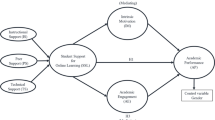
Abstract
In the last special issue devoted to this topic, Pintrich (Educ Psychol Rev 16:385–407, 2004) provided an in-depth critique of his conceptual framework on self-regulated learning (SRL), comparing and contrasting it to Biggs’ student approaches to learning (SAL) perspective. Since then, there have been a number of advances in the study of learning in higher education. To that end, the purpose of this article is to provide a critical analysis of three distinct yet overlapping streams of research in higher education, namely SRL, patterns of learning (including SAL), and student engagement. The theoretical bases of each of these approaches are outlined followed by a review of recent trends. Finally, an integrative model of student learning is proposed, which draws on the strengths of each of these traditions.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, P. A. (1997). Mapping the multidimensional nature of domain learning: The interplay of cognitive, motivational, and strategic forces. In M. L. Maehr & P. R. Pintrich (Eds.), Advances in motivation and achievement (Vol. 10, pp. 213–250). Greenwich: JAI Press.
Alexander, P. A. (2004). A model of domain learning: Reinterpreting expertise as a multidimensional, multistage process. In D. Dai & R. Sternberg (Eds.), Motivation, emotion, and cognition: Integrative perspectives on intellectual functioning and development (pp. 273–298). Mahwah: Erlbaum.
Astin, A. W. (1984). Student involvement: A developmental theory for higher education. Journal of College Student Personnel, 25, 297–308.
Azevedo, R., & Cromley, J. G. (2004). Does training on self-regulated learning facilitate students’ learning with hypermedia? Journal of Educational Psychology, 96, 523–535.
Baeten, M., Kyndt, E., Struyven, K., & Dochy, F. (2010). Using student-centered learning environments to stimulate deep approaches to learning: Factors encouraging or discouraging their effectiveness. Educational Research Review, 5(3), 243–260. doi:10.1016/j.edurev.2010.06.001.
Baeten, M., Struyven, K., & Dochy, F. (2013). Student-centred teaching methods: Can they optimse students’ approaches to learning in professional higher education? Studies in Educational Evaluation, 39, 14–22.
Ben-Eliyahu, A., & Bernacki, M. (2015). Addressing complexities in self-regulated learning: A focus on contextual factors, contingencies, and dynamic relations. Metacognition and Learning, 10, 1–13.
Bernacki, M. L., Nokes-Malach, T. J., & Aleven, V. (2015). Examining self-efficacy during learning: Variability and relations to behavior, performance, and learning. Metacognition and Learning, 10, 99–117. doi:10.1007/s11409-014-9127-x.
Biggs, J. B., & Australian Council for Educational Research (1987). Student Approaches to Learning and Studying. Research Monograph.
Biggs, J. B., Kember, D., & Leung, D. Y. (2001). The revised two-factor Study Process Questionnaire : R-SPQ-2F. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 71, 133–149.
Christenson, S., Reschly, A., & Wylie, C. (Eds.). (2012). Handbook of research on student engagement. New York: Springer.
Coates, H. (2007). A model of online and general campus-based student engagement. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 32(2), 121–141. doi:10.1080/02602930600801878.
Coates, H. (2010). Development of the Australasian Survey of Student Engagement (AUSSE). Higher Education: The International Journal of Higher Education and Educational Planning, 60(1), 1–17.
Coertjens, L., Vanhournout, G., Lindblom-Ylänne, S., & Postareff, L. (2016). Understanding individual differences in approaches to learning across courses: A mixed method approach. Learning and Individual Differences, 51, 69–80.
Corno, L. (1993). The best-laid plans: Modern conceptions of volition and educational research. Educational Researcher, 22, 14–22.
De Clercq, M. I., Galand, B., & Frenay, M. (2013). Chicken or the egg: Longitudinal analysis of the causal dilemma between goal orientation, self-regulation, and cognitive processing strategies in higher education. Studies in Educational Evaluation, 39, 4–13.
Dent, A. L., & Hoyle, R. H. (2015). A framework for evaluating and enhancing alignment in self-regulated learning research. Metacognition and Learning, 10, 165–179.
Dent, A. L., & Koenka, A. C. (2016). The relation between self-regulated learning and academic achievement across childhood and adolescence: A meta-analysis. Educational Psychology Review, 28, 425–474. doi:10.1007/s10648-015-9320-8.
Dinsmore, D. L., & Alexander, P. A. (2012). A critical discussion of deep and surface processing: What it means, how it is measured, the role of context, and model specification. Educational Psychology Review, 24, 499–567.
Donche, V., & Gijbels, D. (2013). Understanding learning pattern development in higher education: A matter of time, context, and measurement. Studies in Educational Evaluation, 39, 1–3.
Dörrenbächer, L., & Perels, F. (2016). Self-regulated learning profiles in college students: Their relationship to achievement, personality, and the effectiveness of an intervention to foster self-regulated learning. Learning and Individual Differences, 51, 229–241. doi:10.1016/j.lindif.2016.09.015.
Duncan, T. G., & McKeachie, W. J. (2005). The making of the motivated strategies for learning questionnaire. Educational Psychologist, 40(2), 117–128. doi:10.1207/s15326985ep4002_6.
Eccles, J. S., & Wang, M. T. (2012). So what is student engagement anyway: Commentary on Section I. In S. Christenson, A. L. Reschy, & C. Wylie (Eds.), Handbook of Research on Student Engagement. Springer.
Entwistle, N. J., & Ramsden, P. (1983). Understanding student learning. London: Croon Helm.
Entwistle, N., McCune, V., & Hounsell, J. (2003). Investigating ways of enhancing university teaching-learning environments: Measuring students’ approaches to studying and perceptions of teaching. In E. De Corte, L. Verschaffel, N. Entwistle, & J. van Merrienboer (Eds.), Powerful learning environments: Unravelling basic components and dimensions. (pp. 89-108). Elsevier Science Limited.
Flavell, J. H. (1979). Metacognition and cognitive monitoring. American Psychologist, 34, 906–911.
Fredricks, J. A., Blumenfeld, P. C., & Paris, A. (2004). School engagement: Potential of the concept, state of the evidence. Review of Educational Research, 74, 59–119. doi:10.3102/00346543074001059.
Fuller, M. B., Wilson, M. A., & Tobin, R. M. (2011). The National Survey of Student Engagement as a predictor of undergraduate GPA: A cross-sectional and longitudinal examination. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 36(6), 735–748. doi:10.1080/02602938.2010.488791.
Hadwin, A., & Järvelä, S. (2011). Social aspects of self-regulated learning: Where social and self meet in the strategic regulation of learning. Teachers College Record, 113(2), 235–239.
Hofer, B. K., & Pintrich, P. R. (1997). The development of epistemological theories: Beliefs about knowledge and knowing and their relation to learning. Review of Educational Research, 67, 88–140.
Kahu, E. R. (2013). Framing student engagement in higher education. Studies in Higher Education, 38, 758–773.
Karabenick, S. A., & Knapp, J. R. (1991). Relationship of academic help-seeking to the use of learning strategies and other instrumental achievement behavior in college students. Journal of Educational Psychology, 83, 221–230. doi:10.1037/0022-0663.83.2.221.
Karabenick, S. A., & Zusho, A. (2015). Examining approaches to research on self-regulated learning: conceptual and methodological considerations. Metacognition and Learning, 10, 151–163.
Khan, P. E. (2014). Theorising student engagement in higher education. British Educational Research Journal, 40, 1005–1018.
Kitsantas, A., Dabbagh, N., Hiller, S., & Mandell, B. (2015). Learning technologies as supportive contexts for promoting college student self-regulated learning. In T. Cleary (Ed.), Self-regulated learning interventions with at-risk youth: Enhancing availability, performance, and well-being. American Psychological Association.
Loyens, S. M. M., Gijbels, D., Coertiens, L., & Cote, D. J. (2013). Students’ approaches to leaning in problem-based learning: Taking into account professional behavior in the tutorial groups, self-study time, and different assessment aspects. Studies in Educational Evaluation, 39, 23–32.
Luo, Y. (2015). Learning ants: A portrait of Chinese college students in mass higher education. In J. C. Shin, G. A. Postiglione, & F. Huang (Eds.), Mass higher education development in East Asia: Strategy, quality, and challenges (pp. 177–188). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
Maehr, M. L., & Zusho, A. (2009). Achievement goal theory: The past, present, and future. In K. Wentzel & A. Wigfield (Eds.), Handbook of Motivation in School (pp. 77–104). NewYork: Routledge.
Marton, F., & Säljö, R. (1976). On qualitative differences in learning: I. Outcome and process. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 46, 4–11.
McCardle, L., & Hadwin, A. (2015). Using multiple, contextualized data sources to measure learners’ perceptions of their self-regulated learning. Metacognition and Learning, 10, 43–75.
McCormick, A. C., Kinzie, J., & Gonyea, R. M. (2013). Student engagement: Bridging research and practice to improve the quality of undergraduate education. In M. B. Paulsen (Ed.), Higher education: Handbook of theory and research, (Vol. 28, pp. 47-92). Dordrecht: Springer.
Muis, K. R., & Franco, G. M. (2009). Epistemic beliefs: Setting the standards for self-regulated learning. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 34(4), 306–318. doi:10.1016/j.cedpsych.2009.06.005.
Muis, K. R., Pekrun, R., Sinatra, G. M., Azevedo, R., Trevors, G., Meier, E., & Heddy, B. C. (2015). The curious case of climate change: Testing a theoretical model of epistemic beliefs, epistemic emotions, and complex learning. Learning and Instruction, 39, 168–183. doi:10.1016/j.learninstruc.2015.06.003.
NSSE - National Survey of Student Engagement (n.d.). Retrieved September 17, 2016, from http://nsse.indiana.edu/. Accessed 17 Sept 2016.
Pace, C. R. (1980). Measuring the quality of student effort. Current Issues in Higher Education, 2, 10–16.
Pace, C. R. (1998). Recollections and reflections. In J. C. Smart (Ed.), Higher education: Handbook of theory and research (Vol. 13, pp. 1–34). New York: Agathon.
Pask, G. (1976). Styles and strategies of learning. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 46, 128–148.
Pintrich, P. R. (2000). The role of goal orientation in self-regulated learning. In M. Boekaerts, P. Pintrich, & M. Zeidner (Eds.), Handbook of Self-regulation (pp. 451–502). San Diego: Academic Press.
Pintrich, P. R. (2004). A conceptual framework for assessing motivation and self-regulated learning in college students. Educational Psychology Review, 16, 385–407.
Pintrich, P. R., & De Groot, E. V. (1990). Motivational and self-regulated learning components of classroom academic performance. Journal of Educational Psychology, 82, 33–40.
Pintrich, P. R., & Zusho, A. (2007). Motivation and self-regulated learning in the college classroom. In R. Perry & J. Smart (Eds.), Handbook on Teaching and Learning in Higher Education. Dordrecht: Springer Publishers.
Richardson, J. T. E. (2013). Research issues in evaluating learning pattern development in higher education. Studies in Educational Evaluation, 39, 66–70.
Richardson, M., Abraham, C., & Bond, R. (2012). Psychological correlates of university students’ academic performance: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychological Bulletin, 138(2), 353–387. doi:10.1037/a0026838.
Schoor, C., Narciss, S., & Körndle, H. (2015). Regulation during cooperative and collaborative learning: A theory-based review of terms and concepts. Educational Psychologist, 50, 97–119. doi:10.1080/00461520.2015.1038540.
Schunk, D. H., & Zimmerman, B. J. (2008). Motivation and self-regulated learning: Theory, research, and applications. New York: Taylor & Francis.
Tinto, V. (1987). Leaving College: Rethinking the Causes and Cures of Student Attrition. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Tinto, V. (1993). Leaving College: Rethinking the Causes and Cures of Student Attrition (2nd ed.). Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Turner, J. C. (2014). Theory-based interventions with middle-school teachers to support student motivation and engagement. In S. Karabenick & T. Urdan (Eds)., Motivational Interventions: Advances in Motivation and Achievement (Volume 18, pp. 341-378). Emerald Group Publishing Limited. doi:10.1108/S0749-742320140000018009.
Veenman, M. V. J. (2011). Alternative assessment of strategy use with self-report: A discussion. Metacognition and Learning, 6, 205–211. doi:10.1007/s11409-011-9080-x.
Vermetten, Y. J., Lodewijks, H. G., & Vermunt, J. D. (2001). The role of personality traits and goal orientations in strategy use. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 26(2), 149–170. doi:10.1006/ceps.1999.1042.
Vermunt, J. D. (1996). Metacognitive, Cognitive, and Affective Aspects of Learning Styles and Strategies: A Phenomenographic Analysis. Higher Education, 31(1), 25–50.
Vermunt, J. D., & Vermetten, Y. J. (2004). Patterns in student learning: Relationships between learning strategies, conceptions of learning, and learning orientations. Educational Psychology Review, 16(4), 359–384.
Winne, P. H., & Baker, R. (2013). The potentials of educational data mining for researching metacognition, motivation, and self-regulated learning. Journal of Educational Data Mining, 5, 1–8.
Winne, P. H., & Hadwin, A. F. (1998). Studying as self-regulated learning. In D. J. Hacker, J. Dunlosky, & A. C. Graesser (Eds.), Metacognition in educational theory and practice (pp. 277–304). Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc..
Winne, P.H., & Perry, N. E (2000). In M. Boekarts, P Pintrich, & M. Zeidner (Eds.), Handbook of Self-regulation (pp. 531-566). San Diego, CA: Academic Press.
Wolters, C. (1998). Self-regulated learning and college students’ regulation of motivation. Journal of Educational Psychology, 90, 224–235.
Wolters, C. A., & Benzon, M. B. (2013). Assessing and predicting college students’ use of strategies for the self-regulation of motivation. Journal of Experimental Education, 81(2), 199–221. doi:10.1080/00220973.2012.699901.
Wolters, C. A., & Hussain, M. (2015). Invesigating grit and its relations with college students’ self-regulated learning and academic achievement. Metacognition and Learning, 10, 292–311.
Wolters, C. A., & Taylor, D. J. (2012). A self-regulated learning perspective on student engagement. In S. Christenson, A. Reschly, & C. Wylie (Eds.), Handbook of research on student engagement. New York: Springer.
Zepke, N. (2014). Student engagement research in higher education: Questioning an academic orthodoxy. Teaching in Higher Education, 19, 697–708. doi:10.1080/13562517.2014.901956.
Zimmerman, B. J. (2008). Investigating Self-Regulation and Motivation: Historical Background, Methodological Developments, and Future Prospects. American Educational Research Journal, 45(1), 166–183. doi:10.3102/0002831207312909.
Zimmerman, B. J., & Martinez-Pons, M. (1986). Development of a structured interview for assessing student use of self-regulated learning strategies. American Educational Research Journal, 23, 614–628.
Zimmerman, B. J., & Schunk, D. H. (2001). Self-regulated learning and academic achievement: Theoretical perspectives. Mahwah: Erlbaum.
Zimmerman, B. J., & Schunk, D. H. (2011). Handbook of self-regulation of learning and performance. New York: Routledge.
Zusho, A., & Edwards, K. (2011). Self-regulation and achievement goals in the college classroom. New Directions in Teaching and Learning, 126, 21–31.
Zusho, A., Pintrich, P. R., & Coppola, B. (2003). Skill and will: The role of motivation and cognition in the learning of college chemistry. International Journal of Science Education, 25, 1081–1094.
Zusho, A., Karabenick, S. A., Bonney, C. R., & Sims, B. R. (2007). Contextual determinants of motivation and help seeking in the college classroom. In R. Perry & J. Smart (Eds.), The scholarship of teaching and learning in higher education: An evidence-based perspective (pp. 611–659). Dordrecht: Springer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
not applicable.
Conflict of interest
I declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zusho, A. Toward an Integrated Model of Student Learning in the College Classroom. Educ Psychol Rev 29, 301–324 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-017-9408-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-017-9408-4