Abstract
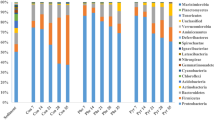
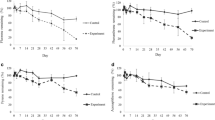
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are of great environmental and human health concerns due to their widespread occurrence, persistence and carcinogenic properties. There is now compelling evidence that the mangrove sediment microbial structure is susceptible to PAHs contamination. The study aimed to assess the effects of PAHs on the nitrogen-fixing bacterial community of mangrove sediment. Three types of PAHs, naphthalene (NAP), a two-ring PAH; fluorene (FLU), a three-ring PAH; and pyrene (PYR), a four-ring PAH; were applied at three doses. After 7 and 24 days of incubation, the nitrogen-fixing bacterial population and diversity were evidenced in the nifH gene polymerase chain reaction denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis profile. DGGE pattern shows that the nitrogen-fixing bacterial community changed significantly with the types and doses of PAHs, and the incubation time. As far as single PAH is concerned, high concentration of PAH has larger impact on the nitrogen-fixing bacteria than low concentration of PAH. Besides, among the three types of PAHs, NAP has the greatest short term toxicity; PYR has the strongest long-term impact, whereas FLU has relatively higher long-time effect. Multidimensional scaling analysis and correspondence analysis are two reliable multivariate analysis methods for investigating the relationship between the nitrogen-fixing bacterial community and PAHs contamination. Investigating the effect of PAHs on the nitrogen-fixing bacterial diversity could yield useful information for understanding the process of biogeochemical cycling of nitrogen in mangrove sediment. The present study reveals that nitrogen-fixing bacterial community can be used as an important parameter indicating the impact of PAHs on mangrove sediment ecosystem.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnelli A, Ascher J, Corti G, Ceccherini MT, Nannipieri P, Pietramellara G (2004) Distribution of microbial communities in a forest soil profile investigated by microbial biomass, soil respiration and DGGE of total and extracellular DNA. Soil Biol Biochem 36:859–868
Bagwell CE, Rocque JR, Smith GW, Polson SW, Friez MJ, Longshore JW, Lovell CR (2002) Molecular diversity of diazotrophs in oligotrophic tropical seagrass bed communities. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 39:113–119
Balashova NV, Kosheleva IA, Golovchenko NP, Boronin AM (1999) Phenanthrene metabolism by Pseudomonas and Burkholderia strains. Process Biochem 35:291–296
Bird C, Martinez JM, O’Donnell AG, Wyman M (2005) Spatial distribution and transcriptional activity of an uncultured clade of planktonic diazotrophic γ proteobacteria in the Arabian sea. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:2079–2085
Blakely JK, Neher DA, Spongberg AL (2002) Soil invertebrate and microbial communities, and decomposition as indicators of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contamination. Appl Soil Ecol 21:71–88
Church MJ, Short CM, Jenkins BD, Karl DM, Zehr JP (2005) Temporal patterns of nitrogenase gene (nifH) expression in the oligotrophic North Pacific Ocean. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:5362–5370
Churchill SA, Harper JP, Churchill PF (1999) Isolation and characterization of a Mycobacterium species capable of degrading three- and four-ring aromatic and aliphatic hydrocarbons. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:549–552
Gadzala-Kopciuch RM, Kluska M, Welniak M, Kroszczyński W, Buszewski B (1999) Aryl chemically bonded phases for determination of selected polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons isolated from environmental samples utilizing SPE/HPLC. Pol J Environ Stud 8:383–387
Goyal AK, Zylstra GJ (1997) Genetics of naphthalene and phenanthrene degradation by Comamonas testosteroni. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 19:401–407
Griffin LF, Calder JA (1977) Toxic effect of water-soluble fractions of crude, refined, and weathered oils on the growth of a marine bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol 33:1092–1096
Henson JM, Hayasaka SS (1982) Effects of the water-soluble fraction of microbiologically or physically altered crude petroleum on the heterotrophic activity of marine bacteria. Mar Environ Res 6:205–214
Hicks BJ, Silvester WB (1985) Nitrogen fixation associated with the New Zealand mangrove (Avicennia marina (Forsk.) Vierh. var. resinifera (Forst. f.) Bakh.). A. Appl Environ Microbiol 49:955–959
Holguin G, Guzman MA, Bashan Y (1992) Two new nitrogen-fixing bacteria from the rhizosphere of mangrove trees: their isolation, identification and in vitro interaction with rhizosphere Staphylococcus sp. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 101:207–216
Holguin G, Vazquez P, Bashan Y (2001) The role of sediment microorganisms in the productivity, conservation, and rehabilitation of mangrove ecosystems: an overview. Biol Fertil Soils 33:265–278
Jensen J, Folker-Hansen P (1995) Soil quality criteria for selected organic compounds. Danish Environmental Protection Agency. Working Report No. 47
Kennedy AC, Smith KL (1995) Soil microbial diversity and the sustainability of agricultural soils. Plant Soil 170:75–86
Kyaruzi JJ, Kyewalyanga MS, Muruke MHS (2003) Cyanobacteria composition and impact of seasonality on their in situ nitrogen fixation rate in a mangrove ecosystem adjacent to Zanzibar town. Western Indian Ocean J Mar Sci 2:35–44
Latimer JS, Zheng J (2003) The sources, transport, and fate of PAHs in the marine environment. In: Douben PET (ed) PAHs: an ecotoxicological perspective. John Wiley & Sons, West Sussex, pp 9–33
Lugomela C, Bergman B (2002) Biological N2-fixation on mangrove pneumatophores: preliminary observations and perspectives. Ambio: A J Human Environ 31:612–613
MacRae JD, Hall KJ (1998) Biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) in marine sediment under denitrifying conditions. Water Sci Technol 38:177–185
Mahmood SK, Rao PR (1993) Microbial abundance and degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 50:486–491
Maliszewska-Kordybach B, Klirnkowicz-Pawlas A, Smreczak B, Janusauskaite D (2007) Ecotoxic effect of phenanthrene on nitrifying bacteria in soils of different properties. J Environ Qual 36:1635–1645
Marchand C, Disnar JR, Lallier-Verg E, Lottier N (2005) Early diagenesis of carbohydrates and lignin in mangrove sediments subject to variable redox conditions (French Guiana). Geochim Cosmochim Acta 69:131–142
Menzie CA, Potocki BB, Santodonato J (1992) Exposure to carcinogenic PAHs in the environment. Environ Sci Technol 26:1278–1284
Muckian L, Grant R, Doyle E, Clipson N (2007) Bacterial community structure in soils contaminated by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Chemosphere 68:1535–1541
Muyzer G (1999) DGGE/TGGE a method for identifying genes from natural ecosystems. Curr Opin Microbiol 2:317–322
Muyzer G, Smalla K (1998) Application of denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) and temperature gradient gel electrophoresis (TGGE) in microbial ecology. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 73:127–141
Muyzer G, Dewaal EC, Uitterlinden AG (1993) Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:695–700
Ogier JC, Son O, Gruss A, Tailliez P, Delacroix-Buchet A (2002) Identification of the bacterial microflora in dairy products by temporal temperature gradient gel electrophoresis. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:3691–3701
Piceno YM, Noble PA, Lovell CR (1999) Spatial and temporal assessment of diazotroph assemblage composition in vegetated salt marsh sediments using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis. Microb Ecol 38:157–167
Poly F, Monrozier LJ, Bally R (2001a) Improvement in the RFLP procedure for studying the diversity of nifH genes in communities of nitrogen fixers in soil. Res Microbiol 152:95–103
Poly F, Ranjard L, Nazaret S, Gourbiere F, Monrozier LJ (2001b) Comparison of nifH gene pools in soils and soil microenvironments with contrasting properties. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:2255–2262
Ravikumar S, Kathiresan K, Ignatiammal STM, Babu Selvam M, Shanthy S (2004) Nitrogen-fixing azotobacters from mangrove habitat and their utility as marine biofertilizers. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 312:5–17
Salles JF, van Veen JA, van Elsas JD (2004) Multivariate Analyses of Burkholderia Species in soil: effect of crop and land use history. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:4012–4020
Schloter M, Dilly O, Munch JC (2003) Indicators for evaluating soil quality. Agric Ecosyst Environ 98:255–262
Schutter M, Sandeno J, Dick R (2001) Seasonal, soil type, and alternative management influences on microbial communities of vegetable cropping systems. Biol Fertil Soils 34:397–410
van Bruggen AHC, Semenov AM (2000) In search of biological indicators for soil health and disease suppression. Appl Soil Ecol 15:13–24
Vazquez P, Holguin G, Puente ME, Lopez-Cortes A, Bashan Y (2000) Phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms associated with the rhizosphere of mangroves in a semiarid coastal lagoon. Biol Fertil Soils 30:460–468
Widmer F, Shaffer BT, Porteous LA, Seidler RJ (1999) Analysis of nifH gene pool complexity in soil and litter at a Douglas fir forest site in the Oregon cascade mountain range. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:374–380
Yao H, He Z, Wilson MJ, Campbell CD (2000) Microbial biomass and community structure in a sequence of soils with increasing fertility and changing land use. Microb Ecol 40:223–237
Young JPW (1992) Phylogenetic classification of nitrogenfixing organisms. In: Stacey G, Burris R, Evans H (eds) Biological nitrogen fixation. Chapman & Hall, New York, pp 43–86
Zani S, Mellon MT, Collier JL, Zehr JP (2000) Expression of nifH genes in natural microbial assemblages in Lake George, New York, detected by reverse transcriptase PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3119–3124
Zhang YY, Dong JD, Yang ZH, Zhang S, Wang YS (2008) Phylogenetic diversity of nitrogen-fixing bacteria in mangrove sediments assessed by PCR-denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Arch Microbiol 190:19–28
Zhou J, Bruns M, Tiedje J (1996) DNA recovery from soils of diverse composition. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:316–322
Zuberer DA, Silver WS (1978) Biological dinitrogen fixation (acetylene reduction) associated with Florida mangroves. Appl Environ Microbiol 35:567–575
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 41176101 and 41076070), the projects of knowledge innovation program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Nos. KZCX2-YW-Q07-02, KSCX2-SW-132, KSCX2-YW-Z-1024 and KSCX2-EW-G-12C) and the key projects in the National Science & Technology Pillar Program in the Eleventh Five-year Plan Period (Nos. 2009BADB2B0606 and 2012BAC07B0402).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, FL., Wang, YS., Sun, CC. et al. Effects of three different PAHs on nitrogen-fixing bacterial diversity in mangrove sediment. Ecotoxicology 21, 1651–1660 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-012-0946-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-012-0946-8