Abstract
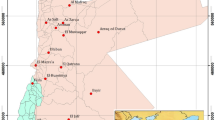
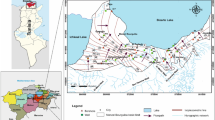
Zeuss–Koutine aquifer, located in southeastern Tunisia, has been used intensively as a primary source to meet the growing needs of the various sectors. Detailed knowledge of the geochemical evolution of groundwater and water quality can enhance understanding of the hydrochemical system, promoting sustainable development and effective management of groundwater resources. To this end, a hydrochemical and statistical investigation was conducted. Groundwater samples have been collected from 13 wells from 1995 to 2005; to understand the sources of dissolved ions and assess the chemical quality of the groundwater. Results demonstrate that among the cations, only the mean concentrations of Na + exceed guideline values set by the World Health Organization (WHO). Regarding the analyzed anions, the concentration of SO\(_{4}^{2-}\) and Cl − are above the WHO allowable concentrations. Total dissolved solids in most groundwater samples are greater than 1,000 mg l − 1, the limit set by the WHO, indicating slightly saline or moderately saline water. In general, a significant increase in the degree of water mineralization was observed in the direction of southwest to northeast following the regional flow direction. Calculated saturation indices show that all water samples were oversaturated with respect to aragonite, calcite, and dolomite, and undersaturated with respect to anhydrite, gypsum, and halite. Based on hydrochemical facies, two types of water predominate in the study area. The first is Ca–Na–SO4–Cl in type and located in the southwest which corresponds to the recharge part of the aquifer. The second type is Na–Ca–Cl–SO4 and located in the east, which corresponds to the discharge part.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhikary, P., Chandrasekharan, H., Chakraborty, D., Kumar, B., & Yadav, B. R. (2009). Statistical approaches for hydrogeochemical characterization of groundwater in West Delhi, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 154, 41–52.
Appelo, C. A. J., & Postma, D. (2005). Geochemistry, groundwater and pollution (2nd ed., p. 321). Rotterdam: Balkema.
Cidu, R., Biddau, R., & Fanfani, L. (2009). Impact of past mining activity on the quality of groundwater in SW Sardinia (Italy). Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 100, 125–132.
Cloutier, V., Lefebvre, R., Therrien, R., & Savard, M. M. (2008). Multivariate statistical analysis of geochemical data as indicative of the hydro-geochemical evolution of groundwater in a sedimentary rock aquifer system. Journal of Hydrology, 353, 294–313.
CVRM (2000). Programa ANDAD. Manual do utilizador. Lisboa: CVRM-Centro de Geosistemas, Instituto Superior Técnico.
Das, M., Kumar, A., Mohapatra, M., & Muduli, S. D. (in press). Evaluation of drinking quality of groundwater through multivariate techniques in urban area. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. doi:10.1007/s10661-009-0991-9.
Davis, J. C. (1986). Statistics and data analysis in geology (p. 224). New York: Wiley.
De Andrade, A. E., Araujo, H., Palacio, Q., Souza, I. H., Alipio de Oliveira, R., & Guerreiro, L. M. J. (2008). Land use effects in groundwater composition of an alluvial aquifer (Trussu River, Brazil) by multivariate techniques. Environmental Research, 106, 170–177.
Desbarats, A. J. (2009). On elevated fluoride and boron concentrations in groundwaters associated with the Lake Saint-Martin Impact Structure, Manitoba. Applied Geochemistry, 24, 915–927. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2009.02.016.
Deutsch, W. J. (1997). Groundwater geochemistry fundamentals and applications to contamination (p. 220). Washington: CRC/Lewis.
DGRE (Direction générale des ressources en eaux) (2005). Annuaires piézométriques en Tunisie. 150 p.
Dixon, W., & Chiswell, B. (1992). The use of hydrochemical sections to identify recharge areas and saline intrusions in alluvial aquifers, southeast Queensland, Australia. Journal of Hydrology, 130, 299–338.
Eaton, A. D., Clesceri, L. S., & Greenberg, A. E. (1995). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (19th ed.). Washington DC: American Public Health Association.
El Yaouti, F., El Mandour, A., Khattach, D., Benavente, J., & Kaufmann, O. (2009). Salinization processes in the unconfined aquifer of Bou-Areg (NE Morocco): A geostatistical, geochemical, and tomographic study. Applied Geochemistry, 24, 16–31.
Feng, Q., & Han, B. (2002). Hydrogeochemical simulation of water–rock interaction under water flood recovery in Renqiu Oilfield, Hebei Province, China. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 21, 156–162.
Fetter, C. W. (1994). Applied hydrogeology (3rd ed., p. 310). New York: Macmillan College Publication.
Freeze, R. A., & Cherry, J. A. (1979). Groundwater. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall.
Gaubbi, E. (1988). Evolution de la piézométrie et de la géochimie de la nappe de Zeuss–Koutine. Master thesis (p. 63). Tunis, Tunisia: University El Manar.
Hidalgo, M. C., & Cruz-Sanjulian, J. (2001). Groundwater composition, hydrochemical evolution and mass transfer in a regional detrital aquifer (Baza basin, southern Spain). Applied Geochemistry, 16, 745–758.
Hounslow, A. W. (1995). Water quality data: Analysis and interpretation (p. 395). Washington: CRC/Lewis.
Jalali, M. (2005). Major ion chemistry in the Bahar area, Hamadan, western Iran. Environmental Geology, 47, 763–772.
Kumar, S. K., Rammohan, V., Sahayam, J. D., & Jeevanandam, M. (2009). Assessment of groundwater quality and hydrogeochemistry of Manimuktha River basin, Tamil Nadu, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 159, 341–351.
Magaritz, M., Nadler, A., Koyumdjisky, H., & Dan, N. (1981). The use of Na/Cl ratio to trace solute sources in a semiarid zone. Water Resource Research, 17, 602–608.
Medina-Gomez, J., & Herrera-Silveira, A. (2003). Estuarine spatial characterization of water quality in a karstic coastal lagoon without anthropogenic disturbance: A multivariate approach. Coastal and Shelf Science, 58, 455–465.
Meybeck, M. (1987). Global chemical weathering of surfıcial rocks estimated from river dissolved loads. American Journal of Science, 287, 401–428.
Morhange, C., & Pirazzoli, P. A. (2005). Mid-Holocene emergence of Southern Tunisian coasts. Marine Geology, 220, 205–213.
OSS (2005). Etude hydrogéologique du système aquifère de la Djeffara tuniso-libyenne. Observatoire du Sahara et du Sahel. Rapport de synthèse, 209 p.
Ouessar, M., Sghaier, M., Mahdhi, N., AbdellI, F., DE Graaff, J., Chaieb, H., et al. (2004). An integrated approach for impact assessment of water harvesting techniques in dry areas: The case of Oued Oum Zessar watershed (Tunisia). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 99, 127–140.
Parkhurst, D. L., & Appelo, C. A. J. (1999). User’s guide to PHREEQC (version 2): A computer program for speciation, batch reaction, one dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations (pp. 99–4259). U.S. Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report.
Rodier, J. (1996). L’Analyse de l’eau: Eaux naturelles, eaux résiduaires, eau de mer (p. 1384). Ed dunod Paris.
Romagny, B., Guillaume, H., Ben Ouezdou, H., & Palluault, S. (2004). Ressources en eau, usages et concurrences dans la Jeffara tunisienne. Documents de recherche du LPED, série Usages, appropriation, gestion des écosystèmes, n° 1, UMR 151 IRD—Université de Provence, 38 p.
Sami, K. (1992). Recharge mechanisms and geochemical processes in a semi-arid sedimentary basin, Eastern cape, South Africa. Journal of Hydrology, 139, 27–48.
Spears, D. A. (1986). Mineralogical control of the chemical evolution of groundwater. In S. T. Trudgill (Ed.), Solute processes (pp. 512). Chichester: Wiley.
Subyani, A. M. (2005). Hydrochemical identification and salinity problem of ground-water in Wadi Yalamlam basin, Western Saudi Arabia. Journal of Arid Environments, 60, 53–66.
Templ, M., Filzmoser, P., & Reimann, C. (2008). Cluster analysis applied to regional geochemical data: Problems and possibilities. Applied Geochemistry, 23, 2198–2213.
World Health Organization (WHO) (2004). Guidelines for drinking water quality, vol. 1 recommendations (3rd). Geneva: WHO.
Yahyaoui, H. (2004). Nappes profondes de la Jeffara de Médenine caractéristiques et evolution. Direction générale des ressources en eau. Tunis. Rapp. Int. 15 p.
Yidana, S. M., Ophori, D., & Banoeng-Yakubob, B. (2008). A multivariate statistical analysis of surface water chemistry data—the Ankobra Basin, Ghana. Journal of Environmental Management, 86, 80–87.
Zhang, Y., Guo, F., Meng, W., & Wang, X. -Q. (2009). Water quality assessment and source identification of Daliao river basin using multivariate statistical methods. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 152, 105–121.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamzaoui-Azaza, F., Ketata, M., Bouhlila, R. et al. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and assessment of drinking water quality in Zeuss–Koutine aquifer, southeastern Tunisia. Environ Monit Assess 174, 283–298 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1457-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1457-9