Abstract
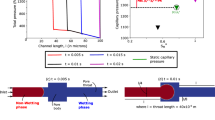
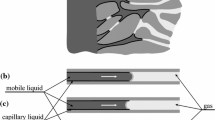
In standard multi-phase flow models on porous media, a capillary pressure saturation relationship developed under static conditions is assumed. Recent experiments have shown that this static relationship cannot explain dynamic effects as seen for example in outflow experiments. In this paper, we use a static capillary pressure model and a dynamic capillary pressure model based on the concept of Hassanizadeh and Gray and examine the behavior with respect to material interfaces. We introduce a new numerical scheme for the one-dimensional case using a Lagrange multiplier approach and develop a suitable interface condition. The behavior at the interface is discussed and verified by various numerical simulations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Charbeneau, R.: Groundwater Hydraulics and Pollution Transport. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River (2000)
Cuesta, C.: Pseudo-parabolic equations with driving convection term. Ph.D. thesis, VU Amsterdam, Netherlands (2003)
Cuesta, C., Duijn, C.V., Hulshof, J.: Infiltration in porous media with dynamic capillary pressure: Travelling waves. Euro. J. Appl. Math 11, 381–397 (2000)
de Neef, M.: Modelling capillary effects in heterogeneous porous media. Ph.D. thesis, University of Delft, The Netherlands (2000)
DiCarlo, D.: Experimental measurements of saturation overshoot on infiltration. Water Resour. Res. 40, W04215 (2004)
DiCarlo, D.: Modeling observed saturation overshoot with continuum additions to standard unsaturated theory. Adv. Water Resour. 40, 1021–1027 (2004)
Hassanizadeh, S., Celia, M., Dahle, H.: Experimental measurements of saturation overshoot on filtration. Vadose Zone J. 1, 38–57 (2002)
Hassanizadeh, S., Gray, W.G.: Mechanics and thermodynamics of multi-phase flow in porous media including interphase boundaries. Adv. Water Res. 13(4), 169–186 (1990)
Hassanizadeh, S., Gray, W.G.: Thermodynamic basis of capillary pressure on porous media. Water Resour. Res. 29(10), 3389–3405 (1993)
Hassanizadeh, S., Oung, O., Manthey, S.: Laboratory experiments and simulations on the significance on non-equilibrium effect in capillary pressure-saturation relationship. In: Unsaturated Soils: Experimental Studies, Proceedings of the International Conference from Experimental Evidence Towards Numerical Models in Unsaturated Soils. Weimar 2005, vol. 93, pp. 3–14 Springer Proceedings in Physics. Springer (2005)
Helmig, R.: Multiphase Flow and Transport Processes in the Subsurface. Springer (1997)
Helmig, R., Huber, R.: Comparison of Galerkin-type discretization techniques for two-phase flow in heterogeneous porous media. Adv. Water Res. 21, 697–711 (1998)
LeFloch, P.: Hyperbolic Systems of Conservation Laws: The Theory of Classical and Nonclassical Shock Waves. Birkhäuser (2002)
Leverett, M.C.: Capillary bahavior in porous soils. Trans. AIME 142, 152–169 (1941)
Manthey, S.: Two-phase processes with dynamic effects in porous media – parameter estimation and simulation. Ph.D. thesis, Institut für Wasserbau. Universität Stuttgart, Germany (2006)
Middendorf, J.: Zur Beschreibung des kapillaren Flüssigkeitstransports. Paper. Ph.D. thesis, Fakultät für Maschinenbau und Verfahrenstechnik, Technische Universitüt Chemnitz, Germany (2000)
Nieber, J., Dautov, R., Egorov, A.: Dynamic capillary pressure mechanism for instability in gravity-driven flows: Review and extension to very dry conditions. In: Das, D.B., Hassanizadeh, S.M. (eds.) Upscaling Multiphase Flow in Porous Media, pp. 147–172. Springer (2005)
Niessner, J., Helmig, R., Jakobs, H., Roberts, J.: Interface conditions and linearization schemes in the Newton iterations for two-phase flow in heterogeneous porous media. Adv. Water Res. 28, 671–687 (2005)
van Duijn, C., Molenaar, J., de Neef, M.: Effects of capillary forces on immiscible two phase flow in heterogeneous porous media. Transp. Porous Media 21, S. 71–93 (1995)
van Duijn, C., Peletier, L.: Nonstationary filtration in partially saturated porous media. Archs. Rat. Mech. Anal. 78, 173–198 (1982)
van Duijn, C., Peletier, L., Pop, I.: A New Class of Entropy Solutions of the Buckley–Leverett Equation. Stichting Centrum voor Wiskunde en Informatica, Amsterdam (2005)
van Genuchten, M.: A close-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 44, 892–898 (1980)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Helmig, R., Weiss, A. & Wohlmuth, B.I. Dynamic capillary effects in heterogeneous porous media. Comput Geosci 11, 261–274 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10596-007-9050-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10596-007-9050-1