Abstract
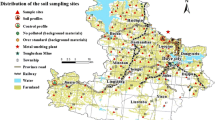
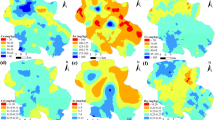
Problems associated with heavy metal characterization in the majority of sites are often due to multiple sources of pollution. This work presents the results through the use of advanced statistical techniques to identify sources of soil heavy metals in a typical Mediterranean city. The multivariable analysis performed on seven metals identified four sources controlling their variability. Cr, Mn, and Ni contents were associated to soil parent materials; Cd and Pb contents were related to anthropogenic activities, specifically industrial activities and traffic; Cu content is controlled by long-term application of inorganic fertilizers in agricultural areas. Finally, zinc concentration is associated to commercial and outdoor activities in the area. These results were supported by the fact that metals associated to parent material (Cr, Mn, and Ni) were better correlated with soil lithogenic properties, while anthropogenic metals were correlated with more variable soil constituents.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adriano, D. C. (2001). Trace elements in the terrestrial environment. Biogeochemistry, bioavailability and risk of metals (2nd ed., p. 880). New York: Springer.
Albasel, N., & Cottenie, A. (1985). Heavy metal contamination near major highways, industrial and urban areas in Belgian grassland. Water, Air and Soil pollution, 24, 103–109.
Alloway B. C. (1995). The origin of heavy metals in soils. In B. J. Alloway (Ed.), Heavy metals in soil. (2nd ed., p. 368).
Andrades, M. (1996). Prácticas de Edafología y Climatología (pp. 14–16). In Universidad de la Rioja (Ed.). Logroño, La Rioja, España.
Aubert, H., & Pinta, M. (1977). Trace elements in soil. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Birke, M., & Rauch, U. (2000). Urban geochemistry in the Berlin metropolitan area. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 22, 233–248.
Bowman, W. S., Faye, G. H., Sutarno, R., McKeague, J. A., & Kodama, H. (1979). Soil samples SO-1, SO-2, SO-3 and SO-4—certified reference materials (p. 34). CANMET Report 79-3, CANMET Mining and Mineral Sciences Laboratories, Ottawa, ON.
Brady, N. C., & Weil, R. R. (2001). The nature and properties of soils (13th ed., p. 960). Englewood: Prentice Hall.
Bretzel, F., & Calderisi, M. (2006). Metal contamination in urban soils of coastal. Tuscany (Italy). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 118, 319–335.
Burrough, P. A., & McDonnell, R. A. (1998). Creating continuous surfaces from point data. In P. A. Burrough, M. F. Goodchild, R. A. McDonnell, P. Switzer, & M. Worboys (Eds.), Principles of geographic information systems. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
C.R.E.M. (2006). Murcia en cifras. 2. Evolución de la población según el Padrón Municipal de Habitantes. Centro Regional de Estadística de Murcia.
Celine, S. L., Xiangdong, L., Wenzhong, S., Sharon, C., & Iain, T. (2006). Metal contamination in urban, suburban, and country park soils of Hong Kong: A study based on GIS and multivariate statistics. Science of the Total Environment, 356, 45–61.
Colgan, A., Hankard, P. K., Spurgeon, D. J., Svendsen, C., Wadsworth, R. A., & Weeks, J. M. (2003). Closing the loop: A spatial analysis to link observed environmental damage to predicted heavy metal emissions. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 22, 970–976.
De Miguel, E., Jiménez de Grado, J., Llamas, J. F., Martín-Dorado, A., & Mazadiego, L. F. (1998). The overlooked contribution of compost application of the trace element load in the urban soil of Madrid (Spain). Science of the Total Environment, 215, 113–122.
De Mora, S., Sheikholeslami, M. R., Wyse, E., Azemard, S., & Cassi, R. (2004). An assessment of metal contamination in coastal sediments of the Caspian Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 48, 61–77.
De Temmerman, L., Vanongeval, L., Boon, W., & Hoenig, M. (2003). Heavy metal content of arable soil in Northern Belgium. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 148, 61–76.
Facchinelli, A., Sacchi, E., & Mallen, L. (2001). Multivariate statistical and GIS-based approach to identify heavy metal sources in soils. Environmental Pollution, 114, 313–324.
Fakayode, S. O., & Onianwa, P. C. (2002). Heavy metals contamination of soil, and bioaccumulation in Guinea grass (Panicum maximun) around Ikeja Industrial estate, Lagos, Nigeria. Environmental Geology, 43, 145–150.
FAO-ISRIC (1990). Guidelines for soil description (3rd ed., p. 70). Roma: F.A.O.
Fernández, A. J., Ternero, M., & Fernández, F. (2004). Source characterisation of fine urban particles by multivariate analysis of trace metals speciation. Atmospheric Environment, 38, 873–886.
Frías, S., Conde, J. E., Rodriguez, B. J. J., Garcia, M. F., & Perez, T. P. J. P. (2003). Classification of commercial wines from the Canary Islands (Spain) by chemometric techniques using metallic contents. Talanta, 59, 335–344.
García-Miragaya, J. (1984). Levels, chemical fractionation and solubility of lead in roadside soils of Caracas, Venezuela. Soil Science, 138, 147–152.
Garty, J., Romen, R., & Galun, M. (1985). Correlation between chlorophyll degradation and amount of some elements in the lichen Ramalinc diriaei (De Not.). Jatta Environmental and Experimental Botany, 25, 67–74.
Gilkes, R. J., & McKenzie, R. M. (1988). Geochemistry and minerology of manganese in soil. In R. D. Grahem (Ed.), Manganese in soil and plants (p. 157). London: Hannam.
Gutiérrez-Galindo, E. A., Muñoz-Barbosa, A., Walter, L., Macías-Zamora, J. V., & Segovia-Zavala, J. A. (2007). Sources and factors influencing the spatial distribution of heavy metals in a coastal lagoon adjacent to the San Quintín volcanic field, Baja California, Mexico. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 54, 1962–1989.
Hanesch, M., Scholger, R., & Dekkers, M. J. (2001). The application of fuzzy means cluster analysis and non-linear mapping to a soil data set for detection of polluted sites. Physical Chemical Earth Sciences, 26, 885–891.
Holmgren, G. G. S., Meyer, M. W., Chaney, R. L., & Daniels, R. B. (1993). Cadmium, lead, zinc, copper and nickel in agricultural soil of the United States of America. Journal of Environmental Quality, 22, 335–348.
I.G.M.E. (1976). Mapa Geológico de España, E. 1:50 000. Murcia. Servicio de Publicaciones del Ministerio de Industria. Madrid. Memoria, 34pp y un mapa fuera de texto.
I.P.C.S. (1995). Environmental health criteria 165: Inorganic lead (p. 300). Genova: World Health Organization, International Programme on Chemical Safety.
I.P.C.S. (1998). Environmental health criteria 200: Copper (p. 360). Genova: World Health Organization, International Programme on Chemical Safety.
Imperato, M., Adamo, P., Naimo, D., Arienzo, M., Stanzione, D., & Violante, P. (2003). Spacial distribution of heavy metals in urban soils of Naples City (Italy). Environmental Polution, 124, 247–256.
Kabata-Pendias, A., & Pendias, H. (1992). Trace elements in soil and plants (2nd ed., p. 315). Boca Raton: CRC.
Kartal, S., Aydın, Z., & Tokalıoglu, S. (2006). Fractionation of metals in street sediment samples by using the BCR sequential extraction procedure and multivariate statistical elucidation of the data. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 132, 80–89.
Liu, W. X., Li, X. D., Shen, Z. G., Wang, D. C., Wai, O. W. H., & Li, Y. S. (2003). Multivariate statistical study of heavy metal enrichment in sediments of the Peral River Estuary. Environmental Pollution, 121, 377–388.
Ljung, K., Selinus, O., Otabbong, E., & Berglund, M. (2006). Metal and arsenic distribution in soil particle sizes relevant to soil ingestion by children. Applied Geochemistry, 21, 1613–1624.
Lucho-Constantino, C. A., Álvarez-Suárez, M., Beltrán-Hernández, R. I., Prieto-García, F., & Poggi-Varaldo, H. M. (2005). A multivariate analysis of the accumulation and fractionation of major and trace elements in agricultural soils in Hidalgo State, Mexico irrigated with raw wastewater. Environment International, 31, 313–323.
Madrid, L., Díaz-Barrientos, E., & Madrid, F. (2002). Distribution of heavy metal contents of urban soils in parks of Seville. Chesmosphere, 49, 1301–1308.
Manta, D. S., Angelone, M., Bellanca, A., Neri, R., & y Sprovieri, M. (2002). Heavy metals in urban soils: A case study from the city of Palermo (Sicily), Italy. The science of the total Environment, 300, 229–243.
Mendiguchía, C., Moreno, C., Galindo, R. M. D., & Garcıía-Vargas, M. (2004). Using chemometric tools to assess anthropogenic effects in river water. A case study: Guadalquivir River (Spain). Analytica Chimica Acta, 515, 143–149.
Micó, C., Recatalá, L., Peris, M., & Sánchez, J. (2006). Assessing heavy metal sources in agricultural soils of an European Mediterranean area by multivariate analysis. Chemosphere, 65, 863–872.
Möller, A., Muller, H. W., Abdullah, A., Abdelgawad, G., & Utermann, J. (2005). Urban soil pollution in Damascus, Syria: Concentrations and patterns of heavy metals in the soils of the Damascus Ghouta. Geoderma, 124, 63–71.
Monastra, V., Derry, L. A., Chadwick, O. A. (2004). Multiple sources of lead in soils from a Hawaiian chronosequence. Chemical Geology, 209, 215–231.
Norusis, M. J. (1993). SPSS for windows base system user’s guide release 6.0. SPSS Inc.
Paoletti, M. G., Lovane, E., & Cortese, M. (1988). Pedofauna bioindicators and heavy metals in five agroecosystens in north-east Italy. Revue Ecologie et Biologie du Sol, 25, 3–58.
Peech, M. (1965). Hidrogen-ion activity. In C. A. Black (Ed.), Methods of soil analysis (2nd ed., pp. 914–916). Madison: American Society of Agronomy.
Peris, M., Recatalá, L., Micó, C., Sánchez, R., & Sánchez, J. (2008). Increasing the knowledge of heavy metal contents and sources in agricultural soils of the European Mediterranean region. Water Air Soil Pollution, 37, 192–25.
Porta, J., López-Acevedo, M., & Roquero, C. (1999). Edafología para la agricultura y el medio ambiente (2 edición). Ediciones Mundi-Prensa.
Risser, J. A., & Baker, D. E. (1990). Testing soils for toxic metals. In R. L. Westerman (Ed.), Soil testing and plant analysis (3rd ed., pp. 275–298). Soil Sci. Soc. Amer. Spec. Publ. 3, Madison, Wi.p.
Rodríguez, J. A., López, M., & Grau, J. M. (2006). Heavy metals contents in agricultural topsoils in the Ebro basin (Spain). Application of the multivariate geoestatistical methods to study spatial variations. Environmental Pollution, 144, 1001–1012.
Romic, M., & Romic, D. (2002). Heavy metals distribution in agricultural top soils in urban area. Environmental Geology, 43, 795–805.
Ruiz-Cortes, E., Reinoso, R., Diaz-Barrientos, E., & Madrid, L. (2005). Concentrations of potentially toxic metals in urban soils of Seville: Relationship with different land uses. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 27, 465–474.
Sánchez-Camazano, M., Sánchez-Martín, M. J., & Lorenzo, L. F. (1998). Significance of soil properties for content and distribution of cadmium and lead in natural calcareous soils. The Science of the Total Environment, 218, 217–226.
Sangui, R., & Sasi, K. S. (2001). Pesticides and heavy metals in agricultural soil of Kampur, India. Environmental Contaminants Toxicology, 67, 446–454.
Singh, B. R. (1994). Trace element availability to plants in agricultural soils, with special emphasis on fertilizer inputs. NRC Canada, 2(2), 133–146.
Smith, L. A., Means, J. L., Chen, A., Alleman, B., Chapman, C. C., Tixier, J. S., et al. (1995). Remedial options for metals-contaminated sites. Boca Raton: Lewis.
Soil Survey Staff (2004). Soil survey laboratory methods manual. Version No. 4.0. USDA NRCS. Soil Survey Investigations Report No. 42. U.S. Govt. Print. Office, Washington, DC.
Tariq, S. R., Shah, M. H., & Shaheen, N. (2006). Multivariate analysis of trace metal levels in tannery effluents in relation to soil and water: A case study from Peshawar, Pakistan. Journal of Environmental Management, 79, 20–29.
Temmerman (1984). Determination of normal levels and upper limit values of trace element in soil. Verleg Chemie Gmbh, D-6940.
Tokahoglu, S., & Kartal, S. (2002). Evaluation of the results of metal analyses for lake sediment samples: A multivariate statistical approach. Chemia Analityczna (Warsaw), 47, 627–638.
Urbano, P. (2001). Tratado de Fitotecnia General (895 pp.). Madrid: Ed. Mundi Prensa.
Valerie, M., Derrya, L.A., & Chadwickb, O.A. (2004). Multiple sources of lead in soils from a Hawaiian chronosequence. Chemical Geology, 209, 215–231.
Vidal, J. (2002). Evaluación de los principales procesos de degradación en Fluvisoles calcáricos de la Huerta de Murcia. Tesis Doctoral, Universidad de Murcia.
Ward, N. L. (1989). Multielement contamination of British motorway environments. In J. P. Vernet (Ed.), Heavy metals in the environment, international conference (Vol. II). Genova: CEP Consultants Edinburgh.
Wei, L., Tieyu, W., Yonglong, L., John, P. G., Yajuan, S., Yuanming, Z., et al. (2007). Landscape ecology of the Guanting Reservoir, Beijing, China: Multivariate and geostatistical analyses of metals in soils. Environmental Pollution, 146, 567–576.
Xue-Song, W., Yong, Q., & Yong-Kang, C. (2006). Heavy meals in urban roadside soils, part 1: Effect of particle size fractions on heavy metals partitioning. Environmental Geology, 50, 1061–1066.
Yaalon, D. (1997). Soils in the Mediterranean region: What makes them different? Catena, 28, 157–169.
Yongming, H. T., Peixuan, D., Junji, C., & Posmentier, E. S. (2006). Multivariate analysis of heavy metal contamination in urban dusts of Xi’an, Central China. Science of the Total Environment, 355, 176–186.
Zhang, C., Wang, L., Li, G., Don, S., Yang, J., & Wang, X. (2002). Grain size effect on multi element concentrations in sediments from the intertidal flats of Bohai Bay, China. Applied Geochemistry, 17, 59–68.
Zhang, H., Ma, D., Xie, Q., & Chen, X. (1990). An approach to studying heavy metal pollution caused by modern city development in Nanjung, China. Environmental Geology, 38(3), 223–228.
Zhou, J., Ma, D., Pan, J., Nie, W., & Wu, K. (2008). Application of multivariate statistical approach to identify heavy metal sources in sediment and waters: A case study in Yangzhong, China. Environmental Geology, 54, 373–380.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Acosta, J.A., Faz, A. & Martinez-Martinez, S. Identification of heavy metal sources by multivariable analysis in a typical Mediterranean city (SE Spain). Environ Monit Assess 169, 519–530 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-1194-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-1194-0