Abstract
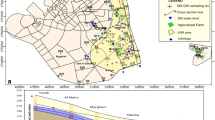
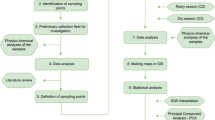
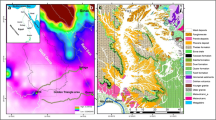
Anticipating the European Water Framework Directive (2000/60/EC), the Italian Government issued Legislative Decree n.152/99 which sets out rules for classifying the environmental status of national water bodies in order to achieve specific qualitative objectives by 2016. The most recent European Groundwater Directive (2006/118/EC), which was only recognized by Italy in early 2009 (Legislative Decree 30/09), requires such resources to be characterized from a qualitative standpoint and the risk of their being polluted by individual pollutants or groups of pollutants to be evaluated. This paper reports a simple methodology, based on easy-to-apply rules, for the rapid classification of groundwater, and the results of its application to the shallow aquifer of the plain of Tavoliere delle Puglie located in south Italy. Data collected during well-water monitoring campaigns carried out from 2002 to 2003 made it possible to assess the environmental status of the Tavoliere which, unfortunately, was found to be characterized by “significant anthropic pressures on quality and/or quantity of groundwater and necessitating specific improvement actions”.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Butturini, A., Bernal, S., Nin, E., Hellin, C., Rivero, L., Sabater, S., et al. (2003). Influences of the stream groundwater hydrology on nitrate concentration in unsaturated riparian area bounded by an intermittent Mediterranean stream. Water Resources Research, 39(4), 1110.
Caldara, M., & Pennetta, L. (1993). Nuovi dati per la conoscenza geologica e morfologica del Tavoliere di Puglia. Bonifica, 3, 25–42.
Colacicco, G. (1953). La carta delle acque sotterranee del Tavoliere - osservazioni e perforazioni eseguite nel biennio 1951–1952. Foggia: Arti Grafiche Pescatore.
Cotecchia, V. (1956). Gli aspetti idrogeologici del Tavoliere delle Puglie. L’Acqua, 11–12, 168–180.
De Girolamo, A. M., Limoni, P. P., Portoghese, I., & Vurro, M. (2002). Il bilancio idrogeologico delle idrostrutture pugliesi: Sovrasfruttamento e criteri di gestione. L’Acqua, 3, 33–45.
Iglesias, A., Garrote, L., Flores, F., & Moneo, M. (2007). Challenges to manage the risk of water scarcity and climate change in the Mediterranean. Water Resources Management, 21, 775–788.
Maggiore, M., Nuovo, G., & Pagliarulo, P. (1996). Caratteristiche idrogeologiche e principali differenze idrochimiche delle falde sotterranee del Tavoliere di Puglia. Memorie Società Geologica Italiana, 51, 669–684.
Maggiore, M., Masciale, R., Massari, R., Pappagallo, G., Passarella, G., & Vurro, M. (2005). Caratteri idrostrutturali del Tavoliere di Puglia ed elaborazione di una carta geolitologica a finalità idrogeologiche. Geologi e Territorio - Periodico di Scienze della Terra dell’Ordine dei Geologi della Puglia, 2, 6–16.
MM.LL.PP- Italian Office of Public Works (Eds.) (1987). Piani dei bacini idrografici fiume Ofanto e Fortore – modello matematico dei sistemi acquiferi sotterranei—rete di controllo dell’acquifero alluvionale. (Bari).
Passarella, G., & Caputo, M. C. (2006). A methodology for space-time classification of groundwater quality. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 115(1–3), 95–117.
Petalas, C., & Lambrakis, N. (2006). Simulation of intense salinization phenomena in coastal aquifers–the case of the coastal aquifers of Thrace. Journal of Hydrology, 324(1–4), 51–64.
Plagnes, V., & Bakalowicz M. (2001). The protection of karst water resources: The example of the Larzac karst plateau (south of France). Environmental Geology, 40(3), 349–358.
Poeter, E. P., & McKenna, S. A. (1995). Reducing uncertainty associated with ground-water flow and transport predictions. Ground Water, 33(6), 899–904.
Weinthal, E., Vengosh, A., Marei, A., Gutierrez, A., & Kloppmann, W. (2005). The water crisis in the Gaza strip: Prospects for resolution. Ground Water, 43(5), 653–660.
Zacharias, I., & Koussouris, T. (2000). Sustainable water management in the European islands. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 25(3), 233–236.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Masciale, R., Barca, E. & Passarella, G. A methodology for rapid assessment of the environmental status of the shallow aquifer of “Tavoliere di Puglia” (Southern Italy). Environ Monit Assess 177, 245–261 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1631-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1631-0