Summary:
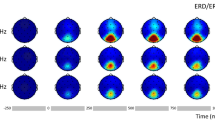
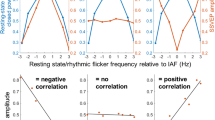
Steady-state visual evoked potentials (SSVEPs) are used in cognitive and clinical studies of brain function because of excellent signal-to-noise ratios and relative immunity to artifacts. SSVEPs also provide a means to characterize preferred frequencies of neocortical dynamic processes. In this study, SSVEPs were recorded with 110 electrodes while subjects viewed random dot patterns flickered between 3 and 30 Hz. Peaks in SSVEP power were observed at delta (3 Hz), lower alpha (7 and 8 Hz), and upper alpha band (12 and 13 Hz) frequencies; the spatial distribution of SSVEP power is also strongly dependent on the input frequency suggesting cortical resonances. We characterized the cortical sources that generate SSVEPs at different input frequencies by applying surface Laplacians and spatial spectral analysis. Laplacian SSVEPs recorded are sensitive to small changes (1–2 Hz) in the input frequency at occipital and parietal electrodes indicating distinct local sources. At 10 Hz, local source activity occurs in multiple cortical regions; Laplacian SSVEPs are also observed in lateral frontal electrodes. Laplacian SSVEPs are negligible at many frontal electrodes that elicit strong potential SSVEPs at delta, lower alpha, and upper alpha bands. One-dimensional (anterior-posterior) spatial spectra indicate that distinct large-scale source distributions contribute SSVEP power in these frequency bands. In the upper alpha band, spatial spectra indicate the presence of long-wavelength (> 15 cm) traveling waves propagating from occipital to prefrontal electrodes. In the delta and lower alpha band, spatial spectra indicate that long-wavelength source distributions over posterior and anterior regions form standing-wave patterns. These results suggest that the SSVEP is generated by both (relatively stationary) localized sources and distributed sources that exhibit characteristics of wave phenomena.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertrand, O., Perrin, F. and Pernier, J. A theoretical justification of the average-reference in topographic evoked potential studies. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol., 1985, 62: 462–464.
Bertrand, O., Perrin, F. and Pernier, J. A theoretical justification of the average reference in topographic evoked potential studies. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol., 1986, 62: 462–464.
Brainard, D.H. The Psychophysics Toolbox. Spatial Vision, 1997, 10: 433–436.
Burkitt, G.R., Silberstein, R.B., Cadusch, P.J. and Wood, A.W. The steady-state visually evoked potential and travelling waves. Clinical Neurophysiology, 2000, 111: 246–258.
Chen, Y., Seth, A.K., Gally, J.A. and Edelman, G.M. The power of human brain magnetoencephalographic signals can be modulated up or down by changes in an attentive visual task. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2003, 100: 3501–3506.
Ding, J., Sperling, G. and Srinivasan, R. SSVEP power modulation by attention depends on the network tagged by the flicker frequency. Cerebral Cortex, 2005, in press.
Edelman, G.M. Building a picture of the brain. Ann. N Y Acad. Sci., 1999, 882: 68–89.
Felleman, D.J. and Van Essen, D.C. Distributed hierarchical processing in the primate cerebral cortex. Cerebral Cortex, 1991, 1: 1–47.
Law, S.K., Nunez, P.L. and Wijesinghe, R.S. High-resolution EEG using spline generated surface Laplacians on spherical and ellipsoidal surfaces. IEEE Trans. Biomed Eng., 1993, 40: 145–153.
Lopes da Silva, F. Functional localization of brain sources using EEG and/or MEG data: volume conductor and source models. Magn. Reson. Imaging, 2004, 22:1533–1538.
Maier, J., Dagnielie, G., Spekreijse, H. and van Dijk, B.W. Principal components analysis for source localization of VEPs in man. Vision Research, 1987: 165–177.
McDonough, R.N. Application of maximum likelihood and maximum entropy method to array processing. In: S. Haykin (Ed.), Nonlinear Methods of Spectral Analysis. Springer Verlag, 1988.
Mountcastle, V.B. Perceptual Neuroscience: The Cerebral Cortex, 1997, Academic Press, NY.
Muller, M.M., Teder, W. and Hillyard, S.A. Magnetoencephalographic recording of steady-state visual evoked cortical activity. Brain Topography, 1997, 9: 163–168.
Nakayama, K. and Mackeben, M. Steady-state visual evoked potentials in the alert primate. Vision Research, 1982, 22: 1261–1271.
Narici, L., Portin, K., Salmelin, R. and Hari, R. Responsiveness of human corical activity to rhythmical stimulation: A three-modality, whole-cortex neuromagnetic investigation. 1998, 7: 209–223.
Nunez, P.L. Wavelike properties of the alpha rhythm. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 1974, 21: 473–482.
Nunez, P.L. Electric Fields of the Brain: The Neurophysics of EEG, 1st Edition, New York: Oxford UP, 1981.
Nunez, P.L. Generation of human EEG by a combination of long and short range neocortical interactions. Brain Topography, 1989, 1: 199–215.
Nunez, P.L. Neocortical Dynamics and Human EEG Rhythms. New York: Oxford University Press, 1995.
Nunez, P.L. Toward a quantitative description of large scale neocortical dynamic function and EEG. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 2000a, 23: 415–437. (Invited target article).
Nunez, P.L. Neocortical dynamic theory should be as simple as possible, but not simpler. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 2000b, 23: 371–398. (Response to 18 commentaries by neuroscientists on target article).
Nunez, P.L. and Srinivasan, R. Electric Fields of the Brain: The Neurophysics of EEG, 2nd Edition, New York: Oxford UP, 2006.
Nunez, P.L., Silberstein, R.B., Cadusch, P.J., Wijesinghe, R.S., Westdorp, A.F. and Srinivasan, R. A theoretical and experimental study of high-resolution EEG based on surface Laplacians and cortical imaging. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, 1994, 90: 40:57.
Nunez, P.L., Srinivasan, R., Westdorp, A.F., Wijesinghe, R.S., Tucker, D.M., Silberstein, R.B. and Cadusch, P.J. EEG coherency. I: Statistics, reference electrode, volume conduction, Laplacians, cortical imaging, and interpretation at multiple scales. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol., 1997, 103: 499–515.
Nunez, P.L., Wingeier, B.M. and Silberstein, R.B. Spatial-temporal structure of human alpha rhythms: Theory, microcurrent sources, multiscale measurements, and global binding of local networks. Human Brain Mapping, 2001, 13: 125–164.
Okada, Y.C., Kaufman, L., Brenner, D. and Williamson, S.J. Modulation transfer functions of the human visual system revealed by magnetic measurements. Vision Research, 1982, 22: 319–333.
Perrin, F., Bertrand, O. and Pernier, J. Scalp current density mapping: value and estimation from potential data. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng., 1987, 34: 283–287.
Perrin, F., Pernier, J., Bertrand, O. and Echallier, J.F. Spherical spline for potential and current density mapping. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol., 1989, 72: 184–187.
Rager, G. and Singer, W. The response of cat visual cortex to flicker stimuli of variable frequency. European J. of Neuroscience, 1998, 10: 1856–1877.
Regan, D. Steady-state evoked potentials. J. Opt. Soc. Am., 1977, 67:1475–1489.
Regan, D. Human brain electrophysiology. New York: Elsevier, 1989.
Schmolesky, M.T., Wang, Y., Hanes, D.P., Thompson, K.G., Leutgeb, S., Schall, J.D. and Leventhal, A.G. Signal timing across the macaque visual system. Journal of Neurophysiology, 1998, 79: 3272–3278.
Silberstein, R.B., Nunez, P.L., Pipingas, A., Harris, P. and Danieli, F. Steady state visually evoked potential (SSVEP) topography in a graded working memory task. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 2001, 42: 219–232.
Silberstein, R.B. Steady-state visually evoked potentials, brain resonances, and cognitive processes. In: P.L. Nunez (Au.), Neocortical Dynamics and Human EEG Rhythms. Oxford University Press, 1995: 272–303.
Silberstein, R.B., Danieli, F. and Nunez, P.L. Fronto-parietal evoked potential synchronization is increased during mental rotation. NeuroReport, 2003, 14: 67–71.
Silberstein, R.B., Song, J., Nunez, P.L. and Park, W. Dynamic sculpting of brain functional connectivity is correlated with performance measures. Brain Topography, 2004, 16:249–254.
Sperkeijse, H., Estevez, O. and Reits, D. Visual evoked potentials and the physiological analysis of visual processes in man. In: J.E. Desmedt (Ed.), Visual Evoked Potentials in Man: New Developments. Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1977: 16–89.
Srinivasan, R., Nunez, P.L., Tucker, D.M., Silberstein, R.B. and Cadusch, P.J. Spatial sampling and filtering of EEG with spline Laplacians to estimate cortical potentials. Brain Topography, 1996, 8: 355–366.
Srinivasan, R., Nunez, P.L. and Silberstein, R.B. Spatial filtering and neocortical dynamics: estimates of EEG coherence. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 1998, 45: 814–826.
Srinivasan, R., Russell, D.P., Edelman, G.M. and Tononi, G. Increased synchronization of neuromagnetic responses during conscious perception. Journal of Neuroscience, 1999, 19(13): 5435–5448.
Srinivasan, R. Internal and external neural synchronization during conscious perception. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, 2004, 19: 1–18.
Srinivasan, R. and Petrovic, S. MEG phase follows conscious perception during binocular rivalry induced by visual stream segregation. Cerebral Cortex, 2005, in press.
Tyler, C.W., Apkarian, P. and Nakayama, K. Multiple spatial frequency tuning of electrical responses from the human visual cortex. Experimental Brain Research, 1978, 33: 535–550.
Wingeier, B.M., Nunez, P.L. and Silberstein, R.B. Spherical harmonic decomposition applied to spatial-temporal analysis of human high-density electroencephalogram. Physical Review E, 2001, 64:051916-1 to 9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research was supported by NIMH grant R01-68004.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srinivasan, R., Bibi, F. & Nunez, P. Steady-State Visual Evoked Potentials: Distributed Local Sources and Wave-Like Dynamics Are Sensitive to Flicker Frequency. Brain Topogr 18, 167–187 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-006-0267-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-006-0267-4