Abstract
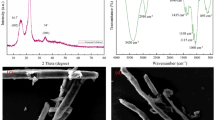
A novel porous adsorbent with high surface area and rigid structure was prepared by crosslinking oxidized microcrystalline cellulose particles with tetrafluoroterephthalonitrile. N2 adsorption–desorption measurements revealed the surface area to be 88.32 m2 g−1 for the porous adsorbent, while it was only 25.74 m2 g−1 for the sample crosslinked using epichlorohydrin. This porous adsorbent showed excellent performance for fast and efficient removal of low-concentration heavy metals from aqueous solution. Adsorption kinetic study demonstrated that, within 5 min, the removal efficiency for Pb2+, Cu2+, and Cd2+ with initial concentration of 10 mg L−1 by this adsorbent was 93.2, 87.5, and 72.3 %, respectively. Moreover, the pseudo-second-order model correlated better to the adsorption kinetic data than the pseudo-first-order model. The effects of other factors, e.g., initial solution pH, adsorption temperature, initial metal concentration, and background electrolytes, on the removal efficiency were also analyzed. Additionally, desorption experiments indicated that this adsorbent could be effectively regenerated using dilute HCl solution.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alsbaiee A, Smith BJ, Xiao L, Ling Y, Helbling DE, Dichtel WR (2016) Rapid removal of organic micropollutants from water by a porous β-cyclodextrin polymer. Nature 529:190–194
Anirudhan TS, Rauf TA, Rejeena SR (2012) Removal and recovery of phosphate ions from aqueous solutions by amine functionalized epichlorohydrin-grafted cellulose. Desalination 285:277–284
Anwar J, Shafique U, Salman M, Waheed-uz-Zaman AS, Anzano JM (2009) Removal of chromium (III) by using coal as adsorbent. J Hazard Mater 171:797–801
Bardajee GR, Hooshyar Z, Shahidi FE (2015) Synthesis and characterization of a novel Schiff-base/SBA-15 nanoadsorbent for removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12:1737–1748
Budd PM, Ghanem BS, Makhseed S, Mckeown NB, Msayib KJ, Tattershall CE (2004) Polymers of intrinsic microporosity (PIMs): robust, solution-processable, organic nanoporous materials. Chem Commun 2:230–231
Cao J, Cao H, Zhu Y, Wang S, Qian D, Chen G, Sun M, Huang W (2017) Rapid and effective removal of Cu2+ from aqueous solution using novel chitosan and Laponite-based nanocomposite as adsorbent. Polymers 9:5
Carta M, Msayib KJ, Mckeown NB (2009) Novel polymers of intrinsic microporosity (PIMs) derived from 1,1-spiro-bis(1,2,3,4- tetrahydronaphthalene)-based monomers. Tetrahedron Lett 50:5954–5957
Chen D, Wang L, Ma Y, Yang W (2016) Super-adsorbent material based on functional polymer particles with a multilevel porous structure. NPG Asia Mater 8:e301
Duan C, Zhao N, Yu X, Zhang X, Xu J (2013) Chemically modified kapok fiber for fast adsorption of Pb2+, Cd2+, Cu2+ from aqueous solution. Cellulose 20:849–860
Fu F, Wang Q (2011) Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: a review. J Environ Manag 92:407–418
Ge F, Li M, Ye H, Zhao B (2012) Effective removal of heavy metal ions Cd2+, Zn2+, Pb2+, Cu2+ from aqueous solution by polymer-modified magnetic nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 211–212:366–372
Ge H, Huang H, Xu M, Chen Q (2016) Cellulose/poly(ethylene imine) composites as efficient and reusable adsorbents for heavy metal ions. Cellulose 23:2527–2537
Ghorai S, Sinhamahpatra A, Sarkar A, Panda AB, Pal S (2012) Novel biodegradable nanocomposite based on XG-g-PAM/SiO2: application of an efficient adsorbent for Pb2+ ions from aqueous solution. Bioresour Technol 119:181–190
Gollavelli G, Chang C, Ling Y (2013) Facile synthesis of smart magnetic graphene for safe drinking water: heavy metal removal and disinfection control. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 1:462–472
Guo L, Sun C, Li G, Liu C, Ji C (2009) Thermodynamics and kinetics of Zn(II) adsorption on crosslinked starch phosphates. J Hazard Mater 161:510–515
Hokkanen S, Bhatnagar A, Sillanpää M (2016) A review on modification methods to cellulose-based adsorbents to improve adsorption capacity. Water Res 91:156–173
Ji F, Li C, Tang B, Xu J, Lu G, Liu P (2012) Preparation of cellulose acetate/zeolite composite fiber and its adsorption behavior for heavy metal ions in aqueous solution. Chem Eng J 209:325–333
Kikuchi T, Tanaka S (2012) Biological removal and recovery of toxic heavy metals in water environment. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 42:1007–1057
Kim UJ, Kuga S (2001) Ion-exchange chromatography by dicarboxyl cellulose gel. J Chromatogr A 919:29–37
Liimatainen H, Visanko M, Sirviö J, Hormi O, Niinimäki J (2012) Enhancement of the nanofibrillation of wood cellulose through sequential periodat-chlorite oxidation. Biomacromolecules 13:1592–1597
Lin S, Juang R (2009) Adsorption of phenol and its derivatives from water using synthetic resins and low-cost natural adsorbents: a review. J Environ Manag 90:1336–1349
Lowell S, Shields JE, Thomas MA, Thommes M (2004) Characterization of porous solids and powders: surface area, pore size and density. Springer, New York
Ma S, Zhan S, Jia Y, Zhou Q (2015) Highly efficient antibacterial and Pb(II) removal effects of AgCoFe2O4-GO nanocomposite. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:10576–10586
Miranda MIG, Bica CID, Nachtigall SMB, Rehman N, Rosa SML (2013) Kinetical thermal degradation study of maize straw and soybean hull celluloses by simultaneous DSC-TGA and MDSC techniques. Thermochim Acta 565:65–71
Mohammed N, Grishkewich N, Berry RM, Tam KC (2015) Cellulose nanocrystal-alginate hydrogel beads as novel adsorbents for organic dyes in aqueous solutions. Cellulose 22:3725–3738
Ozturk A, Artan T, Ayar A (2004) Biosorption of nickel(II) and copper(II) ions from aqueous solution by Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Colloid Surf B Biointerfaces 34:105–111
Seifi L, Torabian A, Kazemian H, Bidhendi GN, Azimi AA, Farhadi F, Nazmara S (2011) Kinetic study of BTEX removal using granulated surfactant-modified natural zeolites nanoparticles. Water Air Soil Pollut 219:443–457
Singh A, Sharma RK, Agrawal M, Marshall FM (2010) Health risk assessment of heavy metals via dietary intake of foodstuffs from the wastewater irrigated site of a dry tropical area of India. Food Chem Toxicol 48:611–619
Sirviö J, Liimatainen H, Niinimäki J, Hormi O (2011) Dialdehyde cellulose microfibers generated from wood pulp by milling-induced periodate oxidation. Carbohydr Polym 86:260–265
Slater AG, Cooper AI (2015) Function-led design of new porous materials. Science 348:988–998
Soler-Illia GJAA, Azzaroni O (2011) Multifunctional hybrids by combining ordered mesoporous materials and macromolecular building blocks. Chem Soc Rev 40:1107–1150
Tseng J, Chang C, Chen Y, Chang C, Chiang P (2007) Synthesis of micro-size magnetic polymer adsorbent and its application for the removal of Cu(II) ion. Colloid Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 295:209–216
Udoetok IA, Dimmick RM, Wilson LD, Headley JV (2016) Adsorption properties of cross-linked cellulose-epichlorohydrin polymers in aqueous solution. Carbohydr Polym 136:329–340
Varma AJ, Chavan VB (1994) Cellulosic diamines as reaction-incorporated fillers in epoxy composites. Cellulose 1:215–219
Visanko M, Liimatainen H, Sirviö J, Hormi O (2015) A cross-linked 2,3-dicarboxylic acid cellulose nanofibril network: a nanoporous thin-film layer with tailored pore size for composite membranes. Sep Purif Technol 154:44–50
Wang B, Lin H, Guo X, Bai P (2014) Boron removal using chelating resins with pyrocatechol functional groups. Desalination 347:138–143
Wei W, Wang Q, Li A, Yang J, Ma F, Pi S, Wu D (2016) Biosorption of Pb(II) from aqueous solution by extracellular polymeric substances extracted from Klebsiella sp. J1: adsorption behavior and mechanism assessment. Sci Rep 6:31575
Xu X, Gao B, Tang X, Yue Q, Zhong Q, Li Q (2011) Characteristics of cellulosic amine-crosslinked copolymer and its sorption properties for Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 189:420–426
Xu X, Gao B, Tan X, Zhang X, Yue Q, Wang Y, Li Q (2013) Nitrate adsorption by stratified wheat straw resin in lab-scale columns. Chem Eng J 226:1–6
Yadav S, Srivastava V, Banerjee S, Weng C, Sharma YC (2013) Adsorption characteristics of modified sand for the removal of hexavalent chromium ions from aqueous solutions: kinetic, thermodynamic and equilibrium studies. CATENA 100:120–127
Yao Y, Xu F, Chen M, Xu Z, Zhu Z (2010) Adsorption behavior of methylene blue on carbon nanotubes. Bioresour Technol 101:3040–3046
Yi J, Zhang L (2008) Removal of methylene blue dye from aqueous solution by adsorption onto sodium humate/polyacrylamide/clay hybrid hydrogels. Bioresour Technol 99:2182–2186
Zhang Y, Yang M, Huang X (2003) Arsenic(V) removal with a Ce(IV)-doped iron oxide adsorbent. Chemosphere 51:945–952
Zhang C, Li P, Huang W, Cao B (2016a) Selective adsorption and separation of organic dyes in aqueous solutions by hydrolyzed PIM-1 microfibers. Chem Eng Res Des 109:76–85
Zhang N, Zang G, Shi C, Yu H, Sheng G (2016b) A novel adsorbent TEMPO-mediated oxidized cellulose nanofibrils modified with PEI: preparation, characterization, and application for Cu(II) removal. J Hazard Mater 316:11–18
Zhou Y, Fu S, Zhang L, Zhan H (2013) Superabsorbent nanocomposite hydrogels made of carboxylated cellulose nanofibrils and CMC-g-p(AA-co-AM). Carbohydr Polym 97:429–435
Acknowledgments
We appreciate financial support from the Open Fund of State Key Laboratory of Offshore Oil Exploitation (CCL2015RCPS0222RNN), National Natural Science Foundation of China (51203187), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (17CX02053), and Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (IRT_14R58).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, J., Fei, D., Tian, X. et al. Novel modified microcrystalline cellulose-based porous material for fast and effective heavy-metal removal from aqueous solution. Cellulose 24, 5565–5577 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1504-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1504-6