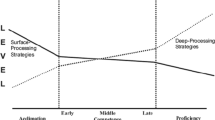
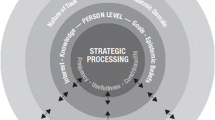
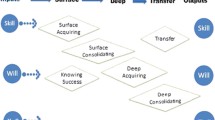
Abstract
The prevailing assumption by some that deep processing promotes stronger learning outcomes while surface processing promotes weaker learning outcomes has been called into question by the inconsistency and ambiguity of results in investigations of the relation between levels of processing and performance. The purpose of this literature review is to examine four areas that may be contributing to the inconsistency and ambiguity of these research results: conceptualization, operationalization, situational factors, and model specification of deep and surface processing. A PsycINFO database search was conducted, and 221 studies were identified for a comprehensive data table. Analysis of these data revealed trends that suggested conceptualization and operationalization of deep and surface processing differed depending on the theoretical frame utilized in each study. Additionally, the choice of theoretical frame also seemed to impact what situational factors may or may not have been present as well as how the model of levels of processing and performance was specified. Results from studies that met certain criteria demonstrated that levels of processing and performance are related, and further, these relations may be moderated by other factors. Implications for future research are discussed that focus on these four areas.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaron, S., & Skakun, E. (1999). Correlation of students’ characteristics with their learning styles as they begin medical school. Academic Medicine, 74, 260–262. doi:10.1097/00001888-199903000-00016.
Abd-El-Khalick, F., & Akerson, V. L. (2004). Learning as conceptual change: Factors mediating the development of preservice elementary teachers’ views of nature of science. Science Education, 88, 785–810. doi:10.1002/sce.10143.
Abraham, R. R., Kamath, A., Upadhya, S., & Ramnarayan, K. (2006). Learning approaches to physiology of undergraduates in an Indian medical school. Medical Education, 40, 916–923. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2929.2006.02547.x.
Aharony, N. (2006). The use of deep and surface learning strategies among students learning English as a foreign language in an Internet environment. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 76, 851–866. doi:10.1348/000709905X79158.
Albaili, M. A. (1993). Psychometric properties of the Inventory of Learning Processes: Evidence from United Arab Emirates college students. Psychological Reports, 72, 1331–1336.
Albaili, M. A. (1994). Learning processes and academic achievement of United Arab Emirates college students. Psychological Reports, 74, 739–746.
Al-Emadi, A. A. (2001). The relationships among achievement, goal-orientation, and study strategies. Social Behavior and Personality, 29, 823–832. doi:10.2224/sbp.2001.29.8.823.
Alesandrini, K. L., Langstaff, J. J., & Wittrock, M. C. (1984). Visual–verbal and analytic–holistic strategies, abilities, and styles. Journal of Educational Research, 77, 151–157.
Alexander, P. A. (1997). Mapping the multidimensional nature of domain learning: The interplay of cognitive, motivational, and strategic forces. In M. L. Maehr & P. R. Pintrich (Eds.), Advances in motivation and achievement (Vol. 10, pp. 213–250). Greenwich: JAI Press.
Alexander, P. A., Schallert, D. L., & Reynolds, R. E. (2009). What is learning anyway? A topographical perspective considered. Educational Psychologist, 44, 176–192. doi:10.1080/00461520903029006.
Alexander, P. A., Dinsmore, D. L., Parkinson, M. M., & Winters, F. I. (2011). Self-regulated learning in academic domains. In B. Zimmerman & D. Schunk (Eds.), Handbook of self-regulation of learning and performance. New York: Routledge.
Ally, B. A., Gold, C. A., & Budson, A. E. (2009). An evaluation of recollection and familiarity in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment using receiver operating characteristics. Brain and Cognition, 69, 504–513. doi:10.1016/j.bandc.2008.11.003.
Anmarkrud, O., & Braten, I. (2009). Motivation for reading comprehension. Learning and Individual Differences, 19, 252–256. doi:10.1016/j.lindif.2008.09.002.
APA. (2010). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Arlin, M. (1986). The effects of quantity and depth of processing on children’s time perception. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 42, 84–98. doi:10.1016/0022-0965(86)90017-2.
Arteche, A., Chamorro-Premuzic, T., Ackerman, P., & Furnham, A. (2009). Typical intellectual engagement as a byproduct of openness, learning approaches, and self-assessed intelligence. Educational Psychology, 29, 357–367. doi:10.1080/01443410902927833.
Aycicegi-Dinn, A., & Caldwell-Harris, C. L. (2009). Emotion-memory effects in bilingual speakers: A levels-of-processing approach. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition, 12, 291–303. doi:10.1017/S1366728909990125.
Baddeley, A. (1990). Human memory: Theory and practice. Hillside, New Jersey: Erlbaum.
Baeten, M., Dochy, F., & Struyven, K. (2008). Students’ approaches to learning and assessment preferences in a portfolio-based learning environment. Instructional Science, 36, 359–374. doi:10.1007/s11251-008-9060-y.
Bandalos, D. L., Finney, S. J., & Geske, J. A. (2003). A model of statistics performance based on achievement goal theory. Journal of Educational Psychology, 95, 604–616. doi:10.1037/0022-0663.95.3.604.
Barab, S. A., Thomas, M. K., & Merrill, H. (2001). Online learning: From information dissemination to fostering collaboration. Journal of Interactive Learning Research, 12, 105–143.
Barnhardt, T. M., & Geraci, L. (2008). Are awareness questionnaires valid? Investigating the use of posttest questionnaires for assessing awareness in implicit memory tests. Memory & Cognition, 36, 53–64. doi:10.3758/MC.36.1.53.
Barton, S. B., & Sanford, A. J. (1993). A case study of anomaly detection: Shallow semantic processing and cohesion establishment. Memory & Cognition, 21, 477–487.
Beishuizen, J. J., & Stoutjesdijk, E. T. (1999). Study strategies in a computer assisted study environment. Learning and Instruction, 9, 281–301. doi:10.1016/S0959-4752(98)00027-9.
Beishuizen, J., Stoutjesdijk, E., & van Putten, K. (1994). Studying textbooks: Effects of learning styles, study task, and instruction. Learning and Instruction, 4, 151–174.
Bentin, S., Moscovitch, M., & Nirhod, O. (1998). Levels of processing and selective attention effects on encoding in memory. Acta Psychologica, 98, 311–341. doi:10.1016/S0001-6918(97)00048-6.
Bentley, P., Driver, J., & Dolan, R. J. (2009). Modulation of fusiform cortex activity by cholinesterase inhibition predicts effects on subsequent memory. Brain: A Journal of Neurology, 132, 2356–2371. doi:10.1093/brain/awp176.
Biggs, J. B. (1978). Individual and group differences in study processes. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 48(3), 266–279.
Biggs, J. (1979). Individual differences in study processes and the quality of learning outcomes. Higher Education, 8, 381–394.
Biggs, J. (1987). The Study Process Questionnaire manual: Student approaches to learning and studying. Hawthorn: Australian Council for Educational Research.
Biggs, J. B. (1992). Why and how do Hong Kong students learn? Using the learning and studying process questionnaires. Hong Kong: Hong Kong University
Biggs, J. (1993). What do inventories of students’ learning processes really measure? A theoretical review and clarification. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 63(1), 3–19.
Biggs, J. (2003). Teaching for quality learning at university (2nd Ed.). Berkshire, England: Open University Press.
Biggs, J., & Moore, P. (1993). The process of learning. Australia: Prentice Hall.
Biggs, J. B., Kember, D., & Leung, Y. P. (2001). The revised two factor Study Process Questionnaire: R-SPQ-2 F. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 71, 133–149.
Biswas, G., Leelawong, K., Schwartz, D., Vye, N., & The Teachable Agents Group at Vanderbilt. (2005). Learning by teaching: A new agent paradigm for educational software. Applied Artificial Intelligence, 19, 363–392. doi:10.1080/08839510590910200.
Black, P. E., & Plowright, D. (2008). How postgraduate pharmacy students develop professional understanding: Re-conceptualising deep, reflective learning. Pharmacy Education, 8, 29–35. doi:10.1080/15602210701880119.
Blaxton, T. A. (1989). Investigating dissociations among memory measures: Support for a transfer-appropriate processing framework. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 15, 657–668.
Block, R. A. (2009). Intent to remember briefly presented human faces and toher pictorial stimuli enhances recognition memory. Memory & Cognition, 37, 667–678. doi:10.3758/MC.37.5.667.
Blom, S., & Severiens, S. (2008). Engagement in self-regulated deep learning of successful immigrant and non-immigrant students in inner city schools. European Journal of Psychology of Education, 23, 41–58. doi:10.1007/BF03173139.
Blumberg, P. (2000). Evaluating the evidence that problem-based learners are self-directed learners: A review of the literature. In D. H. Evenson & C. E. Hmelo (Eds.), Problem-based learning: A research perspective on learning interactions. Mahway, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Boatright-Horowitz, S. L., Langley, M., & Gunnip, M. (2009). Depth-of-processing effects as college students use academic advising web sites. CyberPsychology & Behavior, 12, 331–335. doi:10.1089/cpb.2008.0207.
Boekaerts, M. (2002). Assessment of attitudes about new learners’ roles: Factor analysis of the Beliefs about Working in Groups Questionnaire. Psychological Reports, 90, 986–996. doi:10.2466/PR0.90.3.986-996.
Boldini, A., Russo, R., & Avons, S. E. (2004). One process is not enough! A speed-accuracy tradeoff study of recognition memory. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 11, 353–361.
Boyd, B. D., & Ellis, N. R. (1986). Levels of processing and memory in mentally retarded and nonretarded persons. Intelligence, 10, 1–8. doi:10.1016/0160-2896(86)90024-3.
Boyle, E. A., Duffy, T., & Dunleavy, K. (2003). Learning styles and academic outcome: The validity and utility of Vermunt’s inventory of learning styles in a British higher education setting. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 73, 267–290.
Brébion, G., Amador, X., Smith, M. J., & Gorman, J. M. (1997). Mechanisms underlying memory impairment in schizophrenia. Psychological Medicine, 27, 383–393. doi:10.1017/S0033291796004448.
Brown, M. B., Aoshima, M., Bolen, L. M., Chia, R., & Kohyama, T. (2007). Cross-cultural learning approaches in students from the USA, Japan and Taiwan. School Psychology International, 28, 592–604. doi:10.1177/0143034307085660.
Bryceson, K. (2007). The online learning environment - A new model using social constructivism and the concept of ‘Ba’ as a theoretical framework. Learning Environments Research, 10, 189–206.
Burgess, M. C. R., & Weaver, G. E. (2003). Interest and attention in facial recognition. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 96, 467–480. doi:10.2466/PMS.96.2.467-480.
Camp, C. J., Markley, R. P., & Kramer, J. J. (1983). Spontaneous use of mnemonics by elderly individuals. Educational Gerontology, 9, 57–71. doi:10.1080/0380127830090106.
Campbell, D. T., & Stanley, J. C. (1963). Experimental and quasi-experimental designs for research. Boston: Houghton Mifflin.
Campbell, J., Smith, D., Boulton-Lewis, G., Brownlee, J., Burnett, P. C., Carrington, S., & Purdie, N. (2001). Students’ perceptions of teaching and learning: The influence of students’ approaches to learning and teachers’ approaches to teaching. Teachers and Teaching: Theory and Practice, 7, 173–187. doi:10.1080/13540600120054964.
Cano, F. (2007). Approaches to learning and study orchestrations in high school students. European Journal of Psychology of Education, 22, 131–151.
Cantwell, R. (1997). Cognitive dispositions and nurses’ appraisals of their learning environment. Issues in Educational Research, 7, 19–36.
Cantwell, R. H., & Millard, Y. (1994). The relationship between approach to learning and learning strategies in learning music. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 64, 45–63.
Carrier, L. M. (2003). College students’ choice of study strategies. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 96, 54–56. doi:10.2466/PMS.96.1.54-56.
Cassidy, S. (2007). Assessing ‘inexperienced’ students’ ability to self-assess: Exploring links with learning style and academic personal control. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 32, 313–330. doi:10.1080/02602930600896704.
Cassidy, S., & Eachus, P. (2000). Learning style, academic belief systems, self-report student proficiency and academic achievement in higher education. Educational Psychology, 20, 307–320. doi:10.1080/713663740.
Cerdán, R., & Vidal-Abarca, E. (2008). The effects of tasks on integrating information from multiple documents. Journal of Educational Psychology, 100, 209–222. doi:10.1037/0022-0663.100.1.209.
Challis, B. H., Velichkovsky, B. M., & Craik, F. I. M. (1996). Levels-of-processing effects on a variety of memory tasks: New findings and theoretical implications. Consciousness and Cognition, 5, 142–164.
Chamorro-Premuzic, T., & Furnham, A. (2008). Personality, intelligence and approaches to learning as predictors of academic performance. Personality and Individual Differences, 44, 1596–1603. doi:10.1016/j.paid.2008.01.003.
Chamorro-Premuzic, T., & Furnham, A. (2009). Mainly openess: The relationship between the Big Five personality traits and learning approaches. Learning and Individual Differences, 19, 524–529. doi:10.1016/j.lindif.2009.06.004.
Chamorro-Premuzic, T., Furnham, A., & Lewis, M. (2007). Personality and approaches to learning predict preference for different teaching methods. Learning and Individual Differences, 17, 241–250. doi:10.1016/j.lindif.2006.12.001.
Chang, K.-E., Sung, Y.-T., & Chen, I.-D. (2002). The effect of concept mapping to enhance text comprehension and summarization. Journal of Experimental Education, 71, 5–23.
Cheng, C.-M., Lin, W.-Y., & Tsai, C.-S. (2008). Conscious and unconscious forms of memory in different implicit tests. Cognitive Systems Research, 9, 312–328. doi:10.1016/j.cogsys.2008.05.001.
Chi, M. T. H., Feltovich, P. J., & Glaser, R. (1980). Categorization and representation of physics problems by experts and novices. Cognitive Science, 5, 121–152.
Clump, M. A. (2005). Changes to students’ learning processes following instruction on the topic. Journal of Instructional Psychology, 32, 293–297.
Clump, M. A., & Skogsberg, K. (2003). Differences in learning styles of college students attending similar universities in different geographic locations. College Student Journal, 37, 501–508.
Cohen, J., Cohen, P., West, S. G., & Aiken, L. S. (2003). Applied multiple regression/correlation for the behavioral sciences. Hillsdale: Erlbaum and Associates.
Corson, Y., Verrier, N., & Bucic, A. (2009). False memories and individual variations: The role of field dependence-independence. Personality and Individual Differences, 47, 8–11. doi:10.1016/j.paid.2009.01.036.
Cotton, D. R. E., & Gresty, K. A. (2007). The rhetoric and reality of e-learning: Using the think-aloud method to evaluate an online resource. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 32, 583–600. doi:10.1080/02602930601116920.
Coutinho, S. A., & Neuman, G. (2008). A model of metacognition, achievement goal orientation, learning style and self-efficacy. Learning Environments Research, 11, 131–151. doi:10.1007/s10984-008-9042-7.
Coyne, M. D., McCoach, D. B., & Kapp, S. (2007). Vocabulary intervention for kindergarten students: Comparing extended instruction to embedded instruction and incidental exposure. Learning Disability Quarterly, 30, 74–88.
Craig, M. C., Fletcher, P. C., Daly, E. M., Rymer, J., Cutter, W. J., Brammer, M., & Murphy, D. G. M. (2007). Gonadotropin hormone releasing hormone agonists alter prefrontal function during verbal encoding in young women. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 32, 1116–1127. doi:10.1016/j.psyneuen.2007.09.009.
Craik, F. I. M., & Lockhart, R. S. (1972). Levels of processing: A framework for memory research. Journal of Verbal Learning & Verbal Behavior, 11, 671–684. doi:10.1016/S0022-5371(72)80001-X.
Craik, F. I. M., & Tulving, E. (1975). Depth of processing and the retention of words in episodic memory. Journal of Experimental Psychology. General, 104, 268–294. doi:10.1037/0096-3445.104.3.268.
Crocker, L., & Algina, J. (1986). Introduction to classical and modern test theory. Orlando: Holt, Rinehart and Winston.
Cronbach, L. J. (1971). Validity. In R. L. Thorndike (Ed.), Educational measurement (pp. 443–507). Washington, DC: American Council on Education.
Cutica, I., & Bucciarelli, M. (2008). The deep versus the shallow: Effects of co-speech gestures in learning from discourse. Cognitive Science: A Multidisciplinary Journal, 32, 921–935. doi:10.1080/03640210802222039.
Daselaar, S. M., Veltman, D. J., Rombouts, S. A. R. B., Raaijmakers, J. G. W., & Jonker, C. (2003). Deep processing activates the medial temporal lobe in young but not in old adults. Neurobiology in Aging, 24, 1005–1011. doi:10.1016/S0197-4580(03)00032-0.
deVries, P., & Downie, N. (2000). Ensuring depth of learning in hospitality management programmes - Putting a method into practice. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 19, 385–397. doi:10.1016/S0278-4319(00)00032-3.
Dinsmore, D. L., Alexander, P. A., & Loughlin, S. M. (2008). Focusing the conceptual lens on metacognition, self-regulation, and self-regulated learning. Educational Psychology Review, 20, 391–409. doi:10.1007/s10648-008-9083-6.
Dixon, R. A., & von Eye, A. (1984). Depth of processing and text recall in adulthood. Journal of Reading Behavior, 16, 109–117.
Elander, J. (2003). A discipline-based undergraduate skills module. Psychology Learning & Teaching, 3, 48–55.
Elliot, A. J., McGregor, H. A., & Gable, S. (1999). Achievement goals, study strategies, and exam performance: A mediational analysis. Journal of Educational Psychology, 91, 549–563. doi:10.1037/0022-0663.91.3.549.
Entwistle, N. J. (1977). Strategies of learning and studying: Recent research findings. British Journal of Educational Studies, 25, 225–237.
Entwistle, N. (1988). Styles of learning and teaching. London: David Fulton.
Entwistle, N. J. (1997). Reconstructing approaches to learning: A response to Webb. Higher Education, 33, 213–218.
Entwistle, N. (2000). Promoting deep learning through teaching and assessment: Conceptual frameworks and educational contexts. Paper presented at the TLRP Conference, Leicester (www.ed.ac.uk/etl/publications.html).
Entwistle, N. (2001). Promoting deep learning through teaching and assessment. In L. Suskie (Ed.), Assessment to promote deep learning: Insights from AAHE’s 2000 and 1999 assessment conferences (pp. 9–19). American Association for Higher Education.
Entwistle, N. J., & Ramsden, P. (1983). Understanding student learning. London: Croom Helm.
Evans, C., & Gibbons, N. J. (2007). The interactivity effect in multimedia learning. Computers & Education, 49, 1147–1160. doi:10.1016/j.compedu.2006.01.008.
Evans, B., & Honour, L. (1997). Getting inside knowledge: The application of Entwistle’s model of surface/deep processing in producing open learning materials. Educational Psychology, 17, 127–139. doi:10.1080/0144341970170109.
Fenollar, P., Román, S., & Cuestas, P. J. (2007). University students’ academic performance: An integrative conceptual framework and empirical analysis. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 77, 873–891. doi:10.1348/000709907X189118.
Ferguson-Hessler, M. G., & de Jong, T. (1990). Studying physics texts: Differences in study processes between good and poor performers. Cognition and Instruction, 7, 41–54. doi:10.1207/s1532690xci0701_2.
Ferm, C., & Johansen, G. (2008). Professors’ and trainees’ perceptions of educational quality as related to preconditions of deep learning in musikdidaktik. British Journal of Music Education, 25, 177–191. doi:10.1017/S0265051708007912.
Freed, D. B., Marshall, R. C., & Phillips, D. S. (1998). Comparison of semantically and phonemically based training procedures in an overlearned naming task. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 87, 795–800.
Freeman, M. (1995). Peer assessment by groups of group work. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 20, 289–299.
Froger, C., Taconnat, L., Landré, L., Beigneux, K., & Isingrini, M. (2008). Effects of level of processing at encoding and types of retrieval task in mild cognitive impairment and normal aging. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 31, 312–321. doi:10.1080/13803390802112554.
Fujii, T., Okuda, J., Tsukiura, T., Ohtake, H., Suzuki, M., Kawashima, R., Itoh, M., Fukuda, H., & Yamadori, A. (2002). Encoding-related brain activity during deep processing of verbal materials: A PET study. Neuroscience Research, 44, 429–438. doi:10.1016/S0168-0102(02)00160-8.
Furnham, A., Christopher, A., Garwood, J., & Martin, N. G. (2008). Ability, demography, learning style, and personality trait correlates of student preference for assessment method. Educational Psychology, 28, 15–27. doi:10.1080/01443410701369138.
Gadzella, B. M., & Baloglu, M. (2003). High and low achieving education students on processing, retaining, and retrieval of information. Journal of Instructional Psychology, 30, 99–103.
Gadzella, B. M., & Masten, W. G. (1998). Critical thinking and learning processes for students in two major fields. Journal of Instructional Psychology, 25, 256–261.
Gadzella, B. M., Ginther, D. W., & Williamson, J. D. (1986). Differences in learning processes and academic achievement. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 62, 151–156.
Gadzella, B. M., Ginther, D. W., & Williamson, J. D. (1987). Study skills, learning processes and academic achievement. Psychological Reports, 61, 167–172.
Gadzella, B. M., Ginther, D. W., & Bryant, G. W. (1997a). Prediction of performance in an academic course by scores on measures of learning style and critical thinking. Psychological Reports, 81, 595–602.
Gadzella, B. M., Ginther, D. W., Masten, W. G., & Guthrie, D. (1997b). Predicting students as deep and shallow processors of information. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 84, 875–881.
Gadzella, B. M., Masten, W. G., & Stacks, J. (1998). Students’ stress and their learning strategies, test anxiety, and attributions. College Student Journal, 32, 416–422.
Gadzella, B. M., Stephens, R., & Baloglu, M. (2002). Prediction of educational psychology course grades by age and learning style scores. College Student Journal, 36, 62–68.
Gadzella, B. M., Masten, W. G., & Zascavage, V. (2009). Differences among three groups of men on stress and learning processes. Individual Differences Research, 7, 29–39.
Gallo, D. A., Meadow, N. G., Johnson, E. L., & Foster, K. T. (2008). Deep levels of processing elicit a distinctiveness heuristic: Evidence from the criterial recollection task. Journal of Memory and Language, 58, 1095–1111. doi:10.1016/j.jml.2007.12.001.
Geva, E., & Ryan, E. B. (1985). Use of conjunctions in expository texts by skilled and less skilled readers. Journal of Reading Behavior, 17, 331–346.
Gibbs, G. (1992). Improving quality of learning. Bristol: Technical and Educational Services.
Gibbs, G. R. (1999). Learning how to learn using a virtual learning environment for philosophy. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 15, 221–231. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2729.1999.153096.x.
Gibson, J. M. (2004). Priming problem solving with conceptual processing of relevant objects. Journal of General Psychology, 131, 118–135. doi:10.3200/GENP.131.2.118-135.
Goldman, J. D. G. (2005). Student teacher’s learning about child sexual abuse strategies for primary school: An exploratory study of surface and deep learning. Sex Education, 5, 79–92. doi:10.1080/1468181042000301902.
Grady, C. L., McIntosh, A. R., Rajah, M. N., Beig, S., & Craik, F. I. M. (1999). The effects of age on the neural correlates of episodic encoding. Cerebral Cortex, 9, 805–814. doi:10.1093/cercor/9.8.805.
Graesser, A. C., Singer, M., & Trabasso, T. (1994). Constructing inferences during narrative text comprehension. Psychological Review, 101, 371–395.
Graham, S., & Golan, S. (1991). Motivational influences on cognition: Task involvement, ego involvement, and depth of information processing. Journal of Educational Psychology, 83, 187–194. doi:10.1037/0022-0663.83.2.187.
Greene, B. A., & Miller, R. B. (1996). Influences on achievement: Goals, perceived ability, and cognitive engagement. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 21, 181–192. doi:10.1006/ceps.1996.0015.
Grodsky, A., & Giambra, L. M. (1990). The consistency across vigilance and reading tasks of individual differences in the occurrence of task-unrelated and task-related images and thoughts. Imagination, Cognition and Personality, 10, 39–52. doi:10.2190/6QG5-CXVV-4XUR-7P3K.
Grosschalk, M. J., & Gregg, V. H. (1996). Relaxation and cognitive processing during memory retrieval. Contemporary Hypnosis, 13, 177–185. doi:10.1002/ch.66.
Groves, M. (2005). Problem-based learning and learning approach: Is there a relationship? Advances in Health Sciences Education, 10, 315–326. doi:10.1007/s10459-005-8556-3.
Hancock, T. E., Stock, W. A., Kulhavy, R. W., & Swindell, L. K. (1996). Gender and developmental differences in the academic study behaviors of elementary school children. Journal of Experimental Education, 65, 18–39.
Hara, N., Bonk, C. J., & Angeli, C. (2000). Content analysis of online discussion in an applied educational psychology course. Instructional Science, 28, 115–152. doi:10.1023/A:1003764722829.
Heijne-Penninga, M., Kuks, J. B. M., Hofman, W. H. A., & Cohen-Schotanus, J. (2008). Influence of open- and closed-book tests on medical students’ learning approaches. Medical Education, 42, 967–974. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2923.2008.03125.x.
Henry, K. J., Van Lunen, B. L., Udermann, B., & Onate, J. A. (2009). Curricular satisfaction levels of national athletic trainers’ association-accredited postprofessional athletic training graduates. Journal of Athletic Training, 44, 391–399. doi:10.4085/1062-6050-44.4.391.
Henson, R. N. A., Hornberger, M., & Rugg, M. D. (2005). Further dissociating the processes involved in recognition memory: An fMRI study. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 17, 1058–1073. doi:10.1162/0898929054475208.
Hill, J., & Woodland, W. (2002). An evaluation of foreign fieldwork in promoting deep learning: A preliminary investigation. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 27, 539–555. doi:10.1080/0260293022000020309.
Hilliard, R. I. (1995). How do medical students learn: Medical student learning styles and factors that affect these learning styles. Teaching and Learning in Medicine, 7, 201–210.
Hinojosa, J. A., Martín-Loeches, M., Muñoz, F., Casado, P., & Pozo, M. A. (2004). Electrophysiological evidence of automatic early semantic processing. Brain and Language, 88, 39–46. doi:10.1016/S0093-934X(03)00158-5.
Igo, L. B., Riccomini, P. J., Bruning, R. H., & Pope, G. G. (2006). How should middle-school students with LD approach online note taking? A mixed-methods study. Learning Disability Quarterly, 29, 89–100.
Jacoby, L. L. (1983). Perceptual enhancement: Persistence effects of an experience. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 9, 21–38.
Jacoby, L. L., & Dallas, M. (1981). On the relationship between autobiographical memory and perceptual learning. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 3, 306–340.
Jakoubek, J., & Swenson, R. R. (1993). Differences in use of learning strategies and relation to grades among undergraduate students. Psychological Reports, 73, 787–793.
James, P. (1998). Progressive development of deep learning skills through undergraduate and postgraduate dissertations. Educational Studies, 24, 95–105. doi:10.1080/0305569980240107.
Jay, T., Caldwell-Harris, C., & King, K. (2008). Recalling taboo and nontaboo words. American Journal of Psychology, 121, 83–103.
Jundt, D. K., & Hinsz, V. B. (2002). Influences of positive and negative affect on decisions involving judgmental biases. Social Behavior and Personality, 30, 45–52. doi:10.2224/sbp.2002.30.1.45.
Justicia, F., Pichardo, M. C., Cano, F., Berbén, A. B. G., & De la Fuente, J. (2008). The Revised Two-Factor Study Process Questionnaire (R-SPQ-2 F): Exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses at item level. European Journal of Psychology of Education, 23, 355–372. doi:10.1007/BF03173004.
Kamsteeg, P. A. (1992). Viewpoints in domain representations: A proposal for description and formalization. In H. Kratz (Ed.), Proceedings of the Seventh Canadian Symposium on Instructional Technology. Canadian Association of Course-ware Producers: Alberta.
Kintsch, W. (1998). Comprehension: A paradigm for cognition. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press.
Kirby, J. R., & Pedwell, D. (1991). Students’ approaches to summarisation. Educational Psychology, 11, 297–307. doi:10.1080/0144341910110306.
Klein, A. M., Zwickel, J., Prinz, W., & Frith, U. (2009). Animated triangles: An eye tracking investigation. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 62, 1189–1197. doi:10.1080/17470210802384214.
Klinger, T. H. (2006). Learning approach, thinking style and critical inquiry: The online community. Korean Journal of Thinking & Problem Solving, 16, 91–113.
Koivukari, A. M. (1987). Question level and cognitive processing: Psycholinguistic dimensions of questions and answers. Applied Psycholinguistics, 8, 101–120. doi:10.1017/S0142716400000151.
Kozminsky, E., & Kaufman, G. (1992). Academic achievement and individual differences in the learning processes of Israeli high-school students. Learning and Individual Differences, 4, 335–345. doi:10.1016/1041-6080(92)90018-A.
Lau, S., Liem, A. D., & Nie, Y. (2008). Task- and self-related pathways to deep learning: The mediating role of achievement goals, classroom attentiveness, and group participation. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 78, 639–662. doi:10.1348/000709907X270261.
Leelawong, K., & Biswas, G. (2008). Designing learning by teaching agents: The Betty’s Brain system. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education, 18, 181–208.
Lehman, S., & Schraw, G. (2002). Effects of coherence and relevance on shallow and deep text processing. Journal of Educational Psychology, 94, 738–750. doi:10.1037/0022-0663.94.4.738.
Liem, A. D., Lau, S., & Nie, Y. (2008). The role of self-efficacy, task value, and achievement goals in predicting learning strategies, task disengagement, peer relationship, and achievement outcome. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 33, 486–512. doi:10.1016/j.cedpsych.2007.08.001.
Lockhart, R. S., & Craik, F. I. M. (1990). Levels of processing: A retrospective commentary on a framework for memory research. Canadian Journal of Psychology, 44, 87–112. doi:10.1037/h0084237.
Lockhart, D., & Schmeck, R. R. (1983). Learning styles and classroom evaluation methods: Different strokes for different folks. College Student Journal, 17, 94–100.
Maheswaran, D., & Meyers-Levy, J. (1990). The influence of message framing and issue involvement. Journal of Marketing Research, 27, 361–367.
Major, J. C., & Horton, K. D. (2008). Measuring automatic retrieval in a conceptual priming task. European Journal of Cognitive Psychology, 20, 1027–1042. doi:10.1080/09541440701862190.
Marinkovic, K., Oscar-Berman, M., Urban, T., O’Reilly, C. E., Howard, J. A., Sawyer, K., & Harris, G. J. (2009). Alcoholism and dampened temporal limbic activation to emotional faces. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 33, 1880–1892. doi:10.1111/j.1530-0277.2009.01026.x.
Martin, I. G., Stark, P., & Jolly, B. (2000). Benefiting from clinical experience: The influence of learning style and clinical experience on performance in an undergraduate objective structured clinical examination. Medical Education, 34, 530–534. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2923.2000.00489.x.
Marton, F., & Säljö, R. (1976a). On qualitative differences in learning: I. Outcome and process. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 46(1), 4–11.
Marton, F., & Säljö, R. (1976b). On qualitative differences in learning: II. Outcome as a function of the learner’s conception of the task. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 46(2), 115–127.
Marton, F., & Säljö, R. (1997). Approaches to learning. In F. Marton, D. J. Hounsell, & N. J. Entwistle (Eds.), The experience of learning (2nd ed., pp. 39–58). Edinburgh: Scottish Academic Press.
Marton, F., Hounsell, D., & Entwistle, N. (1984). The experience of learning. Edinburgh: Scottish Academic Press.
Matthews, B., Lietz, P., & Darmawan, I. G. N. (2007). Values and learning approaches of students at an international university. Social Psychology of Education, 10, 247–275. doi:10.1007/s11218-007-9019-x.
Maylor, E. A., Rabbitt, P. M., & Kingstone, A. (1987). Effects of alcohol on word categorization and recognition memory. British Journal of Psychology, 78, 233–239.
McCarthy, P. R., & Meier, S. (1983). Effects of race and psychological variables on college student writing. Journal of Instructional Psychology, 10, 148–157.
McClain, L. (1983). Interval estimation: Effect of processing demands on prospective and retrospective reports. Perception & Psychophysics, 34, 185–189.
McKelvie, S. J., & Pullara, M. (1988). Effects of hypnosis and level of processing on repeated recall of line drawings. Journal of General Psychology, 115, 315–329.
McKeown, M. G., & Beck, I. L. (2004). Direct and rich vocabulary instruction. In J. F. Baumann & E. J. Kame’enui (Eds.), Vocabulary instruction: Research to practice (pp. 13–27). New York: Guilford Publishing Company.
McLaughlin, K., & Mandin, H. (2002). Using ‘concept sorting’ to study learning processes and outcomes. Academic Medicine, 77, 831–836. doi:10.1097/00001888-200208000-00017.
McParland, M., Noble, L. M., & Livingston, G. (2004). The effectiveness of problem-based learning compared to traditional teaching in undergraduate psychiatry. Medical Education, 38(8), 859–867. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2929.2004.01818.x.
Meehan, E. F., & Pilotti, M. (1996). Auditory priming in an implicit memory task that emphasizes surface processing. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 3, 495–498.
Meier, S. T., & Schmeck, R. R. (1985). The burned-out college student: A descriptive profile. Journal of College Student Personnel, 26, 63–69.
Meier, S. T., McCarthy, P. R., & Schmeck, R. R. (1984). Validity of self-efficacy as a predictor of writing performance. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 8, 107–120. doi:10.1007/BF01173038.
Meijer, W. A., de Groot, R. H. M., van Gervan, P. W. M., van Boxtel, M. P. J., & Jolles, J. (2009). Level of processing and reaction time in young and middle-aged adults and the effect of education. European Journal of Cognitive Psychology, 21, 216–234. doi:10.1080/09541440802091780.
Messick, S. (1981). Constructs and their vicissitudes in educational and psychological measurement. Psychological Bulletin, 89, 575–588. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.89.3.575.
Messick, S. (1995). Validity of psychological assessment: Validation of inferences from persons’ responses and performances as scientific inquiry into score meaning. American Psychologist, 50, 741–749. doi:10.1037/0003-066X.50.9.741.
Miller, C. D., Alway, M., & McKinley, D. L. (1987). Effects of learning styles and strategies on academic success. Journal of College Student Personnel, 28, 399–404.
Mills, P. (2003). Group project work with undergraduate veterinary science students. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 28, 527–538. doi:10.1080/02602930301676.
Minasian-Batmanian, L. C., Lingard, J., & Prosser, M. (2005). Differences in students’ perceptions of learning compulsory foundation biochemistry in the health sciences professions. Advances in Health Sciences Education, 10, 279–290. doi:10.1007/s10459-005-1404-7.
Moreno, R., & Mayer, R. E. (2000). Engaging students in active learning: The case for personalized multimedia messages. Journal of Educational Psychology, 92, 724–733. doi:10.1037/0022-06M.92.4.724.
Muis, K. R. (2007). The role of epistemic beliefs in self-regulated learning. Educational Psychologist, 42(3), 173–190.
Murphy, P. K., & Alexander, P. A. (2000). A motivated exploration of motivation terminology. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 25, 3–53. doi:10.1006/ceps.1999.1019.
Murphy, P. K., & Alexander, P. A. (2002). What counts? The predictive powers of subject-matter knowledge, strategic processing, and interest in domain-specific performance. The Journal of Experimental Education, 70, 197–214. doi:10.1080/00220970209599506.
Murphy, S. M., & Tyler, S. (2005). The relationship between learning approaches to part-time study of management courses and transfer of learning to the workplace. Educational Psychology, 25, 455–469.
Muthukrishna, N., & Borkowski, J. G. (1995). How learning contexts facilitate strategy transfer. Applied Cognitive Psychology, 9, 425–446. doi:10.1002/acp.2350090506.
Nairne, J. S., Pandeirada, J. N. S., & Thompson, S. R. (2008). Adaptive memory: The comparative value of survival processing. Psychological Science, 19, 176–180. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9280.2008.02064.x.
Nathanson, A. I., & Botta, R. A. (2003). Shaping the effects of television on adolescents’ body image disturbance: The role of parental mediation. Communication Research, 30, 304–331. doi:10.1177/0093650203030003003.
Nelson, T. O. (1977). Repetition and depth of processing. Journal of Verbal Learning & Verbal Behavior, 16, 151–171. doi:10.1016/S0022-5371(77)80044-3.
Neuville, S., Frenay, M., & Bourgeois, E. (2007). Task value, self-efficacy and goal orientations: Impact on self-regulated learning, choice and performance among university students. Psychologica Belgica, 47, 95–117.
Nichols, J. D. (1996). The effects of cooperative learning on student achievement and motivation in a high school geometry class. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 21, 467–476. doi:10.1006/ceps.1996.0031.
Nijhuis, J. F. H., Segers, M. S. R., & Gijselaers, W. H. (2005). Influence of redesigning a learning environment on student perceptions and learning strategies. Learning Environments Research, 8, 67–93. doi:10.1007/s10984-005-7950-3.
Nijhuis, J., Segers, M., & Gijselaers, W. (2008). The extent of variability in learning strategies and students’ perceptions of the learning environment. Learning and Instruction, 18, 121–134. doi:10.1016/j.learninstruc.2007.01.009.
Niles, S. (1996). Cultural variation in learning strategies: A comparison of Australian and Sri Lankan university students. Journal of Psychology: Interdisciplinary and Applied, 130, 83–94.
N’Kaoua, B., Véron, A.-L. H., Lespinet, V. C., Claverie, B., & Sztark, F. (2002). Time course of cognitive recovery after propofol anaesthesia: A level of processing approach. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 24, 713–719. doi:10.1076/jcen.24.6.713.8401.
Nolen, S. B. (1988). Reasons for studying: Motivational orientations and study strategies. Cognition and Instruction, 5, 269–287. doi:10.1207/s1532690xci0504_2.
Nolen, S. B., & Haladyna, T. M. (1990a). Personal and environmental influences on students’ beliefs about effective study strategies. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 15, 116–130. doi:10.1016/0361-476X(90)90011-O.
Nolen, S. B., & Haladyna, T. M. (1990b). Motivation and studying in high school science. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 27, 115–126. doi:10.1002/tea.3660270204.
Novick, L. R. (1988). Analogical transfer, problem similarity, and expertise. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning. Memory, and Cognition, 14, 510–520.
O’Brien, E. M., & Hart, S. J. (1999). Action learning: The link between academia and industry? Educational Research, 41, 77–89.
Onion, C. W. R., & Bartzokas, C. A. (1998). Changing attitudes to infection management in primary care: A controlled trial of active versus passive guideline implementation strategies. Family Practice, 15, 99–104. doi:10.1093/fampra/15.2.99.
Osorio, A., Ballesteros, S., Fay, S., & Pouthas, V. (2009). The effect of age on word-stem cued recall: A behavioral and electrophysiological study. Brain Research, 1289, 56–68. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2009.07.013.
Oulasvirta, A., Kärkkäinen, L., & Laarni, J. (2005). Expectations and memory in link search. Computers in Human Behavior, 21, 773–789. doi:10.1016/S0747-5632(04)00035-4.
Papinczak, T., Young, L., Groves, M., & Haynes, M. (2008). Effects of a metacognitive intervention on students’ approaches to learning and self-efficacy in a first year medical course. Advances in Health Sciences Education, 13, 213–232. doi:10.1007/s10459-006-9036-0.
Pearce, G., & Lee, G. (2009). Viva voce (oral examination) as an assessment method: Insights from marketing students. Journal of Marketing Education, 31, 120–130. doi:10.1177/0273475309334050.
Pedhazur, E. J. (1997). Multiple regression in behavioral research: Explanation and prediction. New York: Holt, Rinehart, and Winston.
Phan, H. P. (2006). Examination of student learning approaches, reflective thinking, and epistemological beliefs: A latent variables approach. Electronic Journal of Research in Educational Psychology, 10(4), 577–610.
Phan, H. P. (2007). An examination of reflective thinking, learning approaches, and self-efficacy beliefs at the University of the South Pacific: A path analysis approach. Educational Psychology, 27, 789–806. doi:10.1080/01443410701349809.
Phan, H. P. (2008). Unifying different theories of learning: Theoretical framework and empirical evidence. Educational Psychology, 28, 325–340. doi:10.1080/01443410701591392.
Phan, H. P. (2009a). Amalgamation of future time orientation, epistemological beliefs, achievement goals and study strategies: Empirical evidence established. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 79, 155–173. doi:10.1348/000709908X306864.
Phan, H. P. (2009b). Exploring students’ reflective thinking practice, deep processing strategies, effort, and achievement goal orientations. Educational Psychology, 297–313. doi:10.1080/01443410902877988.
Phan, H. P. (2009c). Relationships between goals, self-efficacy, critical thinking and deep processing strategies: A path analysis. Educational Psychology, 29, 777–799. doi:10.1080/01443410903289423.
Phan, H. P., & Deo, B. (2006). Approaches to learning in Educational Psychology and Mathematics: A comparative analysis in the South Pacific region. Presented at the Australian Association for Research in Education (AARE) Conference. South Australia.
Pierce, B. H., Sullivan, A. L., Schacter, D. L., & Budson, A. E. (2005). Comparing source-based and gist-based false recognition in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychology, 19, 411–419. doi:10.1037/0894-4105.19.4.411.
Pintrich, P. R. (2000). The role of goal orientation in self-regulated learning. In M. Boekaerts, P. R. Pintrich, & M. Zeidner (Eds.), Handbook of self-regulation (pp. 451–502). San Diego: Academic.
Pintrich, P. R., & Schrauben, B. (1992). Students’ motivational beliefs and their cognitive engagement on classroom tasks. In D. H. Schunk & J. Meece (Eds.), Students perceptions in the classroom: Causes and consequences (pp. 149–183). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Pitts, M., & Heap, M. (1996). Memory and depth of processing in ‘hypnotized’ and ‘non-hypnotized’ subjects. Contemporary Hypnosis, 13, 129–136. doi:10.1002/ch.60.
Popper, K. R. (1994). The myth of the framework: In defence of science and rationality. London: Routledge.
Powell, S., Tindal, I., & Millwood, R. (2008). Personalized learning and the ultraversity experience. Interactive Learning Environments, 16, 63–81. doi:10.1080/10494820701772710.
Pressley, M., & Afflerbach, P. (1995). Verbal protocols of reading: The nature of constructively responsive reading. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Prosser, M., & Trigwell, K. (1999). Understanding learning and teaching: The experience in higher education. Buckingham, England: Open University Press.
Ragland, J. D., McCarthy, E., Bilker, W. B., Brensinger, C. M., Valdez, J., Kohler, C., Gur, R. E., & Gur, R. C. (2006). Levels-of-processing effect on internal source monitoring in schizophrenia. Psychological Medicine, 36, 641–648. doi:10.1017/S0033291706007094.
Ramsden, P. (1988). Improving learning: New perspectives. London: Kogan Page.
Ramsden, P. (1992). Learning to teach in higher education. London: Routledge.
Ramsden, P. (2003). Learning to teach in higher education. London: Routledge.
Rayner, K. (1998). Eye movements in reading and information processing: 20 years of research. Psychological Bulletin, 124, 372–422.
Richardson, A. G., & Fergus, E. E. (1993). Learning style and ability grouping in the high school system: Some Caribbean findings. Educational Research, 35, 69–76.
Rodriguez, C. M. (2009). The impact of academic self-concept, expectations and the choice of learning strategy on academic achievement: The case of business students. Higher Education Research & Development, 28, 523–539. doi:10.1080/07294360903146841.
Royet, J.-P., Koenig, O., Paugam-Moisy, H., Puzenat, D., & Chasse, J.-L. (2004). Levels-of-processing effects on a task of olfactory naming. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 98, 197–213. doi:10.2466/PMS.98.1.197-213.
Salovaara, H. (2005). An exploration of students’ strategy use in inquiry-based computer-supported collaborative learning. Journal of Educational Studies, 25, 225–237. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2729.2005.00112.x.
Sanchez, E., Garcia-Rodicio, H., & Acuna, S. R. (2009). Are instructional explanations more effctive in the context of an impasse? Instructional Science, 37, 537–563. doi:10.1007/s11251-008-9074-5.
Sandberg, J., & Barnard, Y. (1997). Deep learning is difficult. Instructional Science, 25, 15–36. doi:10.1023/A:1002941804556.
Sandman, C. A. (1993). Memory rehabilitation in Alzheimer’s disease: Preliminary findings. Clinical Gerontologist: The Journal of Aging and Mental Health, 13, 19–33. doi:10.1300/J018v13n04_03.
Sauzéon, H., N’kaoua, B., Lespinet, V., Guillem, F., & Claverie, B. (2000). Age effect in recall performance according to the levels of processing, elaboration, and retrieval cues. Experimental Aging Research, 26, 57–73. doi:10.1080/036107300243687.
Schommer, M., & Surber, J. R. (1986). Comprehension-monitoring failure in skilled adult readers. Journal of Educational Psychology, 78, 353–357. doi:10.1037/0022-0663.78.5.353.
Schunk, D. H. (2008). Metacognition, self-regulation, and self-regulated learning: Research recommendations. Educational Psychology Review, 20, 463–467. doi:10.1007/s10648-008-9086-3.
Scouller, K. (1998). The influence of assessment method on students’ learning approaches: Multiple choice question examination versus assignment essay. Higher Education, 35, 453–472.
Sedikides, C., & Green, J. D. (2000). On the self-protective nature of inconsistency-negativity management: Using the person memory paradigm to examine self-referent memory. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 79, 906–922. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.79.6.906.
Segalowitz, N., Cohen, P., Chan, A., & Prieur, T. (2001). Musical recall memory: Contributions of elaboration and depth of processing. Psychology of Music, 29, 139–148. doi:10.1177/0305735601292004.
Senko, C., & Miles, K. M. (2008). Pursuing their own learning agenda: How mastery-oriented students jeopardize their class performance. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 33, 561–583. doi:10.1016/j.cedpsych.2007.12.001.
She, H.-C., & Chen, Y.-Z. (2009). The impact of multimedia effect on science learning: Evidence from eye movements. Computers & Education, 53, 1297–1307. doi:10.1016/j.compedu.2009.06.012.
Shell, D. F., & Husman, J. (2008). Control, motivation, affect, and strategic self-regulation in the college classroom: A multidimensional phenomenon. Journal of Educational Psychology, 100, 443–459. doi:10.1037/0022-0663.100.2.443.
Shen, L., & Dillard, J. P. (2009). Message frames interact with motivational systems to determine depth of message processing. Health Communication, 24, 504–514. doi:10.1080/10410230903104897.
Shen, J., Hiltz, S. R., & Bieber, M. (2008). Learning strategies in online collaborative examinations. IEEE Transactions on Professional Communication, 51, 63–78. doi:10.1109/TPC.2007.2000053.
Shimamura, A. P. (1986). Priming effects in amnesia: Evidence for a dissociable memory function. [Special Issue: Human memory]. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Experimental Psychology, 38, 619–694.
Shum, D., Sweeper, S., & Murray, R. (1996). Performance on verbal implicit and explicit memory tasks following traumatic brain injury. Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation, 11, 43–53. doi:10.1097/00001199-199604000-00005.
Silberman, E. K., Weingartner, H., Laraia, M., Byrnes, S., & Post, R. M. (1983). Processing of emotional properties of stimuli by depressed and normal subjects. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 171, 10–14. doi:10.1097/00005053-198301000-00003.
Simon, A. F., Fagley, N. S., & Halleran, J. G. (2004). Decision framing: Moderating effects of individual differences and cognitive processing. Journal of Behavioral Decision Making, 17, 77–93. doi:10.1002/bdm.463.
Sinha, S. P., & Kumari, P. (2001). Parental inducement of self-regulation, strategy use and attribution of success/failure among school children. Journal of the Indian Academy of Applied Psychology, 27, 169–174.
Sins, P. H. M., van Joolingen, W. R., Savelsbergh, E. R., & van Hout-Wolters, B. (2008). Motivation and performance within a collaborative computer-based modeling task: Relations between students’ achievement goal orientation, self-efficacy, cognitive processing, and achievement. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 33, 58–77. doi:10.1016/j.cedpsych.2006.12.004.
Sitthiworachart, J., & Joy, M. (2008). Computer support of effective peer assessment in an undergraduate programming class. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 24, 217–231. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2729.2007.00255.x.
Skaggs, L. P., Rocklin, T. R., Dansereau, D. F., & Hall, R. H. (1990). Dyadic learning of technical material: Individual differences, social interaction, and recall. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 15, 47–63. doi:10.1016/0361-476X(90)90005-L.
Smith, S. M., Tindell, D. R., Pierce, B. H., Gilliland, T. R., & Gerkens, D. R. (2001). The use of source memory to identity one’s own episodic confusion errors. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 27, 362–374. doi:10.1037/0278-7393.27.2.362.
Smith, K., Clegg, S., Lawrence, E., & Todd, M. J. (2007). The challenges of reflection: Students learning from work placements. Innovations in Education and Teaching International, 44, 131–141. doi:10.1080/14703290701241042.
Sporer, S. L. (1991). Deep—deeper—deepest? Encoding strategies and the recognition of human faces. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 17, 323–333. doi:10.1037/0278-7393.17.2.323.
Stewart, A. J., Holler, J., & Kidd, E. (2007). Shallow processing of ambiguous pronouns: Evidence for delay. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 60, 1680–1696.
Sullivan, Y. M., & Cantwell, R. H. (1999). The planning behaviours of musicians engaging traditional and non-traditional scores. Psychology of Music, 27, 245–266. doi:10.1177/0305735699272017.
Tait, H., & Entwistle, N. J. (1996). Identifying students at risk through ineffective study strategies. Higher Education, 31, 97–116.
Tehan, G., Fallon, A. B., & Randall, N. (1997). The effect of item and relational processing on incidental long-term memory for order. Memory, 5, 457–482. doi:10.1080/741941431.
Terry, R. L. (1993). How wearing eyeglasses affects facial recognition. Current Psychology, 12, 151–162.
Thill, E. E., & Brunel, P. (1995). Ego-involvement and task-involvement: Related conceptions of ability, effort, and learning strategies among soccer players. International Journal of Sport Psychology, 26, 81–97.
Thomas, C. R., & Gadbois, S. A. (2007). Academic self-handicapping: The role of self-clarity and students’ learning strategies. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 77, 101–119. doi:10.1348/000709905X79644.
Thorndike, E. L., & Gates, A. I. (1929). Elementary principles of education. New York: Macmillan.
Tian, X. (2007). Do assessment methods matter? A sensitivity test. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 32, 387–401. doi:10.1080/02602930600898460.
Toichi, M., & Kamio, Y. (2002). Long-term memory and levels-of-processing in autism. Neuropsychologia, 40, 964–969. doi:10.1016/S0028-3932(01)00163-4.
Tooth, D., Tonge, K., & McManus, I. C. (1989). Anxiety and study methods in preclinical students: Causal relation to examination performance. Medical Education, 23, 416–421. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2923.1989.tb00896.x.
Toppino, T. C., Fearnow-Kenney, M. D., Kiepert, M. H., & Teremula, A. C. (2009). The spacing effect in intentional and incidental free recall by children and adults: Limits on the automaticity hypothesis. Memory & Cognition, 37, 316–325. doi:10.3758/MC.37.3.316.
Tulving, E., & Schacter, D. L. (1990). Priming and human memory systems. Science, 247, 301–306.
Upton, D., & Adams, S. (2006). Individual differences in online learning. Psychology Learning & Teaching, 5, 141–145.
Vaid, J. (1987). Visual field asymmetries for rhyme and syntactic category judgments in monolinguals and fluent early and late bilinguals. Brain and Language, 30, 263–277. doi:10.1016/0093-934X(87)90102-7.
van den Broek, P., Risden, K., & Husebye-Hartmann, E. (1995). The role of readers’ standards for coherence in the generation of inferences during reading. In R. F. Lorch & E. J. O’Brien (Eds.), Sources of coherence in reading (pp. 353–374). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Vansteenkiste, M., Simons, J., Lens, W., Sheldon, K. M., & Deci, E. L. (2004). Motivating learning, performance, and persistence: The synergistic effects of intrinsic goal contents and autonomy-supportive contexts. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 87, 246–260. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.87.2.246.
Verheij, J., Stoutjesdijk, E., & Beishuizen, J. (1996). Search and study strategies in hypertext. Computers in Human Behavior, 12, 1–15. doi:10.1016/0747-5632(95)00015-1.
Verma, B. P. (1994). Hemisphericity and learning styles among students of distance education. Indian Journal of Psychometry & Education, 25, 53–60.
Verma, S. B. (2000). Cognitive and regulation strategies of learning among distance learners. Psycho-Lingua, 30, 43–46.
Vermetten, Y. J., Lodewijks, H. G., & Vermunt, J. D. (2001). The role of personality traits and goal orientations in strategy use. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 26, 149–170. doi:10.1006/ceps.1999.1042.
Vermunt, J. D. H. M., & Van Rijswijk, F. A. W. M. (1988). Analysis and development of students’ skill in self-regulated learning. Higher Education, 17, 647–582.
Vidal-Abarca, E., Martinez, G., & Gilabert, R. (2000). Two procedures to improve instructional text: Effects on memory and learning. Journal of Educational Psychology, 92, 107–116.
Vogel, D., Kennedy, D., & Kwok, R. C. (2009). Does using mobile device applications lead to learning? Journal of Interactive Learning Research, 20, 469–485.
Volet, S. E., & Chalmers, D. (1992). Investigation of qualitative differences in university students’ learning goals, based on an unfolding model of stage development. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 62, 17–34.
Vu, N. V., Van Der Vleuten, C. P. M., & Lacombe, G. (1998). Medical students’ learning processes: A comparative and longitudinal study. Academic Medicine, 73, S25–S27. doi:10.1097/00001888-199810000-00035.
Watkins, D., McInerney, D., Akande, A., & Lee, C. (2003). An investigation of ethnic differences in the motivation and strategies for learning of students in desegregated South African schools. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology, 34, 189–194. doi:10.1177/0022022102250563.
Watson, T. J. (1996). Motivation: That’s Maslow, isn’t it? Management Learning, 27, 447–464. doi:10.1177/1350507696274004.
Wautier, G., & Westman, A. S. (1995). Relationships between learning styles and solutions based on analogies or background knowledge. Psychological Reports, 77, 1115–1120.
Wecker, C., Kohnle, C., & Fischer, F. (2007). Computer literacy and inquiry learning: When geeks learn less. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 23, 133–144. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2729.2006.00218.x.
Weinstein, C. E., & Mayer, R. E. (1986). The teaching of learning strategies. In M. Wittrock (Ed.), Handbook of research on teaching (pp. 315–327). New York: Macmillan.
Weinstein, Y., Bugg, J. M., & Roediger, H. L., III. (2008). Can the survival recall advantage be explained by basic memory process? Memory & Cognition, 36, 913–919. doi:10.3758/MC.36.5.913.
Weldon, M. S., & Bellinger, K. D. (1997). Collective memory: Collaborative and individual processes in remembering. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 23, 1160–1175. doi:10.1037/0278-7393.23.5.1160.
Weldon, M. S., & Roediger, H. L. (1987). Altering retrieval demands reserves the picture superiority effect. Memory and Cognition, 15, 269–280.
Wenger, E. (2006). Learning for a small planet, a research agenda. http://ewenger.com/research/LSPfoundingdoc.doc.
Westman, A. S. (1993). Learning styles are content specific and probably influenced by content areas studied. Psychological Reports, 73, 512–514.
Westman, A. S., & Alexander, N. A. (2004). Epistemological exploration: Generalization of learning styles and analytical skills between academic and religious materials. Psychological Reports, 94, 1083–1088. doi:10.2466/PR0.94.3.1083-1088.
White, B. Y., & Frederiksen, J. R. (1990). Causal model progression as a foundation for intelligent learning environments. Artificial Intelligence, 42, 99–157.
Whiteford, G. E., & McAllister, L. (2007). Politics and complexity in intercultural fieldwork: The Vietnam experience. Australian Occupational Therapy Journal, 54, S74–S83.
Wilding, J. M., & Hayes, S. (1992). Relations between approaches to studying and note-taking behaviour in lectures. Applied Cognitive Psychology, 6, 233–246. doi:10.1002/acp.2350060305.
Winnick, W. A., & Daniel, S. A. (1970). Two kinds of response priming in tachistoscopic word recognition. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 84, 74–81.
Wong, D. K. P., & Lam, D. O. B. (2007). Problem-Based Learning in Social Work: A Study of Student Learning Outcomes. Research on Social Work Practice, 17, 55–65. doi:10.1177/1049731506293364.
Worthington, A. C. (2002). The impact of student perceptions and characteristics on teaching evaluations: A case study in finance education. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 27, 49–64. doi:10.1080/02602930120105054.
Yamauchi, H., & Miki, K. (2000). Effects of students’ perception of teachers’ and parents’ attitudes on their achievement goals and learning strategies. Psychologia: An International Journal of Psychology in the Orient, 43, 188–198.
Yamauchi, H., & Miki, K. (2003). Longitudinal analysis of the relations between perceived learning environment, achievement goal orientations, and learning strategies: Intrinsic-extrinsic regulation as a mediator. Psychologia: An International Journal of Psychology in the Orient, 46, 1–18. doi:10.2117/psysoc.2003.1.
Yan, L., & Kember, D. (2004). Avoider and engager approaches by out-of-class groups: The group equivalent to individual learning approaches. Learning and Instruction, 14, 27–49. doi:10.1016/j.learninstruc.2003.10.001.
Yonelinas, A. P., Kroll, N. E. A., Dobbins, I., Lazzara, M., & Knight, R. T. (1998). Recollection and familiarity deficits in amnesia: Convergence of remember know, process dissociation, and receiver operating characteristic data. Neuropsychology, 12, 323–339.
You, Z., & Jia, F. (2008). Do they learn differently? An investigation of the pre-service teachers from US and China. Teaching and Teacher Education, 24, 836–845.
Zhou, R., Hu, S., Sun, X., & Huang, J. (2006). Involuntary awareness and implicit priming: Role of retrieval context. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 103, 344–353. doi:10.2466/PMS.103.6.344-353.
Zimmerman, B. J., & Pons, M. M. (1986). Development of a structured interview for assessing student use of self-regulated learning strategies. American Educational Research Journal, 23, 614–628.
Acknowledgments
Special thanks to Allan Wigfield, Kathryn Wentzel, Peter Afflerbach, and Gregory Hancock for their comments and suggestions on earlier drafts of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dinsmore, D.L., Alexander, P.A. A Critical Discussion of Deep and Surface Processing: What It Means, How It Is Measured, the Role of Context, and Model Specification. Educ Psychol Rev 24, 499–567 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-012-9198-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-012-9198-7