Abstract
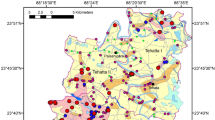
Probable sources and mechanisms of arsenic (As) release in shallow aquifer in eastern Bangladesh are evaluated using statistical analysis of groundwater compositions. Dissolved As in 39 samples ranged from 8.05 to 341.5 μg/L with an average of 95.14 μg/L. Ninety seven percent of wells exceed the WHO limit (10 μg/L) for safe drinking water. Principal component analysis is applied to reduce 16 measured compositional variables to five significant components (principal components—PCs) that explain 86.63% of the geochemical variance. Two component loadings, namely PC 1 and PC 2 (45.31% and 23.05%) indicate the natural processes within the aquifers in which organic matter is a key reactant in the weathering reactions. Four groups of wells are defined by the PCA and each group of wells represents distinct physicochemical characteristics. Among them, group III groundwater shows higher As concentration together with high concentrations of Fe, Mn, dissolved organic carbon, \(\text{PO}_{4}^{3-}\) and \(\text{HCO}_{3}^{-}\) than groups I and II. Speciation calculations suggest that only wells of group III are saturated with respect to siderite, and all groups of samples are supersaturated with respect of rhodochrosite. The relationship of As with these parameters in the different groups of wells of the study area suggests that reductive dissolution of Fe–Mn oxyhydroxides with microbially mediated degradation of organic matter is considered to be the dominant processes to release As in groundwater.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AAN (1999). Arsenic contamination of groundwater in Bangladesh: Interim report of the research at Samta Village. Bangladesh: Asian Arsenic Network, Research Group for Applied Geology and the National Institute for Preventive and Social Medicine.
Acharyya, S. K., Chakraborty, P., Lahiri, S., Raymahashay, B. C., Guha, S., & Bhowmik, A. (1999). Arsenic poising in the Ganges Delta. Nature, 401, 545. doi:10.1038/44052.
Ahmed, K. M., Bhattacharya, P., Hasan, M. A., Akhter, S. H., Alam, S. M. M., Bhuyian, M. A. H., et al. (2004). Arsenic enrichment in groundwater of the alluvial aquifers in Bangladesh: An overview. Applied Geochemistry, 19, 181–200. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2003.09.006.
Ahmed, K. M., Hoque, M., Hasan, M. K., Ravenscroft, P., & Chowdhury, L. R. (1998). Occurrence and origin of water well CH4 gas in Bangladesh. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 51, 697–708.
Akai, J., Izumi, K., Fukuhara, H., Masuda, H., Nakano, S., Yoshimura, T., et al. (2004). Mineralogical and geomicrobiological investigations on groundwater arsenic enrichment in Bangladesh. Applied Geochemistry, 19, 215–230. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2003.09.008.
Allison, J. D., Brown, D. S., & Novo-Gradac, K. J. (1990). MINTEQA2/PRODEFA2A geochemical assessment model for environmental systems version 3.0 user’s manual: Environmental research laboratory. Athens, Georgia: Office of Research and Development, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
Anawer, M. H., Akai, J., Komaki, K., Terao, H., Yoshimura, T., Ishizuka, T., et al. (2003). Geochemical occurrence of arsenic in groundwater of Bangladesh: Sources and mobilization processes. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 77, 109–131. doi:10.1016/S0375-6742(02)00273-X.
BADC (2002). Survey report on irrigation equipment and irrigated area in Boro/2001 season. Bangladesh Agricultural Development Corporation.
Banfield, J. F., Barker, W. W., Welch, S. A., & Taunton, A. (1999). Biological impact on mineral dissolution: Application of the lichen model to understanding mineral weathering in the rhizosphere. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 96, 3404–3411. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.7.3404.
Berg, M., Trang, P. T. K., Stengel, C., Buschmann, J., Viet, P. H., Dan, N. V., et al. (2008). Hydrological and sedimentary controls leading to arsenic contamination of groundwater in the Hanoi area, Vietnam: The impact of iron–arsenic ratios, peat, river bank deposits, and excessive groundwater abstraction. Chemical Geology, 249, 91–112. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.12.007.
Berner, R. A. (1981). A new geochemical classification of sedimentary environments. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 51, 359–365.
BGS & DPHE (2001). Arsenic contamination of groundwater in Bangladesh (Vol. 2). Final Report, BGS Technical Report WC/00/19.
Bhattacharya, P., Chatteriee, D., & Jacks, G. (1997). Occurrence of arsenic contaminated groundwater in alluvial aquifers from the Delta Plains, eastern India: Options for safe drinking water supply. International Journal of Water Resource Management, 13, 79–92.
Bhattacharya, P., Claesson, M., Bundschuh, J., Sracek, O., Fagerberg, J., Jacks, G., et al. (2006). Distribution and mobilization of arsenic in the Río Dulce alluvial aquifers in Santiago del Estero Province, Argentina. Science of the Total Environment, 358, 97–120.
Bhattacharya, P., Jacks, G., Ahmed, K. M., Khan, A. A., & Routh, J. (2002). Arsenic in groundwater of the Bengal Delta Plain aquifers in Bangladesh. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 69, 538–545.
Bhattacharya, P., Welch, A. H., Ahmed, K. M., Jacks, G., & Naidu, R. (2004). Arsenic in groundwater of sedimentary aquifers. Applied Geochemistry, 19, 163–167.
Bhattacharya, P., Welch, A. H., Stollenwerk, K. G., McLaughlin, M. J., Bundschuh, J., & Panaullah, G. (2007). Arsenic in environment: Biology and chemistry. Science of the Total Environment, 379, 109–120.
Buschmann, J., Berg, M., Stengel, C., Winkel, L., Sampson, M. L., Trang, P. T. K., et al. (2008). Contamination of drinking water resources in the Mekong delta floodplains: Arsenic and other trace metals pose serious health risks to population. Environmental International, 34, 756–764. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2007.12.025.
Charlet, L., & Polya, D. A. (2006). Arsenic in shallow, reducing groundwaters in southern Asia: An environmental health disaster. Elements, 2, 91–96.
Clark, I., & Fritz, P. (1997). Environmental isotopes in hydrology. Boca Raton, New York: Lewis.
Cloutier, V., Lefebvre, R., Therrien, R., & Savard, M. M. (2008). Multivariate statistical analysis of geological data as indicative of the hydrogeochemical evolution of groundwater in a sedimentary rock aquifer system. Journal of Hydrology, 353, 294–313.
Davis, J. (1989). Pilot study into optimum well design: IDA 4000 deep tubewell project (Vol. 2). The geology of the alluvial aquifers of Central Bangladesh. British Geological Survey Technical Report WD/89/9.
Davis, J. (1995). The hydrochemistry of alluvial aquifers in central Bangladesh. In H. Nash & G. J. H. McCall (Eds.), Groundwater quality (pp. 9–18). London: Chapman and Hall.
Davis, J. C. (1986). Statistics and data analysis in geology. New York: Wiley.
Dhar, R. K., Biswas, B. K., Samanta, G., Mandal, B. K., Chakraborty, D., Roy, S., et al. (1997). Groundwater arsenic calamity in Bangladesh. Current Science, 73, 48–59.
Dowling, C. B., Poreda, R. J., Basu, A. R., Peters, S. L., & Aggarwal, P. K. (2002). Geochemical study of arsenic release mechanisms in the Bengal Basin groundwater. Water Resource Research, 38(9), 1173. doi:10.1029/2001WR000968.
FAO (1999). FAO’s information system on water and agriculture, Rome, Italy. http://www.fao.org/ag/agl/aglw/aquastat/countries/bangladesh/index.stm.
Farnham, I. M., Johannesson, K. H., Singh, A. K., Hodge, V. F., & Stetzenbach, K. J. (2003). Factor analytical approaches for evaluating groundwater trace element chemistry data. Analytica Chimica Acta, 490, 123–138.
Guo, H., Yang, S., Tang, X., Li, Y., & Shen, Z. (2008). Groundwater geochemistry and its implications for arsenic mobilization in shallow aquifers of the Hrtao Basin. Science of the Total Environment, 393, 131–144.
Halim, M. A., Majumder, R. K., Nessa, S. A., Hiroshiro, Y., Uddin, M. J., Shimada, J., et al. (2008a). Hydrogeochemistry and arsenic contamination of groundwater in the Ganges Delta Plain, Bangladesh. Journal of Hazardous Materials. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.09.046.
Halim, M. A., Majumder, R. K., Nessa, S. A., Oda, K., Hiroshiro, Y., Saha, B. B., et al. (2008b). Groundwater contamination with arsenic in Sherajdikhan, Bangladesh: Geochemical and hydrological implications. Environmental Geology. doi:10.1007/s00254-008-1493-8.
Hasan, M. A., Ahmed, K. M., Sracek, O., Bhattacharya, P., von Bromssen, M., Broms, S., et al. (2007). Arsenic in shallow groundwater of Bangladesh: Investigations from three different physiographic settings. Hydrological Journal, 15, 1507–1522.
Hossain, M. F. (2006). Arsenic contamination in Bangladesh—an overview. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 113, 1–16.
Islam, F. S., Gaultm, A. G., Boothman, C., Polya, D. A., Charnock, J. M., Chatterjee, D., et al. (2004). Role of metal-reducing bacteria in arsenic release from Bengal delta sediments. Nature, 430, 68–71.
Jolliffe, I. T. (2002). Principal component analysis. NY: Springer.
Kaiser, H. F. (1960). The application of electronic computers to factor analysis. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 20, 141–151.
Komor, S. C., & Anderson, H. W., Jr. (1993). Nitrogen isotope as indicators of nitrate source in Minnesota sand-plain aquifers. Ground Water, 31, 260–271.
Mallik, S., & Rajagopal, N. (1996). Groundwater development in the arsenic-affected alluvial belt of West Bengal—some questions. Currier Science, 70, 956–958.
Mandal, B. K., Roy Chowdhury, T., Samanta, G., Basu, G. K., Chowdhury, P. P., Chanda, C. R., et al. (1996). Arsenic in groundwater in seven districts of West Bengal, India: The biggest arsenic calamity in the world. Currier Science, 70, 976–986.
McArthur, J. M., Banerjee, D. M., Hudson-Edwards, K. A., Mishra, R., Purohit, R., Ravenscroft, P., et al. (2004). Natural organic matter in sedimentary basins and its relation to arsenic in anoxic ground water: The example of West Bengal and its worldwide implications. Applied Geochemistry, 19, 1255–1293.
McArthur, J. M., Ravencroft, P., Safiullah, S., & Thirlwall, M. F. (2001). Arsenic in groundwater: Testing pollution mechanism for sedimentary aquifers in Bangladesh. Water Resource Research, 37, 109–117.
Melloul, A., & Collin, M. (1992). The ‘principal component’ statistical methods as a complementary approach to geochemical methods in water quality factor identification; application to the Coastal Plain aquifer of Israel. Journal of Hydrology, 140, 49–73.
Mencio, A., & Mas-Pla, J. (2008). Assessment by multivariate analysis of groundwater–surface water interactions in urbanized Mediterranean streams. Journal of Hydrology, 352, 355–366.
Mukherjee, A., & Fryar, A. E. (2008). Deeper groundwater chemistry and geochemical modeling of the arsenic affected western Bengal basin, West Bengal, India. Applied Geochemistry, 23, 863–894.
Mukherjee, A., Fryar, A. E., & Howell, P. D. (2007). Regional hydrostratigraphy and groundwater flow modeling of the arsenic contaminated aquifers of the western Bengal basin, West Bengal, India. Hydrological Journal, 15, 1397–1418.
Nahar, N. (2007). Impacts of arsenic contamination in groundwater: Case study of some villages in Bangladesh. Environment and Sustainable Development. doi:10.1007/s10668-007-9130-3.
Nickson, R. T., McArthur, J. M., Burgess, W. G., Ahmed, K. M., Ravenscroft, P., & Rahman, M. (1998). Arsenic poisoning of Bangladesh groundwater. Nature, 395, 338.
Nickson, R. T., McArthur, J. M., Ravenscroft, P., Burgess, W. G., & Ahmed, K. M. (2000). Mechanism of arsenic release to groundwater, Bangladesh and West Bengal. Applied Geochemistry, 15, 403–413.
Parkhurst, D. L., & Appelo, C. A. J. (1999). Users guide to PHREEQC (version 2): A computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical modeling. US Geological Survey Water Resources Investigations Report, 99-4259.
Perrin, J. (1998). Arsenic in groundwater at Meherpur, Bangladesh: A vertical pore water profile and rock/water interactions. M. Sc. Thesis (unpublished), University College London.
Polizzotto, M. L., Harvey, C. F., Li, G. C., Badruzzman, B., Ali, A., Newville, M., et al. (2006). Solid-phases and desorption processes of arsenic within Bangladesh sediments. Chemical Geology, 228, 97–111.
Postma, D., & Jakobsen, R. (1996). Redox zonation: Equilibrium constraints on the \(\text{Fe(III)/SO}_{4}^{2-}\) reduction interface. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 60, 3169–3175.
Ravenscroft, P., Burgess, W. G., Ahmed, K. M., Burren, M., & Perrin, J. (2005). Arsenic in groundwater of the Bengal basin, Bangladesh: Distribution, field relations, and hydrogeologic setting. Hydrological Journal, 13, 727–751.
Ravenscroft, P., McArthur, J. M., & Hoque, B. A. (2001). Geochemical and paleohydrological controls on pollution of groundwater by fourth international conference on arsenic exposure and health effects. San Diego, California, 18–22 June 2000.
Saether, O. M., & Caritat, P. (1997). Geochemical processes weathering and groundwater recharge in catchments. Rotterdam/Rookfield: AA Balkema.
Schot, P. P., & van der Wal, J. (1992). Human impact on regional groundwater composition through intervention in natural flow patterns and changes in land use. Journal of Hydrology, 134, 297–313.
Smedley, P. L., & Kinniburgh, D. G. (2002). A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Applied Geochemistry, 17, 517–568.
Smith, A. H., Lingas, E. O., & Rahman, M. (2000). Contamination of drinking-water by arsenic in Bangladesh: A public health emergency. Bulletin of World Health Organization, 78, 1093–1103.
WHO (World Health Organization) (2004). Guidelines for drinking water quality recommendations (Vol. 1, pp. 515). Geneva: WHO.
Zahid, A., Hassan, M., Qumrul Balke, K. D., Flegr, M., & Clark David, W. (2008). Groundwater chemistry and occurrence of arsenic in the Meghna floodplain aquifer, southeastern Bangladesh. Environmental Geology, 54(6), 247–1260. doi:10.1007/s00254-007-0907-3.
Zheng, Y., Stute, M., Van Geen, A., Gavrieli, I., Dhar, R., Simpson, H. J., et al. (2004). Redox control of arsenic mobilization in Bangladesh groundwater. Applied Geochemistry, 19, 201–214.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Halim, M.A., Majumder, R.K., Nessa, S.A. et al. Arsenic in shallow aquifer in the eastern region of Bangladesh: insights from principal component analysis of groundwater compositions. Environ Monit Assess 161, 453–472 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-0760-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-0760-9