Abstract
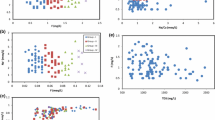
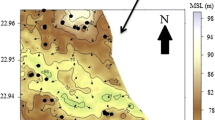
Fluoride-rich groundwater is well known in granite aquifers in India and the world. This study examines the fluoride content of well water in different parts of Talupula area of Anantapur district, Andhra Pradesh. It also focuses on fluorides and their relationship to water-quality parameters and their impacts on humans through groundwater resources. Most parts of the area covered in this region are inherently enriched with fluorides threatening several ecosystems. The fluoride concentration ranges between 0.78 and 6.10 mg L − 1. The alkaline pH and high bicarbonate are responsible for release of fluoride-bearing minerals into groundwater. The arid climate of the region, the granitic rocks and the low freshwater exchange due to periodical drought conditions are the factors responsible for the higher incidence of fluorides in the groundwater resources. Apart from these prevailing natural conditions, years of neglect and lack of restoration programs on terrestrial and aquatic environments have led to accumulative impacts on groundwater, soils, plants, and animals including humans. The people dependent on these groundwater resources are prone to dental fluorosis and mild skeletal fluorosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (1992). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (p. 326). Washington: American Public Health Association.
Athavale, R. N., & Das, R. K. (1999). Beware! Fluorosis is zeroing in on you. Down to Earth, 8, 24–25.
Babulal, D., Jitu, T., Surashree, S., Gohain, B., Dutta, R. K., Himangshu, B. D., et al. (2003). Fluoride and other inorganic constituents in groundwater of Guwahati, Assam, India. Current Science, 85(5), 657–661.
Bårdsen, A., Bjorvatn, K., Sand, K., & Banks, D. (2000). Seasonal variations of fluoride content in groundwater from wells drilled in bedrock. Norges Geologiske Undersøkelse Bulletin, 435, 53–58.
Bhagavan, S. V. B. K., & Raghu, V. (2005). Utility of check dams in dilution of fluoride concentration in groundwater and the resultant analysis of blood serum and urine of villagers, Anantapur district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 27, 97–108.
BIS (2003). Indian standard specifications for drinking water (p. 10). New Delhi: Bureau of Indian Standards.
Brown, E., Skougstad, M. W., & Fishman, M. J. (1970). Methods for collection and analysis of water samples for dissolved minerals and gases (p. 160, Chap. A1, Book 5). Techniques of Water Resources Investigations of the U.S. Geological Survey.
Chatterjee, M. K., & Mohabey, N. K. (1998). Potential fluorosis problems around Chandidongri, Madya Pradesh, India. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 20, 1–4
Chow, V. T. (1964). Handbook for applied hydrology. New York: Mc Graw-Hill.
Collins, W. D. (1923). Graphic representation of water analysis. Industrial Engineering Chemistry, 15, 394.
Davis, S. N., & Dewiest, R. J. M. (1967). Hydrogeology (p. 436). New York: Wiley.
Deshmukh, A. N., Wadaskar, P. M., & Malpe, D. B. (1995). Fluorine in environment. In A. N. Deshmukh, D. B. Yedekar, & K. K. K. Nair (Eds.), Fluorine in environment (pp. 1–20). Gondwana Geological Magazine, Special Issue 9.
Doley, D. (1986). Fluoride effects on vegetation in Australia. In Proceedings of 7th world clean air congress. Sydney, Australia, 25–29 Aug, Clean Air Society of Australia and Newzealand.
Domenico, P. A., & Schwartz, F. W. (1990). Physical and chemical hydrogeology. New York: Wiley.
Doneen, L. D. (1954). Salination of soil by salts in the irrigation water. American Geophysical. Union Transactions, 35, 943–950.
Doneen, L. D. (1962). The influence of crop and soil on percolating water. In Proceedings 1961. Biennial conference on ground water recharge (pp. 156–163).
Doneen, L. D. (1964). Notes on water quality in agriculture. Davis: Water Science and Engineering, Univ. California.
Elloumi, N., Abdallah, F. B., Mezghani, I., Rhouma, A., & Boukhris, M. (2005). Effect of fluoride on almond seedlings in culture solution. Fluoride, 38, 193–198.
Gaciri, S. J., & Davies, T. C. (1993). The occurrence and geochemistry of fluoride in some natural waters of Kenya. Journal of Hydrology, 143, 395–412.
Gibbs, R. J. (1970). Mechanisms controlling worlds water chemistry. Science, 170, 1088–1090.
Hem, J. D. (1991). Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water (3rd Ed., p. 263). Jodhpur, India: United States Geological Survey Professional Paper 2254, Scientific Pub.
Ignacak, J., & Guminska, M. (1991). Fluoride in urine of the population living in polluted environment. Folia Medical Cracov, 32, 83–88.
Jacks, G., Rajagopalan, K., Alveteg, T., & Jonsson, M. (1993). Genesis of high-F groundwaters, Southern India. Applied Geochemistry, 2, 241–244.
Johnson, C. C. Jr. (1979). Land application of waste—An accident waiting to happen. Groundwater, 17, 69–72.
Karanth, K. R. (1989). Hydrogeology (p. 720). New Delhi: McGraw-Hill.
Kelly, W. P. (1940). Permissible composition and concentration of irrigated waters. Proceedings of ASCF, 66, 607.
Kelly, W. P. (1951). Alkali soils—Their formation, properties and reclamation. New York: Reinhold.
Lag, J. (1983). Geomedicine in Scandinavia. In I. Thornton (Ed.), Applied environmental geochemistry (pp. 335–352). New York: Academic.
Machoy, Z., & Machoy-Mokrzynska, A. (1990). Mechanism of fluoride elimination and detoxicfication in living organisms. Fluoride, 23, 151–153.
Marcus, R., Feldman, D. & Kelsey, J. (Eds.) (1996). Osteoporosis (p. 1373). New York: Academic.
Marutatmaja Rao, P. L. K., & Ramamohana Rao, N. V. R. (1988). Studies on the distribution of fluoride in water sources of Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh, India. Journal of Fluorine Chemistry, 41, 9–16.
Muralidharan, D., Nair, A. P., & Sathyanarayana, U. (2002). Fluoride in shallow aquifers in Rajgarh tehsil of Churu district Rajasthan—An arid environment. Current Science, 83, 699–702.
Nagaraja Rao, B. K., Rajurkar, S. T., Ramlingaswamy, G., & Ravindra Babu, B. (1987). Startigraphy, strucutre and evolution of the Cuddaph basin: Purana Basins of Peninsular India Middle to Late Proterozoic. Geological Society of India Memoir, 6, 33–86.
National Research Council (1993). Health effects of ingested fluoride. Washington: National Academy Press.
Paliwal, K. V. (1967). Effect of gypsum application on the quality of irrigation waters. The Madras Agriculture Journal, 59, 646–647.
Peixoto, P. H. P., Pimenta, D. S., & Antunes, F. (2005). Fluoride effects on leaves of aquatic Salvinia auriculata. Pesquisa Agropecuaria Brasileira, 40(8), 727–734
Piper, A. M. (1944). A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analysis. Transactions of the American Geophysical Union, Washington, D.C., 25, 914–923.
Piper, A. M. (1953). A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analysis. Washington, DC: USGS, Ground water note 12.
Pojasek, R. B. (Ed). (1977). Drinking water quality enhancement through protection (p. 614). Ann Arbor: Ann Arbor Publishers.
Raghunath, H. M. (1987). Groundwater (p. 563). New Delhi: Wiley.
Rainwater, F. H., & Thatcher, L. L. (1960). Methods for collection and analysis of water samples (p. 301). U.S. Geological Survey Water Supply Paper, No. 1454.
Ramamohana Rao, N. V., Suryaprakasa Rao, K., & Schulling, R. D. (1993). Fluorine distribution in waters of Nalgonda District, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environmental Geology, 21, 84–89.
Ramesam, V., & Barua, S. K. (1973). Preliminary studies on the mechanisms of controlling salinity in the North Western arid regions of India. Indian Geohydrology, 9, 10–18.
Reddy, N. B., & Prasad, K. S. S. (2003). Pyroclastic fluoride in groundwaters in some parts of Tadipatri Taluk, Anantapur District, Andhra Pradesh. Indian Journal of Environmental Health, 45, 285–288.
Richards, L. A. (Ed). (1954). Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils (p. 160). USDA Hand Book, No. 60.
Sahu, N. K., & Karim, M. A. (1989). Fluoride incidence in natural waters, Gujarat. Journal of Geological Society of India, 6, 450–456.
Sai Sathish, R., Ranjit, B., Ganesh, K. M., Nageswara Rao, G., & Janardhana, C. (2008). A quantitative study on the chemical composition of renal stones and their fluoride content from Anantapur District, Andhra Pradesh, India. Current Science, 94, 104–109.
Sarala, K., & Rao, P. R. (1993). Endemic fluorosis in the village Ralla Ananathapuram in Andhra Pradesh—An epidemiological study. Fluoride, 26, 177–180
Saxena, V. K., & Ahmed, S. (2001). Dissolution of fluoride in groundwater: A water–rock interaction study. Environmental Geology, 40, 1084–1087.
Saxena, V. K., & Ahmed, S. (2003). Inferring the chemical parameters for the dissolution of fluoride in groundwater. Environmental Geology, 43, 731–736.
Schoeller, H. (1965). Qualitative evaluation of ground water resources. In Methods and techniques of groundwater investigation and development (pp. 44–52). Water Resources Series No. 33, UNESCO.
Schoeller, H. (1977). Geochemistry of groundwater. In R. H. Brown, A. A. Konoplyantsev, J. Ineson, V. S. Kovalevsky (Eds.), Groundwater studies—An international guide for research and practice (pp. 1–18). Paris: UNESCO.
Sharma, D. P. R., & Rao, S. L. N. (1997). Fluoride concentration in groundwaters of Vishakapatnam, India. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 58, 241–247.
Short, H. E., Mc Robert, G. R., Bernard, T. W., & Mannadinayar, A. S. (1937). Endemic fluorosis in the Madras Presidency. Indian Journal of Medical Research, 25, 553–561.
Subba Rao, N. (2008). Fluoride in groundwater, Varaha river basin, Vsakhapatnam district, Aandhra Pradesh, India. Environmental Monitoring Assessment, 152, 47–60.
Subba Rao, N., & John Devadas, D. (2003). Fluoride incidence in groundwater in an area of peninsular India. Environmental Geology, 45, 243–251.
Suma Latha, S., Ambika, S. R., & Prasad, S. J. (1999). Fluoride contamination status of groundwater in Karnataka. Current Science, 76, 730–734.
Susheela, A. K. (1993). Studies on some aspects of fluorosis. In C. Gopalan (Ed.), Recent trends in nutrition (pp. 143–156). New Delhi: Oxford Univ. Press.
Susheela, A. K. (1999). Fluorosis management programme in India. Current Science, 77, 1250–1256.
Susheela, A. K. (2001). A treatise on fluorosis (p. 15). Delhi: Fluorosis Research and Rural Development Foundation.
Susheela, A. K., Bhatnagar, M., Cinanasundaram, N., & Saraswathy, T. R. (1999). Structural aberrations in fluorosed human teeth: Biochemical and scanning electron microscopic studies. Current Science, 77, 1677–1681.
Susheela, A. K., Kumar, A., Bhatnagar, M., & Bahadur, M. (1993). Prevalence of endemic fluorosis with gastrointestinal manifestations in people living in some north Indian villages. Fluoride, 26, 97–104.
Suttie, J. W., & Faltin, E. C. (1971). Effect of short period of fluoride ingestion on dental fluorosis in cattle. American Journal of Veterinary Research, 32, 217–222.
Tiwari, A. N., Nawale, V. P., Tambe, J. A., & Satya Kumar, Y. (2008). Correlation of fluoride with bicarbonate in groundwater of exploratory wells in parts of Maharashtra. Journal of Applied Geochemistry, 10, 93–102.
Todd, D. K. (1980). Groundwater hydrology (2nd Ed., p. 535) New York: Wiley.
U.S. Salinity Laboratory (1954). Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkaline soils (p. 160). U.S. Dept. of Agriculture. Hand Book, No. 60.
Venkateswara Rao, K., & Mahajan, C. L. (1989). Survey on water quality with special reference to fluoride content and endemic fluorosis in arid rural parts of South India (Anantapur District, Andhra Pradesh). Asian Environment, 11, 19–28.
Vijayakumar, V., Sai, C. S. T., Rao, P. L. K. M., & Rao, C. S. (1991). Studies on the distribution of fluoride in drinking water sources in Medchal block, Ranga reddy district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Journal of Fluorine Chemistry, 55, 229–236.
Viswanathaiah, M. N., Sastri, J. C. V., & Rame Gowda, B. (1978). Mechanisms controlling the chemistry of ground waters of Karnataka. Indian Mineralogist, 19, 65–69.
Walton, W. C. (1970). Groundwater resources evaluation. New York: McGraw-Hill.
WHO (2004). Guidelines for drinking water quality (p. 515). Geneva: World Health Organization.
Wilcox, L. V. (1955). Classification and use of irrigation water. Washington DC: US Dept. of Agriculture, Circular 969.
Wodeyar, B. K., & Sreenivasan, G. (1996). Occurrence of fluoride in the ground waters and its impact in Peddavankahalla basin, Bellary district, Karnataka A preliminary study. Current Science, 70, 71–73.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arveti, N., Sarma, M.R.S., Aitkenhead-Peterson, J.A. et al. Fluoride incidence in groundwater: a case study from Talupula, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ Monit Assess 172, 427–443 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1345-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1345-3