Abstract
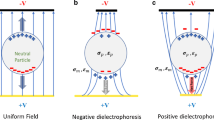
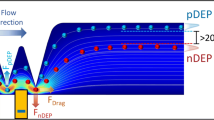
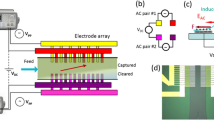
DC-Dielectrophoresis (DC-DEP), the induced motion of the dielectric particles in a spatially non-uniform DC electric field, is applied to separate biological cells by size. The locally non-uniform electric field is generated by an insulating hurdle fabricated within a PDMS microchannel. The cells experience a negative DEP (accordingly a repulsive) force at the corners of the hurdle where the gradient of local electric-field strength is the strongest. The DC-DEP force acting on the cells is proportional to the cells’ size. Thus the moving cells deviate from the streamlines and the degree of deviation is dependent on the cell size. In this paper, we demonstrated by using this method that, combined with the electroosmotic flow, mixed biological cells of a few to tens of micrometers difference in diameter can be continuously separated into different collecting wells. For separating target cells of a specific size, all that is required is to adjust the voltage outputs of the electrodes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.-F. Chou, J.O. Tegenfeldt, O. Bakajin, S.S. Chan, E.C. Cox, N. Darnton, T. Duke, R.H. Austin, Biophys. J. 83, 2170 (2002)
C.-F. Chou, F. Zenhausern, IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 22, 62 (2003)
E.B. Cummings, A.K. Singh, Proceedings SPIE, Santa Clara, CA, 164, (2000)
E.B. Cummings, A.K. Singh, Anal. Chem. 75, 4724 (2003)
P.S. Dittrich, K. Tachikawa, A. Manz, Anal. Chem. 78, 3887 (2006)
D.C. Duffy, J.C. McDonald, O.J.A. Schueller, G.M. Whitesides, Anal. Chem. 70, 4974 (1998)
J. El-Ali, P.K. Sorger, K.F. Jensen, Nature. 442, 403 (2006)
D. Erickson, D. Sinton, D. Li, Lab. Chip. 3, 141 (2003)
L. Feeney, E.R. Berman, Invest. Ophthalmol. 15, 789 (1976)
P.R.C. Gascoyne, J. Vykoukal, Electrophoresis. 23, 1973 (2002)
M. Haritou, D. Yova, S. Loukas, Bioelectrochemistry. 52, 229 (2000)
M.P. Hughes, Electrophoresis. 23, 2569 (2002)
T.B. Jones, Electromechanics of Particles (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1995)
K.H. Kang, X. Xuan, Y. Kang, D. Li, J. Appl. Phys. 99, 064702 (2006a)
K. H. Kang, Y. Kang, X. Xuan, D. Li, Electrophoresis. 27, 694 (2006b)
B.H. Lapizco-Encinas, B.A. Simmons, E.B. Cummings, Y. Fintschenko, Anal. Chem. 76, 1571 (2004a)
B.H. Lapizco-Encinas, B.A. Simmons, E.B. Cummings, Y. Fintschenko, Electrophoresis. 25, 1695 (2004b)
H.A. Pohl, Dielectrophoresis (Cambridge University Press, London, 1978)
C. Prinz, J.O. Tegenfeldt, R.H. Austin, E.C. Cox, J.C. Sturm, Lab. Chip. 2, 207 (2002)
S. Thamilselvan, K.J. Byer, R.L. Hackett, S.R. Khan, J. Urol. 164, 224 (2000)
M. Toner, D. Irimia, Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 7, 77 (2005)
J. Voldman, Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 8, 425 (2006)
X. Xuan, B. Xu, D. Sinton, D. Li, Lab. Chip. 4, 230 (2004)
X. Xuan, B. Xu, D. Li, Anal. Chem. 77, 4323 (2005)
L. Ying, S.S. White, A. Bruckbauer, L. Meadows, Y.E. Korchev, D. Klenerman, Biophys. J. 86, 1018 (2004)
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to thank the Vanderbilt University for the research grants, and thank Jie Wei and Louise Barnett from Vanderbilt-Meharry Center for AIDS Research for assistance in preparing the fixed white blood cells.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, Y., Li, D., Kalams, S.A. et al. DC-Dielectrophoretic separation of biological cells by size. Biomed Microdevices 10, 243–249 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-007-9130-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-007-9130-y