Abstract
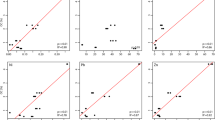
Correlation analyses between measures of toxicity and concentrations of chemical contaminants were conducted for 103 surficial sediments from Sydney Harbour, Australia, and vicinity. Toxicity tests consisted of amphipod survival and reburial tests of whole sediments (Corophium colo), sea urchin fertilisation and larval development tests of pore waters (Heliocidaris tuberculata) and microbial bioluminescence (Microtox®) tests of solvent extracts and pore waters. Toxicity in most tests correlated with concentrations of metallic contaminants, in particular, zinc, lead and copper. Organic contaminants did not correlate as significantly with toxicity. However, Heliocidaris tuberculata showed relationships with organochlorine compounds in samples with low to moderate metals contamination. Toxicity in the Microtox® solvent extract test appeared to be primarily influenced by the presence of sulfur. This study has no precedent in Australia and the results support the validity of using local indigenous species in toxicity tests of field-collected sediments. This toxicity/chemistry dataset may be used in evaluations of sediment quality guidelines recently introduced to Australia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, H. E., Fu, G. and Deng, B.: 1993, ‘Analysis of acid-volatile sulfide (AVS) and simultaneously extracted metals (SEM) for the estimation of potential toxicity in aquatic sediments’, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 12, 1441–1453.
ANZECC and ARMCANZ: 2000, Australian and New Zealand Guidelines for Fresh and Marine Water Quality, Vol. 1, Section 3.5 – Sediment Quality Guidelines, Australian and New Zealand Environment and Conservation Council, and Agriculture and Resource Management Council of Australia and New Zealand. Canberra, Australia.
ASTM: 1998a, ‘Standard guide for collection, storage, characterization and manipulation of sediments for toxicological testing’, E 1391-94, in 1998 Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol. 11.05, ASTM, Philadelphia, PA, U.S.A., pp. 768–788.
ASTM: 1998b, ‘Standard guide for conducting 10-day static sediment toxicity tests with marine and estuarine amphipods’, E 1367 – 92, in 1998 Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol. 11.05, ASTM, Philadelphia, PA, U.S.A., pp.732–757.
AZUR: 1995a, Microtox ® Acute Toxicity Basic Test Procedures, AZUR Environmental, Carlsbad, CA, U.S.A., 63pp.
AZUR: 1995b, Microtox ® Acute Toxicity Comparison & Inhibition Test for Fresh Water and Marine Samples, AZUR Environmental, Carlsbad, CA, U.S.A., p. 29.
Carr, R. S. and Chapman, D. C.: 1995, ‘Comparison of methods for conducting marine and estuarine sediment pore water toxicity tests - Extraction, storage, and handling techniques’, Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 28, 69–77.
Carr, R. S., Long, E. R., Windom, H. L., Chapman, D. C., Thursby, G., Sloane, G. M. and Wolfe, D. A.: 1996, ‘Sediment quality assessment studies of Tampa Bay, Florida’, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 15, 1218–1231.
Di Toro, D. M., Mahony, D. J., Hansen, D. J., Scott, K. B., Hicks, M. B., Mayr, S. M. and Redmond, M. S.: 1990, ‘Toxicity of cadmium in sediments: The role of acid-volatile sulfide’, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 9, 1487–1502.
Fairey, R., Long, E. R., Roberts, C. A., Anderson, B. S., Phillips, B. M., Hunt, J. W., Puckett, H. R. and Wilson, C. G.: 2001, ‘An evaluation of methods for calculating mean sediment quality guideline quotients as indicators of contamination and acute toxicity to amphipods by chemical mixtures’, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 20, 2276–2286.
Fairey, R., Roberts, C., Jacobi, M., Lamerdin, S., Clark, R., Downing, J., Long, E., Hunt, J., Anderson, B., Newman, J., Tjeerdema, R., Stephenson, M. and Wilson, C.: 1998, ‘Assessment of sediment toxicity and chemical concentrations in the San Diego Bay region, California, USA’, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 17, 1570–1581.
Ginn, T. C. and Pastorok, R. A.: 1992, ‘Assessment and management of contaminated sediments in Puget Sound’, in: Burton Jr., G. A. (ed.), Sediment Toxicity Assessment, Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, FL, USA, pp. 371–401.
Hansen, D. J., Berry, W. J., Mahony, J. D., Boothman, W. S., Di Toro, D. M., Robson, D. L., Ankley, G. T., Ma, D., Yan, Q. and Pesch, C. E.: 1996, ‘Predicting the toxicity of metal-contaminated field sediments using interstitial concentration of metals and acid-volatile sulfide normalizations’, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 15, 2080–2094.
Hyne, R. V. and Everett, D. A.: 1998, ‘Application of a benthic euryhaline amphipod, Corophium sp., as a sediment toxicity testing organism for both freshwater and estuarine systems’, Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 34, 26–33.
Jacobs, M. W., Delfino, J. J. and Bitton, G.: 1992, ‘The toxicity of sulfur to Microtox® from acetonitrile extracts of contaminated sediments’, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 11, 1137–1143.
Johnson, B. T. and Long, E. R.: 1998, ‘Rapid toxicity assessment of sediments from estuarine ecosystems: A new tandem in vitro testing approach’, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 17, 1099–1106.
Kohn, N. P., Word, J. Q., Niyogi, D. K., Ross, L. T., Dillon, T. and Moore, D. W.: 1994, ‘Acute toxicity of ammonia to four species of marine amphipod’, Mar. Environ. Res. 38, 1–15.
Long, E. R. and MacDonald, D. D.: 1998, ‘Recommended uses of empirically derived sediment quality guidelines for marine and estuarine ecosystems’, Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 4, 1019–1039.
Long, E. R. and Morgan, L. G.: 1990, ‘The potential for biological effects of sediment-sorbed contaminants tested in the National Status and Trends Program’, NOAA Technical Memorandum NOS OMA 52, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Seattle, Washington, U.S.A., p. 175.
Long, E. R.: 2000, ‘Spatial extent of sediment toxicity in U.S. estuaries and marine bays’, Environ. Monit. Assess. 64, 391–407.
Long, E. R., Field, L. J. and MacDonald, D. D.: 1998, ‘Predicting toxicity in marine sediments with numerical sediment quality guidelines’, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 17, 714–727.
Long, E. R., Hameedi, M. J., Sloane, G. M. and Read, L.: 2001, ‘Chemical contamination, toxicity, and benthic community indices in sediments of the lower Miami River and adjoining portions of Biscayne Bay, Florida’, NOAA Technical Memorandum, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Seattle, Washington, U.S.A.
Long, E. R., Robertson, A., Wolfe, D. A., Hameedi, J. and Sloane, G. M.: 1996b, ‘Estimates of the spatial extent of sediment toxicity in major US estuaries’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 30, 3585–3592.
Long, E. R., Sloane, G. M., Carr, R. S., Johnson, T., Biedenbach, J., Scott, K. J., Thursby, G. B., Crecelius, E., Peven, C., Windom, H. L., Smith, R. D. and Loganathon, B.: 1997, ‘Magnitude and extent of sediment toxicity in four bays of the Florida Panhandle: Pensacola, Choctawhatchee, St. Andrew and Apalachicola’, NOAA Technical Memorandum NOS ORCA 117, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Silver Spring, MD, U.S.A., p. 219.
Long, E. R., Sloane, G. M., Carr, R. S., Scott, K. J., Thursby, G. B. and Wade, T. L.: 1996a, ‘Sediment toxicity in Boston Harbor: Magnitude, extent, and relationships with chemical toxicants’, NOAA Technical Memorandum NOS ORCA 96, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Silver Spring, MD, U.S.A., p. 133.
Long, E. R., MacDonald, D. D., Smith, S. L. and Calder, F. D.: 1995, ‘Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments’, Environ. Manag. 19, 81–97.
MacDonald, D. D., Carr, R. S., Calder, F. D., Long, E. R. and Ingersoll, C. G.: 1996, ‘Development and evaluation of sediment quality guidelines for Florida coastal waters’, Ecotoxicol 5, 253–278.
MacDonald, D. D., DiPinto, L. M., Field, J., Ingersoll, C. G., Long, E. R. and Swartz, R. C.: 2000, ‘Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment effect concentrations for polychorinated biphenyls’, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 19, 1403–1413.
McCready S.: 2004, ‘Evaluation of sediment quality guidelines for application in Australia’, PhD Thesis, University of Sydney, NSW, Australia.
McCready, S., Birch, G. F. and Taylor, S. E.: 2003, ‘Extraction of heavy metals in Sydney Harbour sediments using 1 M HCl and 0.05M EDTA and implications for sediment-quality guidelines’, Austr. J. Earth Sci. 50, 249–255.
McCready, S., Slee, D. J., Birch, G. F. and Taylor, S. E.: 2000, ‘The distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surficial sediments of Sydney Harbour, Australia’, Mar. Pollut. Bull. 40, 999–1006.
McCready, S., Spyrakis, G., Greely, C. R., Birch, G. F. and Long, E. R.: 2004, ‘Toxicity of surficial sediments from Sydney Harbour and vicinity, Australia’, Environ. Monit. Assess. 96, 53–83.
McCready, S., Greely, C. R., Hyne, R. V., Birch, G. F. and Long, E. R.: 2005, ‘Sensitivity of an indigenous amphipod, Corophium colo, to chemical contaminants in laboratory toxicity tests conducted with sediments from Sydney Harbour, Australia, and vicinity, Accepted,’ Environ Toxicol Chem. 24.
Pardos, M., Benninghoff, C., Thomas, R. L. and Khim-Heang, S.: 1999, ‘Confirmation of elemental sulfur toxicity in the Microtox® assay during organic extracts assessment of freshwater sediments’, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 18, 188–193.
Salizatto, M., Bertato, V., Pavoni, B., Ghirardini, A. V. and Ghetti, P. F.: 1998, ‘Sensitivity limits and EC50 values of the Vibrio fischeri test for organic micropollutants in natural and spiked extracts from sediments’, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 17, 655–661.
Simon, J. and Laginestra, E.: 1997, ‘Bioassay for testing sublethal toxicity in effluents, using gametes of sea urchin Heliocidaris tuberculata’, National Pulp Mills Research Program Technical Report No. 20, Canberra: CSIRO, Australia, p. 36
Sokal, R. R. and Rohlf, F. J.: 1981, Biometry, 2nd ed. W.H. Freeman, San Francisco, CA, U.S.A.
Spyrakis, G.: 2002, ‘Assessment of the predictive ability of sediment quality guidelines using sea urchin toxicity tests’, M.Sc. Thesis, University of Sydney, NSW, Australia.
Swartz, R. C.: 1999, ‘Concensus sediment quality guidelines for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon mixtures’, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 18, 780–787.
Thompson, B., Anderson, B., Hunt, J., Taberski, K. and Phillips B.: 1999, ‘Relationships between sediment contamination and toxicity in San Francisco Bay’, Mar. Environ. Res. 48, 285–309.
Thursby, G. B., Heltshe, J. and Scott, K. J.: 1997, ‘Revised approach to toxicity test acceptability criteria using a statistical performance assessment’, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 16, 1322–1329.
US EPA: 2000, Test Methods for Evaluating Solid Wastes, Physical/Chemical Methods (SW-846), CD ROM ver 2.0, US EPA and US Dept. of Commerce National Technical Information Service.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McCready, S., Birch, G.F., Long, E.R. et al. Relationships Between Toxicity and Concentrations of Chemical Contaminants in Sediments from Sydney Harbour, Australia, and Vicinity. Environ Monit Assess 120, 187–220 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-005-9057-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-005-9057-9