Abstract
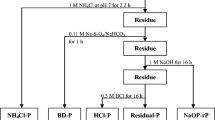
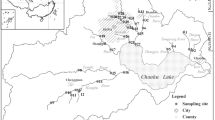
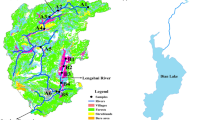
Phosphorus fractions and phosphate adsorption characteristics of 16 sediments from a shallow freshwater lake (Nansi Lake, China) and its inflow estuaries were investigated. In the present study, the sediment phosphorus is fractionated into exchangeable P (exch-P), Al–P, Fe–P, Ca–P, organic P (OP), inorganic P (IP) and total P (TP). The results show that the total phosphorus (TP) content in the sediments ranges from 571.67 to 1,113.55 mg kg−1, and calcium bound phosphorus (Ca–P) is the main fraction of IP. The biologically available phosphorus (BAP) ranges from 32.02 to 229.67 mg kg−1 in the Nansi Lake sediments. Phosphate adsorption on the sediments mainly occurs within 10 h and is completed within 48 h. The content of native adsorbed phosphorus (ωNAP) varies greatly from 6.05 to 194.37 mg kg−1, showing a significant correlation with the total maximal amount of phosphorus adsorbed (TQmax). Adsorption efficiency (m) ranges from 574.79 to 3,220.68 l kg−1 and zero equilibrium phosphorus concentration (CEPC) ranges from 0.010 to 0.157 mg l−1. After the South-to-North Water Diversion Project, the inherent phosphorus present in sediments will be a major threat to the diverted water quality and be a predominant factor determining the trophic status of the lake even if the external load is reduced.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aminot, A., & Andrieux, F. (1996). Concept and determination of exchangeable phosphate in aquatic sediments. Water Research, 30(11), 2805–2811.
Andrieux, F., & Aminot, A. (1997). A two-year survey of phosphorus speciation in the sediments of the Bay of Seine (France). Journal of Continental Shelf Research, 17(10), 1229–1245.
Anshumali & Ramanathan, A. L. (2007). Phosphorus fractionation in surficial sediments of Pandoh Lake, Lesser Himalaya, Himachal Pradesh, India. Applied Geochemistry, 22, 1860–1871.
APHA, AWWA, & WPCF (1998). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (19th ed.). Washington, DC: APHA, AWWA, & WPCF.
Carman, R., & Wulff, F. (1989). Adsorption capacity of phosphorus in Baltic Sea sediments. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 29(5), 447–456.
China EPA (2002). China surface water quality standard (GB3838–2002). Beijing: China EPA.
Christos, Z. K., Dimosthenis, L. G., Ioannis, D. L., & Miltiades, I. K. (2007). Speciation of phosphorus fraction in river sediments by explanatory data analysis. Water Research, 41, 406–418.
Gao, L., Zhou, J. M. M., Yang, H., & Chen, J. (2005). Phosphorus fractions in sediment profiles and their potential contributions to eutrophication in Dianchi Lake. Environmental Geology, 48, 835–844.
Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences (ISSCAS) (1978). Soil physics chemical analysis. Shanghai: Basic Books.
Jensen, H. S., & Andersen, P. O. (1992). Importance of temperature, nitrate and pH for phosphate release from aerobic sediments of four shallow, eutrophic lakes. Limnology and Oceanography, 37(3), 577–589.
Jia, H., Yan, Y. Z., Lü, J. M., & Dong, X. M. (2005). Countermeasure on ecological environmental protection in Nansihu. YunNan Environmental Science, 24(Supplement), 66–69.
Jin, X. C., Wang, S. R., Zhao, H. C., Zhou, X. N., & Chu, J. Z. (2004). Study on the phosphate sorption of the different particle size fractions in the sediments from Wuli Lake and Gonghu Lake. Research of Environmental Sciences, 17(Supplement), 6–10.
Jin, X. C., Wang, S. R., Pang, Y., Zhao, H. C., & Zhou, X. N. (2005). The adsorption of phosphate on different trophic lake sediments. Colloids and Surfaces A, 254, 241–248.
Kaiserli, A., Voutsa, D., & Samara, C. (2002). Phosphorus fractionation in lake sediments—Lake Volvi and Koronia, N. Greece. Chemosphere, 46, 1147–1155.
Kim, L. H., Choi, E., & Stenstorm, M. K. (2003). Sediment characteristics, phosphorus types and phosphorus release rates between river and lake sediments. Chemosphere, 50, 53–61.
Li, B. G., & Guo, B. S. (2006). Chemical forms of inorganic phosphorus in sediments in the middle of the Yellow River. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 25(6), 1607–1610.
Liu, M., Hou, L. J., Xu, S. Y., Ou, D. N., Zhang, B. L., Liu, Q. M., & Yang, Y. (2002). Phosphate adsorption characteristics of Tidal Flat surface sediments and its environmental effect from the Yangtze estuary. Acta Geographica Sinica, 57(4), 397–406.
Liu, L. Y., Gao, X. J., Chen, Z. M., & Song, Z. G. (2005). Distribution and forms of phosphorus in intertidal sediments of the Yangtze estuary. Journal of Fudan University (Natural Science), 44(6), 1033–1036.
Lopez, P., Lluch, X., Vidal, M., & Morgui, J. A. (1996). Adsorption of phosphorus on sediments of the Balearic Islands (Spain) related to their compositon. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 42, 185–196.
Peng, J. F., Wang, B. Z., Song, Y. H., Yuan, P., & Liu, Z. H. (2007). Adsorption and release of phosphorus in the surface sediment of a wastewater stabilization pond. Ecological Engineering, 31, 92–97.
Smith, D. R., Warnemuende, E. A., Haggard, B. E., & Huang, C. (2006). Changes in sediment-water column phosphorus interactions following sediment disturbance. Ecological Engineering, 27, 71–78.
Tallberg, P., Tréguer, P., Beucher, C., & Corvaisier, R. (2008). Potentially mobile pools of phosphorus and silicon in sediment from the Bay of Brest: Interactions and implications for phosphorus dynamics. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 76, 85–94.
Tian, J. R., & Zhou, P. J. (2007). Phosphorus fractions of floodplain sediments and phosphorus exchange on the sediment-water interface in the lower reaches of the Han River in China. Ecological Engineering, 30, 264–270.
Vicente de, I., Cattaneo, K., Cruz-Pizarro, L., Brauer, A., & Guilizzoni, P. (2006). Sedimentary phosphate fractions related to calcite precipitation in an eutrophic hardwater lake (Lake Alserio, northern Italy). Journal of Paleolimnol, 35, 55–64.
Wang, S. R., Jin, X. C., Pang, Y., Zhao, H. C., Zhou, X. N., & Wu, F. C. (2005a). Phosphorus fractions and phosphate sorption characteristics in relation to the sediment compositons of shallow lakes in the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River region, China. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 289, 339–346.
Wang, S. R., Jin, X. C., Zhao, H. C., Zhou, X. N., & Chu, J. Z. (2005b). Phosphate adsorption characteristics onto the sediments from shallow lakes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze river. Environmental Science, 26(3), 39–43.
Wang, Y. C., Wan, G. J., Wang, S. L., Li, S. H., & Huang, R. G. (2000). Forms of phosphorus in sediments of Lake Baihua and Lake Hongfeng, Guizhou. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 20(3), 273–278.
Yang, L. Y., Shen, J., Zhang, Z. L., Sun, Q. Y., & Zhu, Y. X. (2003a). Distribution and ecological risk assessment for heavy metals in superficial sediments of Nansihu Lake. Journal of Lake Science, 15(3), 252–256.
Yang, L. Y., Shen, J., Zhang, Z. L., Zhu, Y. X., & Sun, Q. Y. (2003b) Multivariate analysis of heavy metal and nutrient in surface sediments of Nansihu Lake. China Environmental Science, 23(2), 206–209.
Zhang, L., Fan, C. X., Chi, Q. Q., Wang, J. J., & Qin, B. Q. (2004). Phosphorus species distribution of sediments in Lake Taihu and its main inflow rivers. Geochemistry, 33, 423–432.
Zhang, T. X., Wang, X. R., & Jin, X. C. (2007). Variations of alkaline phosphatase activity and P fractions in sediments of a shallow Chinese eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu). Environmental Pollution, 150, 288–294.
Zhou, Q., Gibson, C. E., & Zhu, Y. (2001). Evaluation of phosphorus bioavailability in sediments of three contrasting lakes in China and the UK. Chemosphere, 42(2), 221–225.
Zhou, A. M., Tang, H. X., & Wang, D. S. (2005). Phosphorus adsorption on natural sediments: Modeling and effects of pH and sediment composition. Water Research, 39, 1245–1254.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
An, W.C., Li, X.M. Phosphate adsorption characteristics at the sediment–water interface and phosphorus fractions in Nansi Lake, China, and its main inflow rivers. Environ Monit Assess 148, 173–184 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-0149-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-0149-6