Abstract
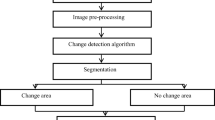
This study explored the spatio-temporal dynamics and evolution of land use/cover changes and urban expansion in Shanghai metropolitan area, China, during the transitional economy period (1979–2009) using multi-temporal satellite images and geographic information systems (GIS). A maximum likelihood supervised classification algorithm was employed to extract information from four landsat images, with the post-classification change detection technique and GIS-based spatial analysis methods used to detect land-use and land-cover (LULC) changes. The overall Kappa indices of land use/cover change maps ranged from 0.79 to 0.89. Results indicated that urbanization has accelerated at an unprecedented scale and rate during the study period, leading to a considerable reduction in the area of farmland and green land. Findings further revealed that water bodies and bare land increased, obviously due to large-scale coastal development after 2000. The direction of urban expansion was along a north-south axis from 1979 to 2000, but after 2000 this growth changed to spread from both the existing urban area and along transport routes in all directions. Urban expansion and subsequent LULC changes in Shanghai have largely been driven by policy reform, population growth, and economic development. Rapid urban expansion through clearing of vegetation has led to a wide range of eco-environmental degradation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilar, A. G., Ward, P. M., & Smith, C. B. Sr. (2003). Globalization, regional development, and megacity expansion in Latin America: Analyzing Mexico city’s peri-urban hinterland. Cities, 20, 3–21.
Cheng, J., Yang, K., Zhao, J., & Wu, J. P. (2009). Impact assessment of land use change in center district of Shanghai based on ecosystem services value (in Chinese). China Environmental Science, 29, 95–100.
Coppin, P., Jonckheere, I., Nackaerts, K., Muys, B., & Lambin, E. (2004). Digital change detection methods in ecosystem monitoring: A review. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 25(9), 1565–1596.
Deng, J. S., Wang, K., Hong, Y., & Qi, J. G. (2009). Spatio-temporal dynamics and evolution of land use change and landscape pattern in response to rapid urbanization. Landscape and Urban Planning, 92, 187–198.
Dewan, A. M., & Yamaguchi, Y. (2009a). Land use and land cover change in Greater Dhaka, Bangladesh: Using remote sensing to promote sustainable urbanization. Applied Geography. doi:10.1016/j.apgeog.2008.12.005.
Dewan, A. M., & Yamaguchi, Y. (2009b). Using remote sensing and GIS to detect and monitor land use and land cover change in Dhaka metropolitan of Bangladesh during 1960–2005. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 150, 237–249.
Fan, F. L., Wang, Y. P., & Wang, Z. S. (2008). Temporal and spatial change detecting (1998–2003) and predicting of land use and land cover in core corridor of Pearl River Delta (China) by using TM and ETM+ images. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 137, 127–147.
Geymen, A., & Baz, I. (2008). Monitoring urban growth and detecting land-cover changes on the Istanbul metropolitan area. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 136(1–3), 449–459.
Gong, S. L., Li, C., & Yang, S. L. (2008). Land subsidence and urban flood prevention safety in Shanghai (in Chinese). Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 4, 96–101.
Hathout, S. (2002). The use of GIS for monitoring and predicting urban growth in East and West St Paul, Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada. Journal of Environmental Management, 66, 229–238.
Herold, M., Goldstein, N. C., & Clarke, K. C. (2003). The spatiotemporal form of urban growth: Measurement, analysis and modeling. Remote Sensing of Environment, 86, 286–302.
Houghton, R. A. (2003). Revised estimates of the annual net flux of carbon to the atmosphere from changes in landuse and landmanagement 1850–2000. Tellus, 55B, 378–390.
Jat, M. K., Garg, P. K., & Khare, D. (2008). Monitoring and modeling of urban sprawl using remote sensing and GIS techniques. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 10(1), 26–43.
Kilic, S., Evrendilek, F., Berberoglu, S., & Demirkesen, A. C. (2006). Environmental monitoring of land-use and land-cover changes in Mediterranean region of Turkey. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 114, 157–168.
Lambin, E. F., Geist, H., & Lepers, E. (2003). Dynamics of land use and cover change in tropical regions. Annual Review of Environment and Resources, 28, 205–241.
Li, B. (2008). Study on impacts of land use change on rain runoff of high-urbanization area in Shanghai (in Chinese). MS Thesis, School of Resource and Environmental Sciences, East China Normal University, China.
Li, X. W., Fang, J. Y., & Piao, S. L. (2003). The intensity and modes of urban landuse growth in Shanghai (in Chinese). Journal of Natural Resources, 18, 412–422.
Li, X. W., Fang, J. Y., & Piao, S. L. (2006). Urban land use development and related spatial mechanism in Shanghai region (in Chinese). Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 15, 34–40.
Li, J. J., Wang, X. R., Wang, X. J., Ma, W. C., & Zhang, H. (2009). Remote sensing evaluation of urban heat island and its spatial pattern of the Shanghai metropolitan area, China. Ecological Complexity. doi:10.1016/j.ecocom.2009.02.002.
Liang, X., & Wang, X. R. (2002). Assessment on the ecological footprint of sustainable development in Shanghai, China (in Chinese). Journal of Fudan University (Natural Science), 41, 388–394.
Lillesand, T. M., & Kiefer, R. W. (1999). Remote sensing and image interpretation. New York: Wiley.
Liu, X., & Lathrop, R. G. Jr. (2002). Urban change detection based on an artificial neural network. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 23, 2513–2518.
Liu, S., Wu, C., & Shen, H. (2000). A GIS-based model of urban land use growth in Beijing (in Chinese). Acta Geographica Sinica, 55, 407–416.
Lucas, I. F. J., Frans, J. M., & Wel, V. D. (1994). Accuracy assessment of satellite derived land-cover data: A review. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 60, 410–432.
Mundia, C. N., & Aniya, M. (2006). Dynamics of land use/cover changes and degradation of Nairobi city, Kenya. Land Degradation and Development, 17(1), 97–108.
Shanghai Statistical Bureau (2009). Shanghai statistical year book 2009 (in Chinese). Shanghai: Chinese Statistical Press.
Shen, Z. W. (1994). Development of Pudong: New pattern of urbanization in China (in Chinese). Shanghai Economic Research, 12, 22–24.
Singh, A. (1989). Digital change detection techniques using remotely sensed data. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 10, 989–1003.
Sorensen, A. (2000). Land readjustment and metropolitan growth: An examination of suburban land development and urban expansion in the Tokyo metropolitan area. Process Plan, 53, 217–330.
United Nations (2001). The state of the world’s cities, 2001. United Nations Centre for Human Settlements, Nairobi, Kenya.
Walcott, S. M., & Pannell, C. W. (2006). Metropolitan spatial dynamics: Shanghai. Habitat International, 30, 199–211.
Wang, C. X., Wang, J., Li, Y. Y., & Da, L. J. (2008a). Diversity, spatial pattern and dynamics of vegetation under urbanization in Shanghai (I): Flora of the remnant natural vegetation and its dynamics change during past fifty years in Sheshan area of Shanghai, China (in Chinese). Journal of East China Normal University (Natural Science), 4, 31–39.
Wang, J. Y., Da, L. J., Song, K., & Li, B. L. (2008b). Temporal variations of surface water quality in urban, suburban and rural areas during rapid urbanization in Shanghai, China. Environmental Pollution, 152, 387–393.
Weng, Y. C. (2007). Spatiotemporal changes of landscape pattern in response to urbanization. Landscape and Urban Planning, 81, 341–354.
Wu, J. C., Shi, X. Q., Xue, Y. Q., Zhang, Y., Wei, Z. X., & Yu, J. (2008). The development and control of the land subsidence in the Yangtze Delta, China. Environmental Geology, 55, 1725–1735.
Xiao, J. Y., Shen, Y. J., Ge, J. F., Tateishi, R., Tang, C. Y., Liang, Y. Q., et al. (2006). Evaluating urban expansion and land use change in Shijiazhuang, China, by using GIS and remote sensing. Landscape and Urban Planning, 75, 69–80.
Xie, X. J., Kang, J. C., Li, W. J., & Zhang, J. P. (2009). Relationship between urbanization and heavy metal pollution in soils in Shanghai suburb (in Chinese). Resources Science, 31, 1250–1256.
Xu, J. G., Liao, B. G., Shen, Q., Zhang, F., & Mei, A. X. (2007). Urban spatial restructuring in transitional economy—Changing land use pattern in Shanghai. Chinese Geographical Science, 17, 19–27.
Yang, X. (2002). Satellite monitoring of urban spatial growth in the Atlanta metropolitan area. Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing, 68, 725–734.
Yeh, A. G. O., & Li, X. (1999). Economic development and agricultural land loss in the Pearl River Delta, China. Habitat International, 23, 373–390.
Yin, Z. E., & Xu, S. Y. (2007). Changes in land use and land cover and their effect on eco-environment in Pudong new area of Shanghai (in Chinese). Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 16, 430–434.
Yu, J., Xu, S. Y., Chen, Z. L., Liu, P. F., & Wang, D. Q. (2000). The change of erosion and deposition tidal flat of Shanghai in the last ten years (in Chinese). Fujian Geography, 15(3), 23–25.
Zhang, X. Y. (2006). RS and GIS-based research on Shanghai land use/cover change with respect to thermal environmental effect (in Chinese). MS Thesis, School of Resource and Environmental Sciences, East China Normal University, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, J., Yin, Z., Zhong, H. et al. Monitoring urban expansion and land use/land cover changes of Shanghai metropolitan area during the transitional economy (1979–2009) in China. Environ Monit Assess 177, 609–621 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1660-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1660-8