Abstract
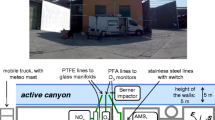
Titanium dioxide is the most important photocatalysts used for purifying applications. If a TiO2- containing material is left outdoors as a form of flat panels, it is activated by sunlight to remove harmful NOx gases during the day. The photocatalytic efficiency of a TiO2-treated mortar for removal of NOx was investigated in the frame of this work. For this purpose a fully equipped monitoring system was designed at a pilot site. This system allows the in situ evaluation of the de-polluting properties of a photocatalytic material by taking into account the climatologic phenomena in street canyons, accurate measurements of pollution level and full registration of meteorological data The pilot site involved three artificial canyon streets, a pollution source, continuous NOx measurements inside the canyons and the source as well as background and meteorological measurements. Significant differences on the NOx concentration level were observed between the TiO2 treated and the reference canyon. NOx values in TiO2 canyon were 36.7 to 82.0% lower than the ones observed in the reference one. Data arising from this study could be used to assess the impact of the photocatalytic material on the purification of the urban environment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrios, A. G., & Pichat, P. (2005). An overview of the state of the art and perspectives on materials and applications of photocatalysis over TiO2. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 35, 655–663.
Ao, C. H., Lee, S. C., Mak, C. L., & Chan, L. Y. (2003). Photodegradation of VOCs and NO for indoor purification using TiO2: promotion versus inhibition effect of NO. Applied Catalysis B, Environmental, 42, 119–129.
Blake, D. M. (2001). Bibliography of work on the heterogeneous photocatalytic removal of hazardous compounds from water and air. National Renewable Energy Laboratory, from http://www.osti.gov/bridge.
Dalton, J. S., Janes, P. A., Jones, N. G., Nicholson, J. A., Hallam, K. R., & Allen, G. C. (2002). Photocatalytic oxidation of Nox gases using TiO2: A surface spectroscopic approach. Environmental Pollution, 120, 415–422.
Fujishima, A., Hashimoto, K., & Watanabe, T. (1999). TiO 2 photocatalysis: Fundamentals and applications. Japan: BKC, Inc.
Ibrahim, H., & Lasa, H. (2002). Photocatalytic conversion of air borne pollutants effect of catalyst type loading in a novel photo-CREC-air unit. Applied Catalysis. B, Environmental, 38, 201–213.
Kaneko, M., & Okura, I. (2002). Photocatalysis science and technology. In Cleaning Atmospheric Environment (pp. 123–155). Tokyo: Kodansha.
Lewandowski, M., & Ollis, D. F. (2004). Photocatalytic oxidation of gas phase aromatic pollutants. In V. Ramamurthy, K. S. Schanze (Eds.), Seminoconductor photochemistry and photophysics (pp. 249–282). New York: Marcel Dekker.
Moussiopoulos, N., Ossanlis, I., Barbas, Ph., & Bartzis, J. (2005). Comparison of numerical and experimental results for the evaluation of the depollution effectiveness of photocatalytic coverings in street canyons’ Paper presented at the 5th International Conference on Urban Air Quality, Valencia, Spain, p.68.
Pichat, P. (2003). Photocatalytic degradation of pollutants in water and air: Basic concepts and applications. In M. A. Tarr (Ed.), Chemical degradation methods for wastes and pollutants: Environmental and industrial applications (pp. 77–119). New York: Marcel Dekker.
Pichat, P., Disdier, J., Hoang-Van, C., Mas, D., Goutailler, G., & Gaysse, C. (2000). Purification/deodorization of indoor air and gaseous effluents by TiO2 photocatalysis. Catalysis Today, 63, 363–369.
Strini, A., Cassese, S., & Schiavi, L. (2005). Measurement of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene and o-xylene gas phase photodegradation by titanium dioxide dispersed in cementitious materials using a mixed flow reactor. Applied Catalysis B, Environmental, 61, 90–97.
Zhang, J., Terukazu, A., Minagawa, M., Kinugawa, K., Yamashita, H., Matsuoka, M., Anpo, M. (2001). Investigations of TiO2 Photocatalysts for the decomposition of NO in the Flow System. Journal of Catalysis, 198, 1–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maggos, T., Plassais, A., Bartzis, J.G. et al. Photocatalytic degradation of NOx in a pilot street canyon configuration using TiO2-mortar panels. Environ Monit Assess 136, 35–44 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-9722-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-9722-2