Abstract
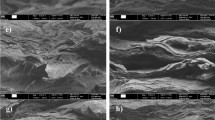
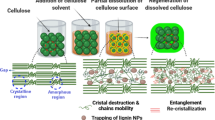
Nanocomposite films consisting of cellulose nanofibrils (CNFs), magnesium hydroxide nanoplatelets (MHNPs) and regenerated cellulose were prepared via simple blending and casting processes. The CNFs were obtained from bamboo pulp by ultrasonic treatment coupled with high shear homogenization. The morphology, structure and properties of the nanocomposite films were comprehensively analyzed using various characterization techniques, including the scanning electron microscope, digital microscope, limiting oxygen index (LOI), micro-scale combustion calorimetry, antibacterial assays, tensile testing, etc. When the MHNP content was optimized to 30 wt%, the nanocomposite film exhibited the best overall properties. The LOI of the composite film increased from 20.0 (0 wt% MHNPs) to 32.7 (30 wt% MHNPs), making it a flame-retardant material in air. In addition, the film containing 30 wt% MHNPs showed excellent antibacterial activity. However, the increase in MHNP content would result in gradual deterioration of the films’ mechanical properties. However, the incorporation of CNFs could significantly suppress this trend. The present work provided a promising pathway for manufacturing multifunctional and high-performance cellulose-based composite films, which were potentially useful for a variety of packaging materials, especially in the biomedical and food packaging fields.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham E, Deepa B, Pothan LA, Jacob M, Thomas S, Cvelbar U, Anandjiwala R (2011) Extraction of nanocellulose fibrils from lignocellulosic fibres: a novel approach. Carbohydr Polym 86:1468–1475
Abraham E, Elbi PA, Deepa B, Jyotishkumar P, Pothen LA, Narine SS, Thomas S (2012) X-ray diffraction and biodegradation analysis of green composites of natural rubber/nanocellulose. Polym Degrad Stab 97:2378–2387
Abraham E, Deepa B, Pothan LA, John M, Narine SS, Thomas S, Anandjiwala R (2013) Physicomechanical properties of nanocomposites based on cellulose nanofibre and natural rubber latex. Cellulose 20:417–427
Agarwal UP, Reiner RS, Ralph SA (2010) Cellulose I crystallinity determination using FT-Raman spectroscopy: univariate and multivariate methods. Cellulose 17:721–733
Alavi MA, Morsali A (2010) Syntheses and characterization of Mg(OH)2 and MgO nanostructures by ultrasonic method. Ultrason Sonochem 17:441–446
Bhatnagar A, Sain M (2005) Processing of cellulose nanofiber-reinforced composites. J Reinf Plast Compos 24:1259–1268
Cady NC, Behnke JL, Strickland AD (2011) Copper-based nanostructured coatings on natural cellulose: nanocomposites exhibiting rapid and efficient inhibition of a multi-drug resistant wound pathogen, A. baumannii, and mammalian cell biocompatibility in vitro. Adv Funct Mater 21:2506–2514
Cao XQ, Vassen R, Stoever D (2004) Ceramic materials for thermal barrier coatings. J Eur Ceram Soc 24:1–10
Cao H, Zheng H, Yin J, Lu Y, Wu S, Wu X, Li B (2010) Mg(OH)2 complex nanostructures with superhydrophobicity and flame retardant effects. J Phys Chem C 114:17362–17368
Cervin NT, Andersson L, Ng JBS, Olin P, Bergström L, Wagberg L (2013) Lightweight and strong cellulose materials made from aqueous foams stabilized by nanofibrillated cellulose. Biomacromolecules 14:503–511
Costerton JW, Stewart PS, Greenberg EP (1999) Bacterial biofilms: a common cause of persistent infections. Science 284:1318–1322
Dawsey TR, McCormick CL (1990) The lithium chloride/dimethylacetamide solvent for cellulose: a literature review. J Macromol Sci Part C Polym Rev 30:405–440
Dong C, Cairney J, Sun Q, Maddan OL, He G, Deng YJ (2010) Investigation of Mg(OH)2 nanoparticles as an antibacterial agent. Nanopart Res 12:2101–2109
Dupont AL (2003) Cellulose in lithium chloride/N,N-dimethylacetamide, optimisation of a dissolution method using paper substrates and stability of the solutions. Polymer 44:4117–4126
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21:885–896
French AD, Santiago Cintrón S (2013) Cellulose polymorphy, crystallite size, and the Segal Crystallinity Index. Cellulose 20:583–588
Fu M, Qu B (2004) Synergistic flame retardant mechanism of fumed silica in ethylene-vinyl acetate/magnesium hydroxide blends. Polym Degrad Stab 85:633–639
Gindl-Altmutter W, Keckes J, Plackner J, Liebner F, Englund K, Laborie MP (2012) All-cellulose composites prepared from flax and lyocell fibres compared to epoxy–matrix composites. Compos Sci Technol 72:1304–1309
Gui H, Zhang X, Liu Y, Dong W, Wang Q, Gao J, Song Z, Lai J, Qiao J (2007) Effect of dispersion of nano-magnesium hydroxide on the flammability of flame retardant ternary composites. Compos Sci Technol 67:974–980
Hall-Stoodley L, Costerton JW, Stoodley P (2004) Bacterial biofilms: from the natural environment to infectious diseases. Nat Rev-Microbiol 2:95–108
He X, Xiao Q, Lu C, Wang Y, Zhang X, Zhao J, Zhang W, Zhang X, Deng Y (2014) Uniaxially aligned electrospun all-cellulose nanocomposite nanofibers reinforced with cellulose nanocrystals: scaff old for tissue engineering. Biomacromolecules 15:618–627
Henrich VE (1976) Thermal faceting of (110) and (111) surfaces of MgO. Surf Sci 57:385–392
Hu W, Peng C, Luo W, Lv M, Li X, Li D, Huang Q, Fan C (2010) Graphene-based antibacterial paper. ACS Nano 4:4317–4323
Jonoobi M, Harun J, Mathew AP, Oksman K (2010) Mechanical properties of cellulose nanofiber (CNF) reinforced polylactic acid (PLA) prepared by twin screw extrusion. Compos Sci Technol 70:1742–1747
Jonoobi M, Mathew AP, Oksman K (2012) Producing low-cost cellulose nanofiber from sludge as new source of raw materials. Ind Crops Prod 40:232–238
Kim SJ, Dwiatmoko AA, Choi JW, Suha YW, Suh DJ, Oh M (2010) Cellulose pretreatment with 1-n-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride for solid acid-catalyzed hydrolysis. Bioresour Technol 10:8273–8279
Knight CC, Ip F, Zeng C, Zhang C, Wang B (2013) A highly efficient fire retardant nanomaterial based on carbon nanotubes and magnesium hydroxide. Fire Mater 37:91–97
Lam C, Lau K, Cheung H, Ling H (2005) Effect of ultrasound sonication in nanoclay clusters of nanoclay/epoxy composites. Mater Lett 59:1369–1372
Laoutid F, Bonnaud L, Alexandre M, Lopez-Cuesta JM, Dubois Ph (2009) New prospects in flame retardant polymer materials: from fundamentals to nanocomposites. Mater Sci Eng R: Rep 23:100–125
Li Y, Sui M, Ding Y, Zhang G, Zhuang J, Wang C (2000) Preparation of Mg (OH)2 nanorods. Adv Mater 12:818–821
Li YC, Mannen S, Morgan AB, Chang SC, Yang YH, Condon B, Grunlan JC (2011) Intumescent all-polymer multilayer nanocoating capable of extinguishing flame on fabric advanced materials 23:3926–3931
Liu Y, Wang X, Qi K, Xin JH (2008) Functionalization of cotton with carbon nanotubes. J Mater Chem 18:3454–3460
Lv J, Qiu L, Qu B (2004) Controlled synthesis of magnesium hydroxide nanoparticles with different morphological structures and related properties in flame retardant ethylene–vinyl acetate blends. Nanotechnology 15:1576–1581
Mishra S, Sonawane SH, Singh RP, Bendale A, Patil K (2004) Effect of nano-Mg(OH)2 on the mechanical and flame-retarding properties of polypropylene composites. J Appl Polym Sci 94:116–122
Olsson RT, Samir MASA, Salazar-Alvarez G, Belova L, Ström V, Berglund LA, Ikkala O, Nogués J, Gedde UW (2010) Making flexible magnetic aerogels and stiff magnetic nanopaper using cellulose nanofibrils as templates. Nat Nanotechnol 5:584–588
Pan X, Wang Y, Chen Z, Pan D, Cheng Y, Liu Z, Lin Z, Guan X (2013) Investigation of antibacterial activity and related mechanism of a series of nano-Mg(OH)2. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:1137–1142
Parikh DV, Nam S, He Q (2012) Evaluation of three flame retardant (FR) grey cotton blend nonwoven fabrics using micro-scale combustion calorimeter. J Fire Sci 30:187–200
Qi H, Cai J, Zhang L, Kuga S (2009) Properties of films composed of cellulose nanowhiskers and a cellulose matrix regenerated from alkali/urea solution. Biomacromolecules 10:1597–1602
Qiu L, Xie R, Ding P, Qu B (2003) Preparation and characterization of Mg(OH)2 nanoparticles and flame-retardant property of its nanocomposites with EVA. Compos Struct 62:391–395
Sain M, Park SH, Suhara F, Law S (2004) Flame retardant and mechanical properties of natural fibre–PP composites containing magnesium hydroxide. Polym Degrad Stab 83:363–367
Schartel B, Potschke P, Knoll U, Abdel-Goad M (2005) Fire behaviour of polyamide 6/multiwall carbon nanotube nanocomposites. Eur Polym J 41:1061–1070
Shen L, Chen Y, Li P (2012) Synergistic catalysis effects of lanthanum oxide in polypropylene/magnesium hydroxide flame retarded system. Compos A Appl Sci Manuf 43:1177–1186
Song G, Ma S, Tang G, Wang X (2010) Ultrasonic-assisted synthesis of hydrophobic magnesium hydroxide nanoparticles. Coll Surf A: Physicochem Eng Asp 364:99–104
Soykeabkaewa N, Arimotob N, Nishinob T, Peijsa T (2008) All-cellulose composites by surface selective dissolution of aligned ligno-cellulosic fibres. Compos Sci Technol 68:2201–2207
Syverud K, Chinga-Carrasco G, Toledo J, Toledo PG (2011) A comparative study of Eucalyptus and Pinus radiata pulp fibres as raw materials for production of cellulose nanofibrils. Carbohydr Polym 84:1033–1038
Tang H, Zhou X, Liu X (2013) Effect of magnesium hydroxide on the flame retardant properties of unsaturated polyester resin. Proced Eng 52:336–341
Tonoli GHD, Rodrigues Filho UP, Savastano H Jr, Bras J, Belgacem MN, Rocco Lahr FA (2009) Cellulose modified fibres in cement based composites. Compos A Appl Sci Manuf 40:2046–2053
Tonoli GHD, Teixeira EM, Corrêa AC, Marconcini JM, Caixeta LA, Pereira-da-Silva MA, Mattoso LHC (2012) Cellulose micro/nanofibres from Eucalyptus kraft pulp: preparation and properties. Carbohydr Polym 89:80–88
Tonoli GHD, Belgacem MN, Siqueira G, Bras J, Savastano H Jr, Rocco Lahr FA (2013) Processing and dimensional changes of cement based composites reinforced with surface-treated cellulose fibres. Cem Concr Compos 37:68–75
Walther A, Timonen JVI, Díez I, Laukkanen A, Ikkala O (2011) Multifunctional high-performance biofibers based on wet-extrusion of renewable native cellulose nanofibrils. Adv Mater 23:2924–2928
Wu J, Yan H, Zhang X, Wei L, Liu X, Xu B (2008) Magnesium hydroxide nanoparticles synthesized in water-in-oil microemulsions. J Coll Interface Sci 324:167–171
Yan C, Xue D, Zou L, Yan X, Wang W (2005) Preparation of magnesium hydroxide nanoflowers. J Cryst Growth 282:448–454
Yang CQ, He Q (2011) Applications of micro-scale combustion calorimetry to the studies of cotton and nylon fabrics treated with organophosphorus flame retardants. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 91:125–133
Yang H, Yang CQ, He Q (2009) The bonding of a hydroxy-functional organophosphorus oligomer to nylon fabric using the formaldehyde derivatives of urea and melamine as the bonding agents. Polym Degrad Stab 94:1023–1031
Yang CQ, He Q, Lyon RE, Hu Y (2010a) Investigation of the flammability of different textile fabrics using micro-scale comb ustion calorimetry. Polym Degrad Stab 95:108–115
Yang Z, Zhou C, Cai J, Yan H, Huang X, Yang H, Cheng R (2010b) Effects of macromolecular compatibilizers containing epoxy groups on the properties of linear low-density polyethylene/magnesium hydroxide composites. Ind Eng Chem Res 49:6291–6301
Yang Z, Wang X, Lei D, Fei B, Xin JH (2012) A durable flame retardant for cellulosic fabrics. Polym Degrad Stab 97:2467–2472
Yue Y, Zhou C, French AD, Xia G, Han G, Wang Q, Wu Q (2012) Comparative properties of cellulose nano-crystals from native and mercerized cotton fibers. Cellulose 19:1173–1187
Zhang W, Hu Z, Zhang Y, Lu C, Deng Y (2013) Gel-spun fibers from magnesium hydroxide nanoparticles and UHMWPE nanocomposite: the physical and flammability properties. Compos B Eng 51:276–281
Zhao J, Zhang W, Zhang X, Zhang X, Lu C, Deng Y (2013) Extraction of cellulose nanofibrils from dry softwood pulp using high shear homogenization. Carbohydr Polym 97:695–702
Zhu H, Zhu Q, Li J, Tao K, Xue L, Yan Q (2011) Synergistic effect between expandable graphite and ammonium polyphosphate on flame retarded polylactide. Polym Degrad Stab 96:183–189
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the Natural Science Foundation of China (51303112 and 51203105) and Young Scholar Fund of Sichuan University (2012SCU11074) for financial support of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, J., Zhang, X., Tu, R. et al. Mechanically robust, flame-retardant and anti-bacterial nanocomposite films comprised of cellulose nanofibrils and magnesium hydroxide nanoplatelets in a regenerated cellulose matrix. Cellulose 21, 1859–1872 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0255-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0255-x