Abstract
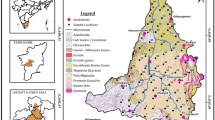
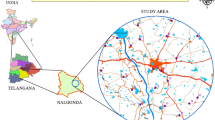
Groundwater is almost globally important for human consumption as well as for the support of habitat and for maintaining the quality of base flow to rivers, while its quality assessment is essential to ensure sustainable safe use of the resources for drinking, agricultural, and industrial purposes. In the current study, 50 groundwater samples were collected from parts of Palar river basin to assess water quality and investigate hydrochemical nature by analyzing the major cations (Ca, Mg, Na, K) and anions (HCO3, Cl, F,SO4, NO3, PO4,CO3, HCO3, and F) besides some physical and chemical parameters (pH, electrical conductivity, alkalinity, and total hardness). Also, geographic information system-based groundwater quality mapping in the form of visually communicating contour maps was developed using ArcGIS-9.2 to delineate spatial variation in physicochemical characteristics of groundwater samples. Wilcox classification and US Salinity Laboratory hazard diagram suggests that 52% of the groundwater fall in the field of C2-S1, indicating water of medium salinity and low sodium, which can be used for irrigation in almost all types of soil with little danger of exchangeable sodium. Remaining 48% is falling under C1-SI, indicating water of low salinity and low sodium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aksoy, A. O., & Scheytt, T. (2007). Assessment of groundwater pollution around Torbali, Izmir, Turkey. Environmental Geology, 53, 19–25. doi:10.1007/s00254-006-0614-5.
Astel, A., Tsakouski, S., Barbieri, P., & Simeonov, V. (2007). Comparison of self-organizing maps classification approach with cluster and principal components analysis for large environmental data sets. Water Research, 41, 4566–4578.
Babiker, I. S., Mohamed, M. A. A., & Hiyama, T. (2007). Assessing groundwater quality using GIS. Water Resources Management, 21, 699–715. doi:10.1007/s11269-006-9059-6.
Baruah, M., Bhattacharyya, K. G., & Patgiri, A. D. (2008). Water quality of shallow groundwater of core city area of Guwahati. In Proceedings of sixteenth national symposium on environment, Haryana, India (pp. 101–106).
BIS (1998). Specifications for drinking water. New Delhi: Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS).
Chang, H. J. (2005). Spatial and temporal variations of water quality in the Han River and its tributaries, Seoul, Korea, 1993–2002. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 161, 267–284.
Chang, H. J. (2007). Comparative streamflow characteristics in urbanizing basins in the Portland Metropolitan Area. Hydrological Processes, 21, 211–222.
Claessens, L., Hopkinson, C., Rastetter, E., & Vallino, J. (2006). Effect of historical changes in land use and climate on the water budget of an urbanizing watershed. Water Resources Research, 42, W03426. doi:10.1029/2005WR004131.
Crosa, G., Froebrich, J., Nikolayenko, V., Stefani, F., Galli, P., & Calamari, D. (2006). Spatial and seasonal variations in the water quality of the Amu Darya River (Central Asia). Water Research, 40, 2237–2245.
Dar, I. A., Sankar, K., & Dar, M. A. (2010a). Spatial assessments of groundwater quality in Mamundiyar Basin, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. doi:10.1007/s10661-010-1702-2.
Dar, M. A., Sankar, K., & Dar, I. A. (2010b). Fluorine contamination in ground water: A major challenge. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. doi:10.1007/s10661-010-1437-0.
Dawe, P. (2006). A statistical evaluation of water quality trends in selected water bodies of Newfoundland and Labrador. Journal of Environmental Engineering and Science, 5(1), 59–73.
Dixit, S., Gupta, S. K., & Tiwari, S. (2005). Nutrient overloading of a freshwater lake in Bhopal, India. Electronic Green Journal, 21, 2–6.
Golditch, S. S. (1938). A study in rock weathering. The Journal of Geology, 46, 17.
Hanrahan, G., Gledhill, M., House, W. A., & Worsfold, P. J. (2003). Evaluation of phosphorus concentrations in relation to annual and seasonal physico-chemical water quality parameters in a U.K. chalk stream. Water Research, 37(15), 3579–3589.
Jerry, A. N. (1986). Basic environmental technology (water supply, waste disposal and pollution control). New York: Wiley.
Kannel, P. R., Lee, S., Kanel, S. R., Khan, S. P., & Lee, Y. S. (2007). Spatialtemporal variation and comparative assessment of water qualities of urban river system: A case study of the River Bagmati (Nepal). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 129(1–3), 433–459.
Karanth, K. R. (1987). Quality of ground water. In K. R. Karanth (Ed.), Ground water assessment development and management (pp. 217–275). New Delhi: Tata McGrawHill.
Meybeck, M. (2002). Riverine quality at the Anthropocene: Propositions for global space and time analysis, illustrated by the Seine River. Aquatic Sciences, 64(4), 376–393.
Nelson, K. C., & Palmer, M. A. (2007). Stream temperature surges under urbanization and climate change: data, models, and responses. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 43, 440–452.
Panday, S. P., Narayanaswamy, V. S., & Hasan, M. Z. (1979). Quality of well waters of Nagapur with regardto nitrates. Indian Journal of Environmental Health, 21, 35–46.
Piper, A. M. (1994). A geographic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analysis. Transactions—American Geophysical Union (Vol. 25, pp. 914–928). Washington D.C.
Simeonov, V., Stratis, J. A., Samara, C., Zachariadis, G., Voutsa, D., Anthemidis, A., et al. (2003). Assessment of the surface water quality in Northern Greece. Water Research, 37, 4119–4124.
Sinha, A. K., Srivastava, K. P., & Sexena, J. (2000). Impact of urbanization on groundwater of Jaipur, Rajasthan. Earth Resources and Environmental Issue.
Stubblefield, A. P., Reuter, J. E., Dahlgren, R. A., & Goldman, C. R. (2007). Use of turbidometry to characterize suspended sediment and phosphorus fluxes in the Lake Tahoe Basin, California, USA. Hydrological Processes, 21, 281–291.
Subrahmanyam, K., & Yadaiah, P. (2001). Assessment of the impact of industrial effluents on water quality in Patancheru and environs, Medak district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Hydrogeology Journal, 9, 297–312. doi:10.1007/s100400000120.
Tijani, M. N. (1994). Hydrochemical assessment of groundwater in Moro area, Kwara State, Nigeria. Environmental Geology, 24, 194–202.
Wilcox, L. V. (1948). The quality of water for irrigation uses (40 pp.). U.S. Dept. Agri. Tech. Bull. 962, Washington, DC, USDA.
Wilcox, L. V. (1955). Classification and use of irrigation waters. USD Circular No. 969. Washington DC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dar, M.A., Sankar, K. & Dar, I.A. Major ion chemistry and hydrochemical studies of groundwater of parts of Palar river basin, Tamil Nadu, India. Environ Monit Assess 176, 621–636 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1608-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1608-z