson H.D. Bradshaw R.N. Holmes J.B.J. Elkins (1980) ArticleTitleLitterfall, stemflow, and throughfall nutrient fluxes in an alluvial swamp forest Ecology 61 827–835
J. Campo M. Maass V.J. Jarammillo A. Martinez-Yrizar J. Sarukhan (2001) ArticleTitlePhosphorus cycling in a Mexican tropical dry forest ecosystem Biogeochemistry 53 161–179 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1010663516029
A. Carlisle A.H.F. Brown E.J. White (1966) ArticleTitleThe organic matter and nutrient elements in the precipitation beneath a sessile oak (Quercus petraea) canopy J. Ecol. 54 87–98
P.J. Dillon W.B. Kirchner (1975) ArticleTitleThe effects of geology and land use on the export of phosphorus from watersheds Water Res. 9 135–148 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0043-1354(75)90002-0
Draxler R.R. and Rolph G.D. 2003. HYSPLIT (HYbrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory) Model access via NOAA ARL READY Web-site (http://www.arl.noaa.gov/ready/hysplit4.html). NOAA Air Resources Laboratory, Silver Spring, MD.
S.J. Eisenreich P.J. Emmling A.M. Beeton (1977) ArticleTitleAtmospheric loading of phosphorus and other chemicals to lake Michigan J. Great Lakes Res. 3 291–304
S. Gallet B. Jahn M. Torii (1996) ArticleTitleGeochemical characterization of the Luochuan loess-paleosol sequence China and paleoclimatic implications Chem. Geol. 133 67–88 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0009-2541(96)00070-8
L. Gardner (1990) ArticleTitleThe role of rock weathering in the phosphorus budget of terrestrial watersheds Biogeochemistry 11 97–110 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00002061
C.E. Gibson Y. Wu D. Pinkerton (1995) ArticleTitleSubstance budgets of an upland catchment: the significance of atmospheric phosphorus inputs Freshwater Biol. 33 385–392
A.J.P. Gore (1968) ArticleTitleThe supply of six elements by rain to an upland peat area J. Ecol. 56 483–495
W.F. Graham R.A. Duce (1979) ArticleTitleAtmospheric pathways of the phosphoruc cycle Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 43 1195–1208
R. Harriman (1978) ArticleTitleNutrient leaching from fertilized forest watersheds in Scotland J. Appl. Ecol. 15 933–942
K.E. Havens J. DeCosta (1984) ArticleTitleThe effects of acidification and phosphorus addition on phytoplankton biomass and productivity in a circum-neutral mesotrophic lake receiving acid precipitation Arch. Hydrobiol. Suppl. 69 443–476
C.D. Hendry C.W. Berish E.S. Edgerton (1984) ArticleTitlePrecipitation chemistry of Turrialba Costa Rica Water Resour. Res. 20 1677–1684
K. Inoue T. Naruse (1987) ArticleTitlePhysical, chemical, and mineralogical characteristics of modern eolian dust in Japan and rate of dust deposition Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 33 327–345
E. Ishii (1979) ArticleTitle‘Kosa’ observed with the satellite Himawari and an electron microscope Kisho 9 22–25
R.A. Jahnke (2000) The phosphorus cycle M. Jacobson R.J. Charlson H. Rodhe G.H. Orians (Eds) Earth System Science: from Biogeochemical Cycles to Global Change Academic Press New York 360–376
A.D. Jassby J.E. Reuter R.P. Axler C.R. Goldman S.H. Hackley (1994) ArticleTitleAtmospheric deposition of nitrogen and phosphorus in the annual nutrient load of Lake Tahoe (California-Nevada) Water Resour. Res. 30 2207–2216 Occurrence Handle10.1029/94WR00754
F.L. Johnson P.G. Risser (1974) ArticleTitleBiomass, annual net primary production, and dynamics of six mineral elements in a post oak-blackjack oak forest Ecology 55 1246–1258
C. Jordan (1987) ArticleTitleThe precipitation chemistry at rural sites in Northern Ire-land Record Agric. Res. 35 53–66
T.E. Jordan D.L. Correll D.E. Weller N.M. Goff (1995) ArticleTitleTemporal variation in precipitation chemistry on the shore of the chesapeake bay Water Air Soil Poll. 83 263–284
J. Kopacek L. Prochazkova J. Hejzlar (1997) ArticleTitleTrends and seasonal patterns of bulk deposition of nutrients in the Czech Republic Atmos. Environ. 31 797–808 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S1352-2310(96)00261-0
Kunimatsu 1995. Characteristic and pollutants load of river runoff from forests. Biwako Kenkyusho Shoho 14: 6–15 (in Japanese).
Kuo S. 1996. Phosphorus. In: Soil Science Society of America (eds) Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 3. Chemical Methods - SSSA Book Series no.5, pp. 869–919.
W.M.J. Lewis (1981) ArticleTitlePrecipitation chemistry and nutrient loading by precipitation in a tropical watershed Water Resour. Res. 17 169–181
W. Maher L. Woo (1998) ArticleTitleProcedures for the storage and digestion of natural waters for the determination of filterable reactive phosphorus, total filterable phosphorus and total phosphorus Anal. Chim. Acta. 375 5–47 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0003-2670(98)00274-8
C. Migon V. Sandroni (1999) ArticleTitlePhosphorus in rainwater: Partitioning inputs and impact on the surface coastal ocean Limnol. Ocean. 44 1160–1165
G. Mothes R. Koschel G. Proft (1985) The chemical environment S.J. Casper (Eds) Lake Stechlin. A Temperate Oligotrophic Lake W. Junk Lancaster 87–125
J.W. Murray (1992) The Oceans S. Butcher R. Charlson G. Orians G. Wolfe (Eds) Global Biogeochemical Cycles Academic Press San Diego 175–211
E.I. Newman (1995) ArticleTitlePhosphorus inputs to terrestrial ecosystems J. Ecol. 83 713–726
R. Psenner (1984) ArticleTitleThe proportion of empneuston and total atmospheric inputs of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in the nutrient budget of a small mesotrophic lake (Piburger seeAustria) Intern. Rev. ges. Hydrobiol. 69 23–39
G. Persson O. Broberg (1985) ArticleTitleNutrient concentrations in the acidified Lake Gardsjon: The role of transport and retention of phosphorus, nitrogen and DOC in watershed and lake Ecol. Bull. 37 158–175
K. Pye (1987) Aeolian Dust and Dust Deposits Academic Press London
Redfield G.W. 1998. Quantifying atmospheric deposition of phosphorus: a conceptual model and literature review for environmental management. Technical Publication WRE No. 360. South Florida Water Management DistrictWest Palm BeachFL.
D.W. Schindler R.W. Newbury K.G. Beaty P. Campbell (1976) ArticleTitleNatural water and chemical budgets for a small precam-brian lake basin in Central Canada J. Fish. Res. B. Canada 33 2526–2543
R.D. Shaw A.M. Trimbee M.H. Fricker E.E. Prepas (1989) ArticleTitleAtmospheric deposition of phosphorus and nitrogen in central Alberta with emphasis on narrow lake Water Air Soil Poll. 43 119–134 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00175588
R.F. Sober M.H. Bates (1979) ArticleTitleThe atmospheric contribution of phosphorus to an aquatic ecosystem Water Air Soil Poll. 11 63–69 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00163519
S. Sugita (1993) ArticleTitleA model of pollen source area for an entire lake surface Quat. Res. 39 239–244 Occurrence Handle10.1006/qres.1993.1027
M. Sugiyama (1996) ArticleTitleSimultaneous multi-element analysis of aquatic suspended particulate matter Bunseki Kagaku. 45 667–675
W.T. Swank G.S. Henderson (1976) ArticleTitleAtmospheric input of some cations and anions to forest ecosystems in North Carolina and Tennessee Water Resour. Res. 12 541–546
S. Tsukuda M. Sugiyama Y. Harita K. Nishimura (2004) ArticleTitleA methodological re-examination of atmospheric phosphorus input estimates based on spatial microheterogeneity Water Air Soil Poll. 152 333–347
S. Tsukuda M. Sugiyama Y. Harita K. Nishimura (2005) ArticleTitleAtmospheric bulk deposition of soluble phosphorus in Ashiu Experimental Forest Central Japan: source apportionment and sample contamination problem Atmos. Environ. 39 823–836 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.atmosenv.2004.10.028
J.D.H. Williams J-M Jaquet R.L. Thomas (1976) ArticleTitleForms of phosphorus in the surficial sediments of lake Erie J. Fish. Res. B. Canada 33 413–429
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsukuda, S., Sugiyama, M., Harita, Y. et al. Atmospheric Phosphorus Deposition in Ashiu, Central Japan – Source Apportionment for the Estimation of True Input to a Terrestrial Ecosystem. Biogeochemistry 77, 117–138 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-005-1943-2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-005-1943-2