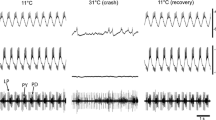
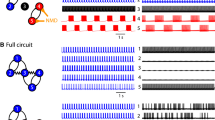
Abstract
It is possible to work out the neural circuity of many invertebrate central pattern generators (CPGs) thereby providing a basis for linking cellular processes to actual behaviors. This review summarizes the infrastructure of the two CPGs in the lobster stomatogastric ganglion in terms of circuitry, ionic conductances and chemical modulation by amines and peptides. Analysis of the circuit using modeling techniques including the use of electronic neurons closes the chapter.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abarbanel, H. D. I., Huerta, R., Rabinovich, M., Rulkov, N. F., Rowat, P. F., and Selverston, A. I. (1996). Synchronized action of synaptically coupled chaotic model neurons. Neural. Comput. 8:50–65.
Ayers, J. L., and Selverston, A. I. (1979). Monosynaptic entrainment of an endogenous pacemaker network: A cellular mechanism for von Holst’s magnet effect. J. Comp. Physiol. 129:5–17.
Ayers, J. L., and Selverston, A. I. (1984). Synaptic perturbation and entrainment of gastric mill rhythm of the spiny lobster. J. Neurophysiol. 51:113–125.
Baro, D. J., Cole, C. L., Zarrin, A. R., Hughes, S., and Harris-Warrick, R. M. (1994). Shal gene expression in identified neurons of the pyloric network in the colster stomatogastric ganglion. Receptorsy Channels 2:193–205.
Baro, D. J., Levini, R. M., Kim, M. T., Willms, A. R., Lanning, C. C., Rodriguez, H. E., and Harris-Warrick, R. M. (1997). Quantitative single-cell-reverse transcription-PCR demonstrates that A-current magnitude varies as a linear function of shal gene expression in identified stomatogastric neurons. J. Neurosci. 17:6597–6610.
Bartos, M., Manor, Y., Nadim, F., Marder, E., and Nusbaum, M. P. (1999). Coordination of fast and slow rhythmic neuronal circuits. J. Neurosci. 19:6650–6660.
Beenhakker, M. P., Blitz, D. M., and Nusbaum, M. P. (2004). Long acting activation of rhythmic neuronal activity by a novel mechanosensory system in the crustacean stomatogastric nervous system. J. Neurophysiol. 91:78–91.
Bucher, D., Thirumalai, V., and Marder, E. (2003). Axonal dopamine receptors activate peripheral spike initiation in a stomatogastric motor neuron. J. Neurosci. 23:6866–6875.
Cazalets, J. R., Nagy, F., and Moulins, M. (1990). Suppressive control of the crustacean pyloric network by a pair of identified interneuron. I. Modulation of the motor pattern. J. Neurosci. 10:448–457.
Christie, A. E., Stein, W., Quinlan, J. E., Beenhakker, M. P., Marder, E., and Nusbaum, M. P. (2004). Actions of histaminergic/peptidergic projection neuronon rhythmic motor patterns in the stomatogastric nervous system of the crab Cancer borealis. J. Comp. Neurol. 469:153–169.
Combes, D., Meyrand, P., and Simmers, J. (1999a). Motor pattern specification by dual descending pathways to a lobster rhythm-generating network. J. Neurosci. 19:3610–3619.
Combes, D., Meyrand, P., and Simmers, J. (1999b). Dynamic restructuring of a rhythmic motor program by a single mechanoreceptor neuron in lobster. J. Neurosci. 19:3620–3628.
Elson, R. C., and Selverston, A. I. (1995). Slow and fast synaptic inhibition evoked by pattern-generating neurons of the gastric mill network in spiny lobsters. J. Neurophysiol. 74:1996–2011.
Elson, R. C., Huerta, R., Abarbanel, H., Rabinovich, M., and Selverston, A. (1999). Dynamic control of irregular bursting in an identified neuron of an oscillatory circuit. J. Neurophysiol. 82:115–122.
Falke, M., Huerta, R., Rabinovich, M. I., Abarbanel, H. D. I., Elson, R. C., and Selverston, A. I. (2000). Modeling observed chaotic oscillations in bursting neurons: The role of calcium dynamics and IP3. Biol. Cyber. 82:517–527.
Getting, P. A. (1989). Emerging principles governing the operation of neural networks. Ann. Rev. Neurosci. 12:185–204.
Gola, M., and Selverston, A. I. (1981). Ionic requirements for bursting activity in lobster stomatogastric neurons. J. Comp. Physiol. 145:191–207.
Golowasch, J., and Marder, E. (1992). Ionic currents of the lateral pyloric neuron of the stomatogastric ganglion of the crab. J. Neurophysiol. 67:318–331.
Graubard, K., and Hartline, D. K. (1991). Voltage clamp analysis of intact stomatogastric neurons. Brain Res. 557:241–254.
Heinzel, H. G. (1988). Gastric mill activity in the lobster I. Spontaneous modes of chewing. J. Neurophysiol. 59:528–550.
Hempel, C. M., Vincent, P., Adams, S. R., Tsien, R. Y., and Selverston, A. I. (1996). Spatio-temporal dynamics of cAMP signals in an intact neural circuit. Nature 384:166–169.
Hindmarsh, J. L., and Rose, R. M. (1984). A model of neuronal bursting using three coupled first order differential equations. Proc. Roy. Soc. London B. 221:87–102.
Johnson, B. R., Kloppenburg, P., and Harris-Warrick, R. M. (2003). Dopamine modulation of calcium currents in pyloric neurons of the lobster stomatogastric ganglion. J. Neurophysiol. 90:631–643.
Katz, P. S., and Harris-Warrick, R. M. (1990a). Actions of identified neuromodulatory neurons in a simple motor system. TINS 13:367–373.
Katz, P. S., and Harris-Warrick, R. M. (1990b). Neuromodulation of the crab pyloric central pattern generator by serotonergic/cholinergic proprioceptive afferents. J. Neurosci. 10:1495–1512.
Katz, P. S., and Harris-Warrick, R. M. (1990c). Serotonergic/cholinergic muscle receptor cells in the crab stomatogastric nervous system. II. Rapid nicotinic and prolonged modulatory effects on neurons in the stomatogastric ganglion. J. Neurophysiol. 62(2):571–581.
Le Masson, G., Le Masson, S., and Moulins, M. (1995). From conductances to neural network prperties: Analysis of simple circuits using the hybrid network method. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 64:201–220.
Marder, E., and Meyrand, P. M. (1989). Chemical modulation of oscillatory neural circuit. In Jacklet, J. (ed.), Neuronal and Cellular Oscillators, Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, pp. 317–338.
Maynard, D. M. (1972). Simpler networks. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 193:59–72.
Maynard, D. M., and Selverston, A. I. (1975). Organization of the stomatogastric ganglion of the spiny lobster. IV. The pyloric system. J. Comp. Physiol. 100:161–182.
Miller, J. P., and Selverston, A. I. (1979). Rapid killing of single neurons by irradiation of intracellularly injected dye. Science 206:702–704.
Miller, J. P., and Selverston, A. I. (1982). Mechanisms underlying pattern generation in lobster stomatogastric ganglion as determined by selective inactivation of identified neurons. IV. Network properties of pyloric system. J. Neurophysiol. 48:1416–1432.
Mulloney, B., and Selverston, A. I. (1974). Organization of the stomatogastric in the spiny colster. J. Comp. Physiol. 91:53–78.
Nadim, F., Manor, Y., Kopell, N., and Marder, E. (1999). Synaptic depression creates a switch that controls the frequency of an oscillatory circuit. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 96:8206–8211.
Nagy, F., and Moulins, M. (1981). Proprioceptive control of the bilaterally organized rhythmic activity of the oesophageal neuronal network in the Cape lobster Jasus lalandii. J. Exp. Biol. 90:231–251.
Nagy, F., and Dickinson, P. S. (1983). Control of a central pattern generator by an identified modulatory interneurone in crustacea. I. Modulation of the pyloric motor output. J. Exp. Biol. 105:33–58.
Pinto, R. D., Elson, R., Scucs, A., Rabinovich, M., Selverston, A. I., and Abarbanel, H. D. I. (2001). Extended dynamic clamp: controlling up to four neurons using a single desktop computer and interface. J. Neurosci. Methods. 108:39–48.
Rezer, E., and Moulins, M. (1983). Expression of the crustacean pyloric pattern generator in the intact animal. J. Comp. Physiol. 153:17–28.
Selverston, A. I. (1980). Are central pattern generators understandable ? Behav. Brain Sci. 3:535–571.
Simmers, A. J., and Moulins, M. (1988). A disynaptic sensorimotor pathway in the lobster stomatogastric system. J. Neurophysiol. 59:740–756.
Szucs, A., Varona, P., Volkovskii, A. R., Abarbanel, D. D. I., Rabinovich, M. I., and Selverston, A. I. (2000). Interacting biological and electronic neurons generate realistic oscillatory rhythms. Neuroreport 11:563–569.
Tierney, A. J., and Harris-Warrick, R. M. (1992). Physiological role of the transient potassium current in the pyloric circuit of the lobster stomatogastric ganglion. J. Neurophysiol. 67:599–609.
Turrigiano, G. G., and Selverston, A. I. (1990). A cholecystokinin-like hormone activates a feeding-related neural circuit in lobster. Nature 344:866–868.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Selverston, A.I. A Neural Infrastructure for Rhythmic Motor Patterns. Cell Mol Neurobiol 25, 223–244 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-005-3154-8
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-005-3154-8