Abstract
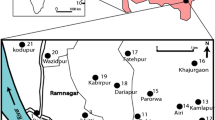
In present study focus has been given on estimating quality and toxicity of waste with respect to heavy metals and its impact on groundwater quality, using statistical and empirical relationships between different hydrochemical data, so that easy monitoring may be possible which in turn help the sustainable management of landfill site and municipal solid waste. Samples of solid waste, leachate and groundwater were analyzed to evaluate the impact of leachates on groundwater through the comparison of their hydrochemical nature. Results suggest the existence of an empirical relationship between some specific indicator parameters like heavy metals of all three above mentioned sample type. Further, K/Mg ratio also indicates three groundwater samples heavily impacted from leachate contamination. A good number of samples are also showing higher values for \( NO^{ - }_{3} \) and Pb than that of World Health Organization (WHO) drinking water regulation. Predominance of Fe and Zn in both groundwater and solid waste samples may be due to metal plating industries in the area. Factor analysis is used as a tool to explain observed relation between numerous variables in term of simpler relation, which may help to deduce the strength of relation. Positive loading of most of the factors for heavy metal clearly shows landfill impact on ground water quality especially along the hydraulic gradient. Cluster analysis, further substantiates the impact of landfill. Two major groups of samples obtained from cluster analysis suggest that one group comprises samples that are severely under the influence of landfill and contaminated leachates along the groundwater flow direction while other assorted with samples without having such influence.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (1995). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (19th ed.). Washington, DC: American Public Health Association
Baedecker, M. J., & Apgar, M. A. (1984). Hydrochemical Studies at a Landfill in Delaware. In J. Bredehoeft (Ed.), Groundwater Contamination (pp.127–138). Washington, DC: National Academy.
Barker, J. F., Barbash, J. E., & Labonte, M. (1988). Groundwater contamination at a landfill sited on fractured carbonate and shale. Contaminant Hydrology, 3,127–138.
Berner-Kay, E., & Berner, R. A. (1987). The global water cycle, Geochemistry and Environment. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall (396 pp)
Brown, C. H. (1998). Applied Multivariate statistics in Geohydrology and Related Sciences. Berlin: Springer.
Cattel, R. B. (1965). Factor analysis: Introduction to essentials. Biometrics, 21, 190–215.
CPCB (2000). Status of Solid Waste Generation, Collection, Treatment and Disposal in Metrocities, Series: CUPS/46/1999–2000
Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), (2004). Management of Municipal Solid Waste. New Delhi, India: Ministry of Environment and Forest.
Davis, J. C. (1986). Statistics, data analysis in geology. New York: Wiley.
Danielsson, A., Cato, I., Carman, R., & Rahm, L. (1999). Spatial clustering of metals in the sediments of the Skagerrak/kattegat. Applied Geochemistry, 14, 689–706.
Edmond, J. M., Palwer, M. R., Measures, C. F., Grant, B., & Stallard, R. F. (1995). The fluvial geochemistry and denudation rate of the Guayana Shield in Venezuela. Geochimica et cosmochimica acta, 59, 3301–3323.
EPTRI (1995). Status of solid waste disposal in Metropolis Hyderabad. Hyderabad, India: Environmental Protection Training and Research Institute (46 pp).
Flyhammar, P. (1995). Leachate quality and environmental effects of active Swedish municipal landfill. In R. Cossu, H. T. Christensen, & R. Stogmann (Eds.), Proceeding Sardinia 95.Fifth Int. Landfill symposium (pp. 551–557), Vol. II.
Fovell, R., & Fovell, M. Y. (1993). Climate zones of the conterminous United States defined using cluster analysis. Journal of Climate, 6, 2103–2135.
Futta, D., Yoscos, C., Haralambous, K. J., & Loizidou, M. (1997). An assessment of the effect of landfill leachate on groundwater quality. Proceeding Sardinia 97. Sixth Int. landfill symposium S. Margherita di Pule, Gagliari Italy, 13–17 October, pp. 181–187.
Gaily, R. M., & Gorelick, S. M. (1993). Design of optimal, reliable plume capture schemes: application to the Gloucester landfill groundwater contamination problem. Groundwater, 31, 107–114.
Gharaibeh, S. H., & Masad, A. (1989). Die Problomatite der Ahallbeseitingung in Jordan. Fallstudie Fur Enstasicklungs lander. Wasser und Boden, 10, 620–622.
Guler, C., & Thyne, D. G. (2004). Hydrological and geological factors controlling surface and groundwater chemistry in Indian Wells-Owens valley area, southeastern California, USA. Journal of Hydrology, 285, 177–198.
Gupta, S., Mohan, K., Prasad, R., Gupta, S., & Kansal, (1998). A solid waste management in India: Options and opportunities. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 24, 137–154.
Handa, B. K. (1988). Content of potassium in groundwater in India. Fertilizer News, 33(11), 15–27.
Hem, J. D. (1991). Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural groundwater. U.S Geological Survey Water Supply, 1473 pp.
Huh, Y., Tsoi, M. Y., Zaitiser, A., & Edward, J. N. (1998). The fluvial geochemistry of the river of eastern Siberia. I. Tributaries of Lena River draining the sedimentation platform of the Siberia Craton. Geochimica et cosmochimica acta, 62, 1657–1676.
Kjeldsen, P., Bjarg, P., Rugger, K., Pedsersen, J. K., Skov, B., Forverskov, A., et al. (1993). Assessing the variability in leachate from an old municipal landfill. In R. Gosso, H.T. Christensen, & R. R., Stegman (Eds.), Presidents Sardinia 93, Fourth Int. Landfill Symposium (pp. 1514–1531).
Kumar, D., & Alappat, B. G. (2005). Analysis of leachate Pollution index and formulation of sub-lechate pollution indices. Waste Management and Research 23(3), 230–239.
Kumar, M., Kumari, K., Ramanathan, A. L., & Saxena, R. (2007). A comparative evaluation of groundwater suitability for irrigation and drinking purposes in two agriculture dominated districts of Punjab, India. Environmental Geology, doi:10.1007/s00254-007-0672-3.
Kumar, M., Ramanathan, A. L., Rao, M. S., & Kumar, B. (2006). Identification and evaluation of hydrogeochemical processes in the groundwater environment of Delhi, India. Environmental Geology 50, 1025–1039.
Kurumbein,W. C., & Graybill, F. A. (1965). An introduction to statistical models in geology. New York: McGraw-Hill
Laaksoharju, M., Skarman, C., & Skarman, E., (1999). Multivariate mixing and mass balance (M3) calculation, a new tool for decoding hydrogeochemical information. Applied Geochemistry, 14, 861–871.
Laine, D. L., Parra, J. O., & Owen, T. E. (1982). Application of an automatic Earth resistivity system for detecting groundwater migration under a municipal landfill. In: Proceedings of NWWAConference on Surface and Borehole Geophysical Methods in Groundwater Investigations (pp. 34–51). 12–14 February 1982
Loizidon, M., & Kapetanios, E. (1993). Effect of leachate from landfills in under groundwater quality. The Science of the Total Environment, 128, 69–81.
Meju, M. A. (1993). Geophysical mapping of polluted groundwater in a closed landfill site. In:Proceedings of the Third International Congress of Brazilian Geophysical Society (Expanded).
Nath, K. J. (1984) Metropolitan solid waste management in India. In J. R. Holmes (Ed.), Managing Solid Wastes in Developing Countries. New York: Wiley, 304.
NEERI Report (1994). Investigation into contamination of French wells at Ahmadabad. National Environmental Engineering Research Institute (NEERI), Nagpur, India.
Nema, P., Ojha, C. S. P., Kumar, A., & Khanna, P. (2001). Techno-economic evaluation of soil-aquifer treatment using primary effluent at Ahmadabad, India. Water Research, 35(9), 2179–2190.
Newell, G. J., Hopkins, L. P., & Bedient, P. B. (1990). A hydrogeologic data for groundwater modeling. Journal of Groundwater, 28, 703–714.
Rajesh, R., Sreedhara Murthy, T. R., & Raghavan, B. R. (2002). The utility of multivariate statistical techniques in hydrogeochemical studies: an example from Karnataka, India. Water Research, 36, 2437–2442.
Robinson, H. C., Barber, C., & Maris, P. J. (1982). Generation and treatment of leachate from domestic wastes in landfills. Water & Pollution Control, 54, 465–478.
Shapiro, L., & Brannock, W. W. (1962). Rapid analysis of silicate, carbonate, and phosphate rocks. U.S. Geological Survey Bulletin (pp. A1–A56).
Sharma, S. (1996). Applied multivariate techniques. New York: Wiley.
Tejero, M. I., Fantelli, L. M., Diaz, I. R., & Azanto, N. M. (1993). Characteristics and treatment of leachate in the Meruleo landfill (Spain). In R. Cossu, H. I. Christensen, & R. Stegman (Eds), Proceeding Sardinia 93, farteInt. landfill symposium (pp. 1033–1042).
Usunoff, E. J., & Guzman-Guzman, A. (1989). Multivariate analysis in hydrogeochemistry: an example of the use factor and correspondence analyses. Groundwater, 27, 27–34.
Vendrame, I., & Pinho, M. F. (1997). Groundwater quality in Taubate Landfill, Brazil. In: J. Chilton, A. A. Balkema (Ed.), Groundwater in the Urban Environment (pp. 559–564) Rotterdam.
WHO (2004) Guidelines for drinking water quality-II (p. 333). Geneva: Environmental Health Criteria, 5.
Yedla, S., & Parikh, J. (2001). Solid Waste Management-Current Status and Strategies for the Future 12–14 December 2002. India: Bangalore.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, U.K., Kumar, M., Chauhan, R. et al. Assessment of the impact of landfill on groundwater quality: A case study of the Pirana site in western India. Environ Monit Assess 141, 309–321 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-9897-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-9897-6