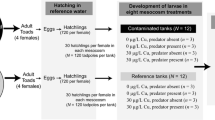
Abstract
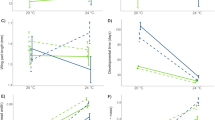
This work represents one of very few studies showing intergenerational effects of terrestrial pollution with heavy metals in a terrestrial predatory invertebrate. We demonstrate that carabid beetles Pterostichus oblongopunctatus (Coleoptera, Carabidae) inhabiting metal polluted environment have altered life-history parameters in comparison to those from reference area populations. We observed decreased hatchability of eggs in field collected animals fed with uncontaminated food, which suggests that carabids from heavily polluted sites are not able to fully avoid the risk of secondary poisoning via contaminated prey. The adult fresh body mass of young imagines from the first laboratory generation reared in uncontaminated conditions was affected by pollution level at the sites of beetles’ origin. However, we did not observe any effects of site contamination in the second laboratory generation. Therefore, we conclude that although genetic adaptation has not occurred in the populations chronically exposed to toxic metal concentrations, there is evidence of intergenerational maternal effects of metal pollution.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Au DWT, Lee CY, Chan KL, Wu RSS (2001) Reproductive impairment of sea urchins upon chronic exposure to cadmium Part I: effects on gamete quality. Environ Pollut 111:1–9
Bayley M, Baatrup E, Heimbach U, Bjerregaard P (1995) Elevated copper levels during larval development cause altered locomotor behaviour in the adult carabid beetle Pterostichus cupreus L (Coleoptera: Carabidae). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 32:166–170
Butovsky RO, van Straalen NM (1995) Copper and zinc contents in trophic chains of terrestrial arthropods in the Moscow region. Pedobiologia 39:481–487
Carroll SP, Hendry AP, Reznick DN, Fox CW (2007) Evolution on ecological time-scales. Funct Ecol 21(3):387–393
Endler JA (1986) Natural selection in the wild. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Evans G (1975) The life of beetles. George Allen & Unwin Ltd, London
Gomot A (1998) Toxic effects of cadmium on reproduction, development, and hatching in the freshwater snail Lymnaea stagnalis for water quality monitoring. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 41:288–297
Grant A (2002) Pollution tolerant species and communities: intriguing toys or invaluable monitoring tools? Hum Environ Risk Assess 8:955–970
Hoffmann AA, Parsons PA (1994) Evolutionary genetics and environmental stress. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Hopkin SP (1989) Ecophysiology of metals in invertebrates. Elsevier Applied Science Publishers Ltd., London, New York
Hopkin SP, Martin MH (1985) Transfer of heavy metals from leaf litter to terrestrial invertebrates. J Sci Food Agric 36:538–539
Hunter BA, Johnson MS, Thompson DJ (1987) Ecotoxicology of copper and cadmium in a contaminated grassland ecosystem. II. Invertebrates. J Appl Ecol 24:587–599
Janssen MPM, Bruins A, De Vries TH, van Straalen NM (1991) Comparison of cadmium kinetics in four soil arthropod species. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 20:305–312
Kapeja E, Janusz W, Zając KP, Żurek R (1990) Stan zanieczyszczenia powietrza atmosferycznego w rejonie Kombinatu Górniczo-Hutniczego “Bolesław”. Zesz Nauk AGH w Krakowie 32:11–20
Klerks PL, Levinton JS (1989) Rapid evolution of metal resistance in a benthic oligochaete inhabiting a metal-polluted site. Biol Bull Mar 176:135–141
Kramarz P (1999) Dynamics of accumulation and decontamination of cadmium and zinc in carnivorous invertebrates 1: the ground beetle, Poecilus cupreus L. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 63:531–537
Kramarz P, Laskowski R (1997) Effect of zinc contamination on life history parameters of a ground beetle, Poecilus cupreus. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 59:525–530
Lagisz M, Kramarz P, Laskowski R, Tobor M (2002) Population parameters of the beetle Pterostichus oblongopunctatus F from metal contaminated and reference areas. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 69:243–249
Lagisz M, Kramarz P, Niklińska M (2005) Metal kinetics and respiration rates in F1 generation of carabid beetles (Pterostichus oblongopunctatus F.) originating from metal-contaminated and reference areas. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 48(4):484–489
Lindqvist L, Block M, Tjalve H (1995) Distribution and excretion of Cd, Hg, methyl-Hg and Zn in the predatory beetle Pterostichus niger (Coleoptera: Carabidae). Environ Toxicol Chem 14:1195–1201
Maryański M, Kramarz P, Laskowski R, Niklińska M (2002) Decreased energetic reserves, morphological changes and accumulation of metals in carabid beetles (Poecilus cupreus L.) exposed to zinc- or cadmium-contaminated food. Ecotoxicology 11(2):127–139
Mousseau TA, Fox CW (1998) The adaptive significance of maternal effects. Trends Ecol Evol 13:403–407
Mozdzer T, Kramarz P, Piskiewicz A, Niklińska M (2003) Effects of cadmium and zinc on larval growth and survival in the ground beetle, Pterostichus oblongopunctatus. Environ Int 28:737–742
Posthuma L, van Straalen NM (1993) Heavy-metal adaptation in terrestrial invertebrates: a review of occurrence, genetics, physiology and ecological consequences. Comp Biochem Physiol C 106:11–38
R Development Core Team (2007) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. http://www.R-project.org
Reznick DN, Ghalambor CK (2001) The population ecology of contemporary adaptations: what empirical studies reveal about the conditions that promote adaptive evolution. Genetica 112–113:183–198
Scheifler R, Gomot-de Vaufleury A, Toussaint ML, Badot PM (2002) Transfer and effects of cadmium in an experimental food chain involving the snail Helix aspersa and the predatory carabid beetle Chrysocarabus splendens. Chemosphere 48:571–579
Schmidt GH, Ibrahim NMM, Abdallah MD (1991) Toxicological studies on the long-term effects of heavy metals (Hg, Cd, Pb) in soil on the development of Aiolopus thalassinus (Fabr.) (Saltatoria: Acrididae). Sci Total Environ 107:109–133
Schmidt GH, Ibrahim NMM, Abdallah MD (1992) Long-term effects of heavy metals in food on development of Aiolopus thalassinus, Saltatoria: Acrididae. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 23:375–382
Sibly RM, Calow P (1989) A life-cycle theory of responses to stress. Biol J Linn Soc 37:101–116
Sota T (1985) Limitation of reproduction by feeding condition in a Carabid beetle, Carabus yaconinus. Res Popul Ecol 27:171–184
Spurgeon DJ, Hopkin SP (2000) The development of genetically inherited resistance to zinc in laboratory-selected generations of the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Environ Pollut 109:193–201
Stark JD, Banks JE (2001) The toxicologists’s and ecologists’ point of view—unification through a demographic approach. In: Kammenga R, Laskowski R (eds) Demography in ecotoxicology. Wiley & Sons Ltd., London, pp 9–23
Stone D, Jepson P, Kramarz P, Laskowski R (2001) Response to multiple stressors along a gradient of heavy metal pollution. Environ Pollut 113:239–244
Stone D, Jepson P, Laskowski R (2002) Trends in detoxification enzymes and heavy metal accumulation in ground beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae) inhabiting a gradient of pollution. Comp Biochem Physiol C 132:105–112
van Straalen N, Hoffmann A (2000) Review of experimental evidence for physiological costs of tolerance to toxicants. In: Kammenga R, Laskowski R (eds) Demography in ecotoxicology. Wiley & Sons Ltd., London, pp 147–158
Walker CH, Hopkin SP, Sibly RM, Peakall DB (2001) Principles of ecotoxicology. Taylor and Francis, London
Zar JH (1999) Biostatistical analysis. Prentice Hall, New Jersey
Acknowledgements
We thank the many individuals, who assisted us with collection of data in the field and in the laboratory, including Paulina Kramarz, Maciej Maryański, Maria Niklińska, Tomasz Skalski and Piotr Zygmunt. Ian Rickard helped improve the manuscript. Financial support was provided by the National Committee for Scientific Research (Grant No 6 PO4F 043 18) and the Institute of Environmental Sciences of the Jagiellonian University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lagisz, M., Laskowski, R. Evidence for between-generation effects in carabids exposed to heavy metals pollution. Ecotoxicology 17, 59–66 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-007-0176-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-007-0176-7