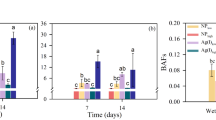
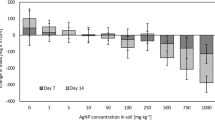
Abstract
Silver nanoparticles have been incorporated into a wide variety of consumer products, ideally acting as antimicrobial agents. Silver exposure has long been known to cause toxic effects to a wide variety of organisms, making large scale production of silver nanoparticles a potential hazard to environmental systems. Here we describe the first evidence that an organism may be able to sense manufactured nanoparticles in a complex, environmentally relevant exposure and that the presence of nanoparticles alters the organism’s behavior. We found that earthworms (Eisenia fetida) consistently avoid soils containing silver nanoparticles and AgNO3 at similar concentrations of Ag. However, avoidance of silver nanoparticles occurred over 48 h, while avoidance of AgNO3 was immediate. It was determined that avoidance of silver nanoparticles could not be explained by release of silver ions or any changes in microbial communities caused by the introduction of Ag. This leads us to conclude that the earthworms were in some way sensing the presence of nanoparticles over the course of a 48 h exposure and choosing to avoid exposure to them. Our results demonstrate that nanoparticle interactions with organisms may be unpredictable and that these interactions may result in ecologically significant effects on behavior at environmentally relevant concentrations.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahamed M, Karns M, Goodson M, Rowe J, Hussain SM, Schlager JJ, Hong YL (2008) DNA damage response to different surface chemistry of silver nanoparticles in mammalian cells. Toxicol Appl Pharm 233:404–410
Alvarenga P, Palma P, Goncalves AP, Fernandes RM, de Varennes A, Vallini G, Duarte E, Cunha-Queda AC (2008) Evaluation of tests to assess the quality of mine-contaminated soils. Environ Geochem Health 30:95–99
Asharani PV, Wu YL, Gong ZY, Valiyaveettil S (2008) Toxicity of silver nanoparticles in zebrafish models. Nanotechnology 19:1–8
Bar-Ilan O, Albrecht RM, Fako VE, Furgeson DY (2009) Toxicity assessments of multisized gold and silver nanoparticles in zebrafish embryos. Small 5:1897–1910
Bengtsson G, Nordstrom S, Rundgren S (1983) Population-density and tissue metal concentration of Lumbricids in forest soils near a brass mill. Environ Pollut Ser A 30:87–108
Blaser SA, Scheringer M, MacLeod M, Hungerbuhler K (2008) Estimation of cumulative aquatic exposure and risk due to silver: contribution of nano-functionalized plastics and textiles. Sci Total Environ 390:396–409
Bonkowski M, Griffiths BS, Ritz K (2000) Food preferences of earthworms for soil fungi. Pedobiologia 44:666–676
Chae YJ, Pham CH, Lee J, Bae E, Yi J, Gu MB (2009) Evaluation of the toxic impact of silver nanoparticles on Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes). Aquat Toxicol 94:320–327
Choi O, Hu ZQ (2008) Size dependent and reactive oxygen species related nanosilver toxicity to nitrifying bacteria. Environ Sci Technol 42:4583–4588
Choi O, Deng KK, Kim NJ, Ross L, Surampalli RY, Hu ZQ (2008) The inhibitory effects of silver nanoparticles, silver ions, and silver chloride colloids on microbial growth. Water Res 42:3066–3074
Curry JP, Schmidt O (2006) The feeding ecology of earthworms—a review. Pedobiologia 50:463–477
Daoust CM, Bastien C, Deschenes L (2006) Influence of soil properties and aging on the toxicity of copper on compost worm and barley. J Environ Qual 35:558–567
Darwin C (1881) The formation of vegetable mould through the action of worms with observations on their habits. J. Murray, London
Doube BM, Schmidt O, Killham K, Correll R (1997) Influence of mineral soil on the palatability of organic matter for lumbricid earthworms: a simple food preference study. Soil Biol Biochem 29:569–575
Eijsackers H, Beneke P, Maboeta M, Louw JPE, Reinecke AJ (2005) The implications of copper fungicide usage in vineyards for earthworm activity and resulting sustainable soil quality. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 62:99–111
Findlay RH, Dobbs FC (1993) Quantitative description of microbial communities using lipid analysis. In: Kemp PF, Sherr BF, Sherr EB, Cole JJ (eds) Handbook of methods in aquatic microbiology. FL Pages, Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, pp 271–294
Gongalsky KB, Belorustseva SA, Kuznetsova DM, Matyukhin AV, Pelgunova LA, Savin FA, Shapovalov AS (2009) Spatial avoidance of patches of polluted chernozem soils by soil invertebrates. Insect Sci 16:99–105
Gottschalk F, Sonderer T, Scholz RW, Nowack B (2009) Modeled environmental concentrations of engineered canomaterials (TiO2, ZnO, Ag, CNT, fullerenes) for different regions. Environ Sci Technol 43:9216–9222
Griffitt RJ, Luo J, Gao J, Bonzongo JC, Barber DS (2008) Effects of particle composition and species on toxicity of metallic nanomaterials in aquatic organisms. Environ Toxicol Chem 27:1972–1978
Horn MA, Schramm A, Drake HL (2003) The earthworm gut: an ideal habitat for ingested N2O-producing microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:1662–1669
Hund-Rinke K, Lindemann M, Simon M (2005) Experiences with novel approaches in earthworm testing alternatives. J Soils Sediments 5:233–239
ISO (2008) Soil quality—Avoidance test for determining the quality of soils and effects of chemicals on behavior—Part 1: test with earthworms (Eisenia fetida and Eisenia andrei). International Organization for Standardization, 17512-1
Klok C, Goedhart PW, Vandecasteele B (2007) Field effects of pollutants in dynamic environments. A case study on earthworm populations in river floodplains contaminated with heavy metals. Environ Pollut 147:26–31
Knapp MF, Mill PJ (1968) Chemoreception and efferent sensory impulses in Lumbricus terrestris Linn. Comp Biochem Physiol 25:523–528
Kvitek L, Vanickova M, Panacek A, Soukupova J, Dittrich M, Valentova E, Prucek R, Bancirova M, Milde D, Zboril R (2009) Initial study on the toxicity of silver nanoparticles (NPs) against Paramecium caudatum. J Phys Chem C 113:4296–4300
Laban G, Nies LF, Turco RF, Bickham JW, Sepulveda MS (2010) The effects of silver nanoparticles on fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas) embryos. Ecotoxicology 19:185–195
Langdon CJ, Hodson ME, Arnold RE, Black S (2005) Survival, Pb-uptake and behaviour of three species of earthworm in Pb treated soils determined using an OECD-style toxicity test and a soil avoidance test. Environ Pollut 138:368–375
Laverack MS (1960) Tactile and chemical perception in earthworms-I. Responses to touch, sodium chloride, quinine and sugars. Comp Biochem Physiol 1:155–163
Laverack MS (1961) Tactile and chemical perception in earthworms-II. Responses to acid pH solutions. Comp Biochem Physiol 2:22–34
Loureiro S, Soares AMVM, Nogueira AJA (2005) Terrestrial avoidance behaviour tests as screening tool to assess soil contamination. Environ Pollut 138:121–131
Lukkari T, Haimi J (2005) Avoidance of Cu- and Zn-contaminated soil by three ecologically different earthworm species. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 62:35–41
Lukkari T, Aatsinki M, Vaisanen A, Haimi J (2005) Toxicity of copper and zinc assessed with three different earthworm tests. Appl Soil Ecol 30:133–146
Mill PJ (1982) Recent developments in earthworm neurobiology. Comp Biochem Physiol Part A Physiol 73:641–661
Morones JR, Elechiguerra JL, Camacho A, Holt K, Kouri JB, Ramirez JT, Yacaman MJ (2005) The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 16:2346–2353
Nahmani J, Hodson ME, Black S (2007) Effects of metals on life cycle parameters of the earthworm Eisenia fetida exposed to field-contaminated, metal-polluted soils. Environ Pollut 149:44–58
Navarro E, Piccapietra F, Wagner B, Marconi F, Kaegi R, Odzak N, Sigg L, Behra R (2008) Toxicity of silver nanoparticles to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Environ Sci Technol 42:8959–8964
PA USE (1996) Method 3052: microwave assisted acid digestion of siliceous and organically based matrices. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC USA
PA USE (1998) Method 6020a: inductively coupled plasma—mass spectrometry. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC USA
Panacek A, Kvitek L, Prucek R, Kolar M, Vecerova R, Pizurova N, Sharma VK, Nevecna T, Zboril R (2006) Silver colloid nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and their antibacterial activity. J Phys Chem B 110:16248–16253
Panacek A, Kolar M, Vecerova R, Prucek R, Soukupova J, Krystof V, Hamal P, Zboril R, Kvitek L (2009) Antifungal activity of silver nanoparticles against Candida spp. Biomaterials 30:6333–6340
Parker GH, Metcalf CR (1906) The reactions of earthworms to salts: a study in protoplasmic stimulation as a basis of interpreting the sense of taste. Am J Physiol 17:0055–0074
Roh JY, Sim SJ, Yi J, Park K, Chung KH, Ryu DY, Choi J (2009) Ecotoxicity of silver nanoparticles on the soil nematode Caenorhabditis elegans using functional ecotoxicogenomics. Environ Sci Technol 43:3933–3940
Rombke J, Jansch S, Didden W (2005) The use of earthworms in ecological soil classification and assessment concepts. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 62:249–265
Saxe JK, Impellitteri CA, Peijnenburg WJGM, Allen HE (2001) Novel model describing trace metal concentrations in the earthworm, Eisenia andrei. Environ Sci Technol 35:4522–4529
Schutter ME, Dick RP (2000) Comparison of fatty acid methyl ester (FAME) methods for characterizing microbial communities. Soil Sci Soc Am J 64:1659–1668
Shoults-Wilson WA, Reinsch BC, Tsyusko OV, Bertsch PM, Lowry GV, Unrine JM (2010a) Toxicity of silver nanoparticles to the earthworm (Eisenia fetida): the role of particle size and soil type. Soil Sci Soc Am J (in press). doi:10.2136/sssaj2010.0127nps
Shoults-Wilson WA, Reinsch BC, Tsyusko OV, Bertsch PM, Lowry GV, Unrine JM (2010b) Role of particle surface coating for bioaccumulation and reproductive toxicity of silver in earthworms (Eisenia fetida) exposed to silver nanoparticles. Nanotoxicology (in Press) doi:10.3109/17435390.2010.537382
Sokal RR, Rohlf FJ (2003) Biometry, 3rd edn. W. H. Freeman and Company, New York
Sousa A, Pereira R, Antunes SC, Cachada A, Pereira E, Duarte AC, Goncalves F (2008) Validation of avoidance assays for the screening assessment of soils under different anthropogenic disturbances. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 71:661–670
Spurgeon DJ, Lofts S, Hankard PK, Toal M, McLellan D, Fishwick S, Svendsen C (2006) Effect of pH on metal speciation and resulting metal uptake and toxicity for earthworms. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:788–796
Stephenson GL, Kaushik A, Kaushik NK, Solomon KR, Steele T, Scroggins RP (1998) Use of an avoidance-response test. In: Sheppard SC, Bembridge J, Holmstrup M, Posthuma L (eds) Advances in earthworm ecotoxicology. SETAC Press, Pensacola
Unrine JM, Hopkins WA, Romanek CS, Jackson BP (2007) Bioaccumulation of trace elements in omnivorous amphibian larvae: implications for amphibian health and contaminant transport. Environ Pollut 149(2):182–192
Van Zwieten L, Rust J, Kingston T, Merrington G, Morris S (2004) Influence of copper fungicide residues on occurrence of earthworms in avocado orchard soils. Sci Total Environ 329:29–41
Vijver MG, Vink JPM, Miermans CJH, van Gestel CAM (2003) Oral sealing using glue: a new method to distinguish between intestinal and dermal uptake of metals in earthworms. Soil Biol Biochem 35:125–132
Vorobeichik EL (1998) Populations of earthworms (Lumbricidae) in forests of the middle urals in conditions of pollution by discharge from copper works. Russ J Ecol 29:85–91
Wentsel RS, Guelta MA (1988) Avoidance of brass powder-contaminated soil by the earthworm, Lumbricus terrestris. Environ Toxicol Chem 7:241–243
Wright MA (1972) Factors governing ingestion by earthworm Lumbricus-Terrestris (L), with special reference to apple leaves. Ann Appl Biol 70:175–188
Yeardley RB, Lazorchak JM, Gast LC (1996) The potential of an earthworm avoidance test for evaluation of hazardous waste sites. Environ Toxicol Chem 15:1532–1537
Yeo MK, Kang M (2008) Effects of nanometer sized silver materials on biological toxicity during zebrafish embryogenesis. Bull Korean Chem Soc 29:1179–1184
Acknowledgments
We thank M. Lacey, E. Harding and L. Wang for assistance with sample processing, S. Hunyadi for providing some of the nanoparticles studied, J. Kupper for performing FAME analysis and J. Nelson for assistance with GC analysis. Major funding for this research was provided by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (U.S. EPA) Science to Achieve Results Grant RD 833331. This material is also based in part upon work supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF), the U.S. EPA and the Center for the Environmental Implications of NanoTechnology (CEINT) EF-0830093. Any opinions, findings, conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the NSF or the EPA. This work has not been subjected to EPA review and no official endorsement should be inferred.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shoults-Wilson, W.A., Zhurbich, O.I., McNear, D.H. et al. Evidence for avoidance of Ag nanoparticles by earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Ecotoxicology 20, 385–396 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-010-0590-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-010-0590-0