Abstract
Air pollution monitoring programs aim to monitor pollutants and their probable adverse effects at various locations over concerned area. Either sensitivity of receptors/location or concentration of pollutants is used for prioritizing the monitoring locations. The exposure-based approach prioritizes the monitoring locations based on population density and/or location sensitivity. The hazard-based approach prioritizes the monitoring locations using intensity (concentrations) of air pollutants at various locations. Exposure and hazard-based approaches focus on frequency (probability of occurrence) and potential hazard (consequence of damage), respectively. Adverse effects should be measured only if receptors are exposed to these air pollutants. The existing methods of monitoring location prioritization do not consider both factors (hazard and exposure) at a time. Towards this, a risk-based approach has been proposed which combines both factors: exposure frequency (probability of occurrence/exposure) and potential hazard (consequence).
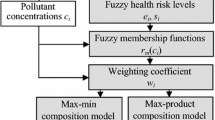
This paper discusses the use of fuzzy synthetic evaluation technique in risk computation and prioritization of air pollution monitoring locations. To demonstrate the application, common air pollutants like CO, NO x , PM10 and SO x are used as hazard parameters. Fuzzy evaluation matrices for hazard parameters are established for different locations in the area. Similarly, fuzzy evaluation matrices for exposure parameters: population density, location and population sensitivity are also developed. Subsequently, fuzzy risk is determined at these locations using fuzzy compositional rules. Finally, these locations are prioritized based on defuzzified risk (crisp value of risk, defined as risk score) and the five most important monitoring locations are identified (out of 35 potential locations). These locations differ from the existing monitoring locations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bates, D. V.: 1992, ‘Health indices of the adverse effects of air pollution: The question of coherence’, Environ. Res. 59, 336–349.
Baldauf, R. W., Lane, D. D., Marotz, G. A., Barkman, H. W. and Pierce, T.: 2002, ‘Application of a risk assessment based approach to designing ambient air quality monitoring networks for revaluating non-cancer health impacts’, Environ. Monit. Assess. 78, 213–227.
Baldauf, R. W., Lane, D. D. and Marotz, G. A.: 2001, ‘Ambient air quality monitoring network design for assessing human health impacts from exposure to air borne contaminants’, Environ. Monit. Assess. 66, 63–76.
Bonissone, P. P.: 1997, ‘Soft computing: The convergence of emerging reasoning technologies’, Soft Comput. 1, 6–18.
Burnett, R. T., Dales, R. E., Brook, J. R., Raizenne, M. E. and Krewski, D.: 1997, ‘Association between ambient carbon monoxide levels and hospitalization for congestive heart failure in the elderly in 10 Canadian cities’, Epidemiology 8, 162–167.
Chen, S. J. and Hwang, C. L.: 1992, Fuzzy Multiple Attribute Decision-Making, Springer-Verlag, NY.
Cheng, C.-H. and Lin, Y.: 2002, ‘Evaluating the best main battle tank using fuzzy decision theory with linguistic criteria evaluation’, Eur. J. Oper. Res. 142, 174–186.
Goldberg, A. S., Burnett, R. T., Valois, M. F., Flegel, K., Bailer III, J. C., Brook, J., Vincent, R. and Radon, K.: 2003, ‘Association between ambient air pollution and daily mortality among persons with congestive heart failure’, Environ. Res. 91, 8–20.
Harrison, R. M. and Deacon, A. R.: 1998, ‘Spatial correlation of automatic air quality monitoring at urban background sites: Implications for network design’, Environ. Technol. 19, 121–132.
Khan, F. I., Sadiq, R. and Husain, T.: 2002, ‘GreenPro-I: A risk-based life cycle assessment and decision-making methodology for process plant design’, Environ. Model. Software 17, 669–692.
Kwon, H.-J., Cho, S.-H., Nyberg, P. and Pershagen, G.: 2001, ‘Effects of ambient air pollution on daily mortality in a cohort of patients with congestive heart failure’, Epidemiology 12, 413–419.
Klir, G. J. and Yuan, B.: 1995, Fuzzy Sets and Fuzzy Logic - Theory and Applications, Prentice-Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA.
Lascio, L. D., Gisolfi, A., Albunia, A., Galardi, G. and Moschi, F.: 2002, ‘A fuzzy-based methodology for the analysis of diabetic neuropathy’, Fuzzy Sets Syst. 129, 203–228.
Lowrence, W. W.: 1976, Of Acceptable Risk, William Kaufmann, Los Altos, CA.
Lawry, J.: 2001, ‘A methodology for computing with words’, Int. J. Approx. Reason. 28, 51–89.
Lee, C. C.: 1990a, ‘Fuzzy logic in control systems: Fuzzy logic controller – I’, IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 20(2), 404–418.
Lee, C. C.: 1990b, ‘Fuzzy logic in control systems: Fuzzy logic controller – II’, IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 20(2), 419–435.
Lee, H.-M.: 1996, ‘Applying fuzzy set theory to evaluate the rate of aggregative risk in software development’, Fuzzy Sets Syst. 79, 323–336.
Lu, R.-S. and Hu, J.-Y.: 1999, ‘Analysis of reservoir water quality using fuzzy synthetic evaluation’, Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 13, 327–336.
Lu, R.-S. and Lo, S.-L.: 2002, ‘Diagnosing reservoir water quality using self-organizing maps and fuzzy theory’, Water Res. 36, 2265–2274.
Ott, W. R.: 1978, Environmental Indices: Theory and Practice, Ann Arbor Science Publishers Inc., pp. 371.
Morris, R. D., Naumova, E. N.: 1998, ‘Carbon monoxide and hospital admissions for congestive heart failure: Evidence of an increased effect at low temperatures’, Environ. Health Perspect. 106, 649–653.
Ricci, P. F., Sagen, L. A. and Whipple, C. G.: 1981, Technological risk assessment series E: Applied Series No. 81.
Rowe, N.: 1977, Risk: An Anatomy of Risk, John Wiley and Sons, NY.
Saaty, T. L.: 1988, Multicriteria Decision-Making: The Analytic Hierarchy Process, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA, USA.
Sadiq, R. and Rodriguez, M. J.: 2004, ‘Fuzzy synthetic evaluation of disinfection by-products – a risk-based indexing system’, J. Environ. Manage. 73(1), 1–13.
Sadiq, R., Kleiner, Y. and Rajani, B. B.: 2004, ‘Aggregative risk analysis for water quality failure in distribution networks’, Aqua-Journal Water Supply: Res. Technol. 53(4), 41–61.
Sadiq, R., Rajani, B. and Kleiner, Y.: in press, ‘A fuzzy-based method to evaluate soil corrosivity for prediction of water main deterioration, ASCE’, J. Infrastruct. Syst.
Seaton, A., MacNee, W., Donaldson, K. and Godden, D.: 1995, ‘Particulate air pollution and acute health effect’, Lancet 345, 176–178.
Silvert, W.: 2000, ‘Fuzzy indices of environmental conditions’, Ecol. Model. 130(1–3), 111–119.
Somlikova, R. and Wachowiak, M. P.: 2001, ‘Aggregation operators for selection problems’, Fuzzy Sets Syst. 131, 23–34.
United States Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA): 1998, Revised Draft User’s Guide for the AMS/EPA Regulatory Model (AERMOD), Pacific Environmental Services Inc., Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, USA, p. 324.
Yager, R. R.: 1980, ‘A general class of fuzzy connectives’, Fuzzy Sets Syst. 4, 235–242.
Zadeh, L. A.: 1996, ‘Fuzzy logic computing with words’, IEEE Trans. – Fuzzy Syst. 4(2), 103–111.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, F.I., Sadiq, R. Risk-Based Prioritization of Air Pollution Monitoring Using Fuzzy Synthetic Evaluation Technique. Environ Monit Assess 105, 261–283 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-005-3852-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-005-3852-1