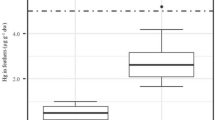
Abstract
Trace element concentrations were measured in Pacific Dunlin (Calidris alpina pacifica) to identify factors that influence accumulation and to assess toxicity risks. We report concentrations of cadmium, copper, and zinc in kidneys as well as copper, lead, mercury, selenium and zinc in feathers. Relationships between element concentrations and Dunlin age, sex, bill length, habitat preference, trophic level, and sample group were investigated with regression analyses. Stable isotope ratios of carbon and nitrogen in Dunlin muscle tissue were used to determine habitat preference and trophic level, respectively. Cadmium concentrations in kidneys were significantly related to habitat preference: [Cd] in estuarine foragers >[Cd] in terrestrial foragers. Cadmium accumulation was age-dependent as concentrations increased significantly within 10 months of hatch dates but not afterward. Concentrations of cadmium and zinc in kidneys as well as lead and mercury in feathers were below those known to cause deleterious effects in birds. In contrast, selenium concentrations in feathers (range: 2.1–14.0 µg/g) were often at levels associated with toxicity risks (>5 µg/g). Toxicity thresholds are not available for copper in kidneys or copper and zinc in feathers; however, measured concentrations of these elements were within documented ranges for sandpipers. Future studies should assess potential impacts of selenium on embryonic development in Dunlin and other sandpipers. Risk assessments would yield more conclusive results for all elements if impacts under ecologically relevant stresses (e.g. development in the wild, migration, predation) were better understood.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barjaktarovic L, Elliott JE, Scheuhammer AM (2002) Metal and metallothionein concentrations in Scoter (Melanitta spp.) from the Pacific Northwest of Canada, 1989–1994. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 43:486–491
Beninger PG, Elner RW, Morancais M, Decottignies P (2011) Downward trophic shift during breeding migration in the shorebird Calidris mauri (Western Sandpiper). Mar Ecol Prog Ser 428:259–269. doi:10.3354/meps09050
Beyer WN, Connor EE, Gerould S (1994) Estimates of soil ingestion by wildlife. J Wildl Manag 58:375–382
Blomqvist S, Frank A, Petersson LR (1987) Metals in liver and kidney tissues of autumn-migrating Dunlin Calidris alpina and Curlew Sandpiper Calidris ferruginea staging at the Baltic Sea. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 35:1–13
Bortolotti GR (2010) Flaws and pitfalls in the chemical analysis of feathers: bad news-good news for avian chemoecology and toxicology. Ecol Appl 20:1766–1774
Braune BM, Noble DG (2009) Environmental contaminants in Canadian shorebirds. Environ Monitor Assess 148:185–204. doi:10.1007/s10661-007-0150-0
Bryan G, Langston W (1992) Bioavailability, accumulation and effects of heavy-metals in sediments with special reference to United-Kingdom estuaries—a review. Environ Pollut 76:89–131. doi:10.1016/0269-7491(92)90099-V
Burger J (1993) Metals in avian feathers: bioindicators of environmental pollution. In: Hodgson E (ed) Reviews in environmental toxicology. Toxicology Communications Inc, Raleigh
Burger J (1995) Heavy metal and selenium levels in feathers of Herring Gulls (Larus argentatus): differences due to year, gender, and age at Captree, Long Island. Environ Monit Assess 38:37–50. doi:10.1007/BF00547125
Burger J (2008) Assessment and management of risk to wildlife from cadmium. Sci Total Environ 389:37–45
Burger J, Gochfeld M (1990) Tissue-levels of lead in experimentally exposed Herring Gull (Larus argentatus) chicks. J Toxicol Environ Health 29:219–233
Burger J, Gochfeld M (1994) Behavioral impairments of lead-injected young Herring Gulls in nature. Fundam Appl Toxicol 23:553–561. doi:10.1006/faat.1994.1140
Burger J, Gochfeld M (1997) Risk, mercury levels, and birds: relating adverse laboratory effects to field biomonitoring. Environ Res 75:160–172
Burger J, Gochfeld M (1999) Heavy metals in Franklin’s gull tissues: age and tissue differences. Environ Toxicol Chem 18:673–678
Burger J, Seyboldt S, Morganstein N, Clark K (1993) Heavy-metals and selenium in feathers of 3 shorebird species from Delaware Bay. Environ Monit Assess 28:189–198
Burger J, Gochfeld M, Sullivan K, Irons D (2007) Mercury, arsenic, cadmium, chromium lead, and selenium in feathers of Pigeon Guillemots (Cepphus columba) from Prince William Sound and the Aleutian Islands of Alaska. Sci Total Environ 387:175–184. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.07.049
Butler RW, Vermeer K (1994) The abundance and distribution of estuarine birds in the Strait of Georgia, British Columbia. Canadian Wildlife Service technical report number 83. Canadian Wildlife Service, Ottawa
Chiou P, Chen K, Yu B (1997) Toxicity, tissue accumulation and residue in egg and excreta of copper in laying hens. Anim Feed Sci Technol 67:49–60. doi:10.1016/S0377-8401(96)01139-X
Clark AJ, Scheuhammer AM (2003) Lead poisoning in upland-foraging birds of prey in Canada. Ecotoxicology 12:23–30
Cloern JE, Canuel EA, Harris D (2002) Stable carbon and nitrogen isotope composition of aquatic and terrestrial plants of the San Francisco Bay estuarine system. Limnol Oceanogr 47:713–729
Cundy A, Croudace I, Thomson J, Lewis J (1997) Reliability of salt marshes as ‘‘geochemical recorders’’ of pollution input: a case study from contrasting estuaries in southern England. Environ Sci Technol 31:1093–1101. doi:10.1021/es960622d
Decho A (1990) Microbial exopolymer secretions in ocean environments—their role(s) in food webs and marine processes. Oceanogr Mar Biol Ann Rev 28:73–153
Dykstra CR, Karasov WH (1992) Changes in gut structure and function in House Wrens (Troglodytes aedon) in response to increased energy demands. Physiol Zool 65:422–442
Eagles-Smith CA, Ackerman JT, De La Cruz SEW, Takekawa JY (2009) Mercury bioaccumulation and risk to three waterbird foraging guilds is influenced by foraging ecology and breeding stage. Environ Pollut 157:1993–2002
Eisler R (1987) Mercury hazards to fish, wildlife, and invertebrates: a synoptic review. U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service biological report 85(1.10)
Eisler R (2000) Handbook of chemical risk assessment, Vol. 1: metals. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton
Evans Ogden LJ, Hobson KA, Lank DB (2004) Blood isotopic (delta C-13 and delta N-15) turnover and diet-tissue fractionation factors in captive Dunlin (Calidris alpina pacifica). Auk 121:170–177
Evans Ogden LJ, Hobson KA, Lank DB, Bittman S (2005) Stable isotope analysis reveals that agricultural habitat provides an important dietary component for non-breeding Dunlin. Avian Cons Ecol 1:3
Evans Ogden LJ, Bittman S, Lank DB (2008) A review of agricultural land use by shorebirds with special reference to habitat conservation in the Fraser River Delta, British Columbia. Can J Plant Sci 88:71–83
Ferns P, Anderson J (1994) Cadmium in the diet and body-tissues of Dunlins Calidris alpina, from the Bristol Channel, UK. Environ Pollut 86:225–231. doi:10.1016/0269-7491(94)90194-5
Fox M, Tao S, Stone C, Fry B (1984) Effects of zinc, iron and copper deficiencies on cadmium in tissues of Japanese Quail. Environ Health Perspect 54:57–65. doi:10.2307/3429791
Franson JC, Pain DJ (2011) Lead in birds. In: Beyer WN, Meador JP (eds) Environmental contaminants in biota. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Furness R, Muirhead S, Woodburn M (1986) Using bird feathers to measure mercury in the environment—relationships between mercury content and molt. Mar Pollut Bull 17:27–30. doi:10.1016/0025-326X(86)90801-5
Gasaway W, Buss I (1972) Zinc toxicity in the Mallard duck. J Wildl Manag 36:1107–1117. doi:10.2307/3799239
Gill RE, Handel CM, Ruthrauff DR (2013) Intercontinental migratory connectivity and population structuring of Dunlins from western Alaska. Condor 115:525–534
Goede A (1985) Mercury, selenium, arsenic and zinc in waders from the Dutch Wadden Sea. Environ Pollut Ser A 37:287–309. doi:10.1016/0143-1471(85)90119-9
Goede A, Debruin M (1985) Selenium in a shore bird, the Dunlin, from the Dutch Waddenzee. Mar Pollut Bull 16:115–117. doi:10.1016/0025-326X(85)90535-1
Goede A, Nygard T, Debruin M, Steinnes E (1989) Selenium, mercury, arsenic and cadmium in the lifecycle of the Dunlin, Calidris alpina, a migrant wader. Sci Total Environ 78:205–218. doi:10.1016/0048-9697(89)90034-X
Gutiérrez JS, Masero JA, Abad-Gomez JM, Villegas A, Sanchez-Guzman JM (2011) Understanding the energetic costs of living in saline environments: effects of salinity on basal metabolic rate, body mass and daily energy consumption of a long-distance migratory shorebird. J Exp Biol 214:829–835. doi:10.1242/jeb.048223
Heinz G (1993) Selenium accumulation and loss in Mallard eggs. Environ Toxicol Chem 12:775–778. doi:10.1002/etc.5620120419
Hobson KA, Clark RG (1992) Assessing avian diets using stable isotopes. 1. Turnover of C-13 in tissues. Condor 94:181–188
Hogstad O (1996) Accumulation of cadmium, copper and zinc in the liver of some passerine species wintering in central Norway. Sci Total Environ 183:187–194. doi:10.1016/0048-9697(95)05060-4
Holmes RT (1971) Latitudinal differences in breeding and molt schedules of Alaskan Red-backed Sandpipers (Calidris alpina). Condor 73:93–99
Hui CA (1998) Metal and trace element burdens in two shorebird species at two sympatric wintering sites in southern California. Environ Monit Assess 50:233–247
Hui CA, Beyer WN (1998) Sediment ingestion of two sympatric shorebird species. Sci Total Environ 224:227–233
Hui CA, Takekawa JY, Warnock SE (2001) Contaminant profiles of two species of shorebirds foraging together at two neighboring sites in south San Francisco Bay, California. Environ Monit Assess 71:107–121
Jackson N, Stevenson MH, Kirkpatrick GM (1979) Effects of the protracted feeding of copper sulphate-supplemented diets to laying, domestic fowl on egg production and on specific tissues, with special reference to mineral content. Br J Nutr 42:253–266
Kim J, Koo T (2008) Heavy metal concentrations in feathers of Korean shorebirds. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 55:122–128. doi:10.1007/s00244-007-9089-y
Kim J, Park S, Koo T (2007) Lead and cadmium concentrations in shorebirds from the Yeongjong Island, Korea. Environ Monit Assess 134:355–361
Kuwae T, Beninger PG, Decottignies P, Mathot KJ, Lund DR, Elner RW (2008) Biofilm grazing in a higher vertebrate: the Western Sandpiper, Calidris mauri. Ecology 89:599–606. doi:10.1890/07-1442.1
Kuwae T, Miyoshi E, Hosokawa S, Ichimi K, Hosoya J, Amano T, Moriya T, Kondoh M, Ydenberg RC, Elner RW (2012) Variable and complex food web structures revealed by exploring missing trophic links between birds and biofilm. Ecol Lett 15:347–356. doi:10.1111/j.1461-0248.2012.01744.x
Levengood JM, Sanderson GC, Anderson WL, Foley GL, Skowron LM, Brown PW (1999) Acute toxicity of ingested zinc shot to game-farm Mallards. Ill Nat Hist Surv Bull 36:1–36
Lewis SA, Furness RW (1991) Mercury accumulation and excretion in laboratory reared Black-headed gull Larus ridibundus chicks. Arch Environ Chem Toxicol 21:316–320
Lucia M, Andre J, Gontier K, Diot N, Veiga J, Davail S (2010) Trace element concentrations (mercury, cadmium, copper, zinc, lead, aluminium, nickel, arsenic, and selenium) in some aquatic birds of the southwest Atlantic Coast of France. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 58:844–853. doi:10.1007/s00244-009-9393-9
Luoma SN, Davis JA (1983) Requirements for modeling trace metal partitioning in oxidized estuarine sediments. Mar Chem 12:159–181
Mathot KJ, Lund DR, Elner RW (2010) Sediment in stomach contents of Western Sandpipers and Dunlin provide evidence of biofilm feeding. Waterbirds 33:300–306. doi:10.1675/063.033.0305
McCormick J, St. Clair CT, Bendell LI (2014) Concentrations and partitioning of metals in intertidal biofilms: implications for metal bioavailability to shorebirds. Ecotoxicology 23:229–235
McFarland C, Bendell-Young L, Guglielmo C, Williams T (2002) Kidney, liver and bone cadmium content in the Western Sandpiper in relation to migration. J Environ Monit 4:791–795. doi:10.1039/b206045k
McWilliams SR, Karasov WH (2001) Phenotypic flexibility in digestive system structure and function in migratory birds and its ecological significance. Comp Biochem Physiol A 128:579–593
Michener R, Lajitha K (2007) Stable isotopes in ecology and environmental science, 2nd edn. Blackwell Publishing, Singapore
Myklebust I, Pedersen H (1999) Accumulation and distribution of cadmium in Willow Ptarmigan. Ecotoxicology 8:457–465. doi:10.1023/A:1008912003597
Nielson SE, Boyce MS, Stenhouse GB (2004) Grizzly bears and forestry I. Selection of clearcuts by grizzly bears in west-central Alberta. Can Forest Ecol Manag 199(1):51–65
Norris DR, Lank DB, Pither J, Chipley D, Ydenberg RC, Kyser TK (2007) Trace element profiles as unique identifiers of Western Sandpiper (Calidris mauri) populations. Can J Zool 85:579–583. doi:10.1139/Z07-024
Nriagu JO (1989) A global assessment of natural sources of atmospheric trace metals. Nature 338:47–49
Oh S, Nakaue H, Deagen J, Whanger P, Arscott G (1979) Accumulation and depletion of zinc in chick tissue metallothioneins. J Nutr 109:1720–1729
Ohlendorf HM, Heinz GH (2011) Selenium in birds. In: Beyer WN, Meador JP (eds) Environmental contaminants in biota. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Prater AJ, Marchant AJ, Vuorinen J (1977) Guide to the identification and ageing of Holarctic Waders, field guide 17. British Trust for Ornithology, Tring
Scheuhammer AM (1987) The chronic toxicity of aluminium, cadmium, mercury, and lead in birds: a review. Environ Pollut 46:263–295
Schlekat C, Decho A, Chandler G (1998) Sorption of cadmium to bacterial extracellular polymeric sediment coatings under estuarine conditions. Environ Toxicol Chem 17:1867–1874. doi:10.1897/1551-5028(1998)017<1867:SOCTBE>2.3.CO;2
Shepherd PCF (2001) Space use, habitat preferences, and time-activity budgets of non-breeding Dunlin (Calidris alpina pacifica) in the Fraser River Delta, B.C. Phd dissertation, Simon Fraser University, BC
Sileo L, Beyer W, Mateo R (2003) Pancreatitis in wild zinc-poisoned waterfowl. Avian Pathol 32:655–660. doi:10.1080/03079450310001636246
Spallholz JE, Hoffman DJ (2002) Selenium toxicity: cause and effects in aquatic birds. Aquat Toxicol 57:27–37
St. Clair CT (2012) Heavy metals, selenium and pacific Dunlin: patterns of accumulation, exposure from prey and toxicity risks. MSc thesis, Simon Fraser University
Stein W, Williams TD (2006) Causes and consequences of post-growth age-dependent differences in small intestine size in a migratory sandpiper (Calidris mauri, Western Sandpiper). Funct Ecol 20:142–150
Stock M, Herber RFM, Geron HMA (1989) Cadmium levels in oystercatcher Haematopus ostralegus from the German Wadden Sea. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 53:227–239
Tessier A, Campbell P (1987) Partitioning of trace-metals in sediments—relationships with bioavailability. Hydrobiologia 149:43–52. doi:10.1007/BF00048645
Tessier A, Buffle J, Campbell PGC (1994) Uptake of trace metals by aquatic organisms. In: Buffle J, Devitre RR (eds) Chemical and biological regulation of aquatic systems. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 197–231
Thomas CA, Bendell-Young LI (1998) Linking the sediment geochemistry of an intertidal region to metal bioavailability in the deposit feeder Macoma balthica. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 173:197–213
Thompson DR (1996) Mercury in birds and terrestrial mammals. In: Beyer WN, Heinz GH, Redmond-Norwoods AW (eds) Environmental contaminants in wildlife: interpreting tissue concentrations. CRC Press, Boca Raton
U.S. Department of the Interior (U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, Bureau of Reclamation, Geological Survey, Bureau of Indian Affairs) (1998) R.A. Engberg (ed), Guidelines for interpretation of the biological effects of selected constituents in biota, water, and sediment: national irrigation water quality program, USDOI, BOR, Denver, CO, pp 139–184 (http://www.usbr.gov/niwqp/guidelines/)
Vancouver Airport Fuel Facilities Corporation (VAFFC) (2012) Vancouver airport fuel delivery project, environmental assessment certificate application, supplement 5: Fraser River Delta biofilm: Sensitivity to a jet A fuel spills—summary report
Vermeer K, Castilla J (1991) High cadmium residues observed during a pilot-study in shorebirds and their prey downstream from the El-Salvador copper mine, Chile. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 46:242–248
Warnock ND, Takekawa JY, Bishop MA (2004) Migration and stopover strategies of individual Dunlin along the Pacific coast of North America. Can J Zool 82:1687–1697. doi:10.1139/Z04-154
Wayland AM, Scheuhammer M (2011) Cadmium in birds. In: Beyer WN, Meador JP (eds) Environmental contaminants in biota. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Wedekind KJ, Titgemeyer EC, Twardock AR, Baker DH (1991) Phosphorus, but not calcium affects manganese absorption and turnover in chicks. J Nutr 121:1776–1786
White D, Finley M (1978) Uptake and retention of dietary cadmium in Mallard ducks. Environ Res 17:53–59. doi:10.1016/0013-9351(78)90060-9
White D, King K, Prouty R (1980) Significance of organochlorine and heavy-metal residues in wintering shorebirds at Corpus Christi, Texas, 1976-77. Pestic Monit J 14:58–63
Acknowledgments
Funding for this research was provided by SFU, a NSERC Discovery grant to L. Bendell, and Environment Canada via the Centre for Wildlife Ecology at SFU. O. Busby, G. Slater, and D. Ball assisted in sample acquisition. L. Evans Ogden and D. Lank provided a foundation of logistical and ecological knowledge. Assistance with permitting, field and lab work, data analysis, and figure production was provided by K. Chan, H. Walling, C. Smith, J. Barrett, P. van Veelen, W. Stein, U. Somjee, C. Palomera, K. Pillay, L. Du Gas, K. Gorman, K. Wegner, G. Leung, and A. Bykov. Comments from two anonymous reviewers also helped to improve the manuscript. We acknowledge the support of IIRMES at Cal. State Long Beach and SIF at UC Davis. Finally, we recognize the sacrifice of the animals examined in this research so that we could learn to better address their needs and stresses in the future.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
St. Clair, C.T., Baird, P., Ydenberg, R. et al. Trace elements in pacific Dunlin (Calidris alpina pacifica): patterns of accumulation and concentrations in kidneys and feathers. Ecotoxicology 24, 29–44 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1352-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1352-1