Abstract
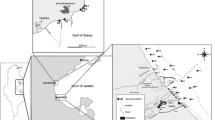
A study of chemical and sedimentological parameters integrated with benthic foraminifera investigation was conducted along the northern coast of Gabes Gulf. Thirty-two samples were studied and a total of 68 benthic foraminiferal species were identified. Heavy metals enrichment factors and total hydrocarbon concentrations showed both metal and petrogenic pollution related mainly to phosphogypsum, sewage, and fishing activities. Statistical analysis (bivariate correlation and hierarchical cluster analysis) show a possible control of these pollutants on density, diversity, as well as the taxonomic composition of the benthic foraminiferal assemblages. The extent to which the population was found less dense and less diversified corresponded to the degree to which the sediment was contaminated. In these contaminated sites, an increase in relative abundance of opportunistic species such Ammonia tepida and Haynesina germanica was found. Far from pollution, foraminiferal assemblages are dominated by species characteristic of Mediterranean shallow water (Ammonia beccarii, Ammonia parkinsoniana, Elphidium crispum, Elphidium williamsoni, Elphidium advenum, Peneroplis planatus, Peneroplis pertesus).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aloulou, F., Kallel, M., Dammak, M., Elleuch, B., & Saliot, A. (2009). Even-numbered n-alkanes/n-alkenes predominance in surface sediments of Gabes Gulf in Tunisia. Environmental Earth Sciences, 61, 1–10.
Alve, E. (1991a). Benthic foraminifera in sediment cores reflecting heavy metal pollution in Sørf jord, western Norway. Journal of Foraminiferal Research, 21, 1–19.
Alve, E. (1991b). Benthic foraminifera reflecting heavy metal pollution in Sérfjord, Western Norway. Journal of Foraminiferal Research, 34, 1641–1652.
Alve, E. (1993). Benthic foraminiferal responses to estuarine pollution: A review. Geological Society of America, Abstract with Programs, 25, 137.
Alve, E. (1995). Benthic foraminiferal responses to estuarine pollution: A review. Journal of Foraminiferal Research, 25, 190–203.
Alve, E., & Nagy, J. (1986). Estuarine foraminiferal distribution in Sandebukta, a branch of the Olso fjord. Journal of Foraminiferal Research, 16(4), 261–284.
Alve, E., & Olsgard, F. (1999). Benthic foraminiferal colonization in experiments with copper-contaminated sediments. Journal of Foraminiferal Research, 29(3), 186–195.
Al-Zamel, A. Z., Al-Sarawi, M. A., Khader, S. R., & Al-Rifaiy, I. A. (2009). Benthic foraminifera from polluted marine environment of Sulaibikhat Bay (Kuwait). Environmental Monitoring Assessment, 149, 395–409.
Antony, A. (1968). Studies on the shelf water foraminiferal off the Kerala coast. Bulletin Department Marine Biology Oeanography, 4, 11–54.
Armynot du Châtelet, E., Debenay, J. P., & Soulard, R. (2004). Foraminiferal proxies for pollution monitoring in moderately polluted harbors. Environmental Pollution, 127, 27–40.
Bandy, O. L., Ingle, J. C., & Resig, J. M. (1964). Modifications of foraminiferal distributions by the Orange County outfall California. Marine Technology Society Transaction, 1, 54–76.
Bates, J. M., & Spencer, R. S. (1979). Modification of foraminiferal trends by the Chesapeake–Elizabeth sewage outfall, Virginia Beach, Virginia. Journal of Foraminiferal Research, 9, 125–140.
Ben Othmane, S. (1971). Observations hydrologiques, dragages, et chalutage dans le sud-est tunisien. Bulletin Institut Océanographie Pêche Salammbôo, 2, 103–120.
Bhalla, S. N., & Nigam, R. (1986). Recent foraminifera from polluted marine environment of Velsao Beach, south Goa, India. Revue de Paléobiologie, 5, 43–46.
Buckley, D. E., Owens, E. H., Schafer, C. T., Vilks, G., Cranston, R. E., Rashid, M. A., et al. (1974). Canso Strait and Chedabucto Bay: A multidisciplinary study of the impact of man on the marine environment. Geological Survey of Canada, Paper 74–30, 133–160.
Burone, L., Venturini, N., Sprechmann, P., Valente, P., & Muniz, P. (2006). Foraminiferal responses to polluted sediments in the Montevideo coastal zone, Uruguay. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 52, 61–73
Buzas, M. A. (1965). The distribution and abundance of foraminifera in Long Island Sound. Smithson. Smithsonian Institution Miscellaneous Collection, 149, 1–89.
Cearreta, A. M., Irabien, M. J., Ulibarri, I., Yusta, I., Croudace, I. W., & Cundy, A. B. (2002). Recent salt marsh development and natural regeneration of reclaimed areas in the Plentzia Estuary, N Spain. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 54, 863–886.
Coccioni, R. (2000). Benthic foraminifera as bioindicators of heavy metal pollution—A case study from the Goro Lagoon (Italy). In R. E. Martin (Ed.), Environmental micropaleontology: The application of microfossils to environmental geology (pp. 71–103). New York: Kluwer/Plenum.
Debenay, J. P., Tsakiridis, E., Soulard, R., & Grossel, H. (2001). Factors determining the distribution of foraminiferal assemblages in Port Joinville Harbor (Ile d’Yeu, France): The influence of pollution. Marine Micropaleontology, 43, 75–118.
Ellison, R. L., Broome, R., & Oglivie, R. (1986). Foraminiferal response to trace metal contamination in the Patapsco river and Baltimore Harbour, Maryland. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 17(9), 419–423.
Fishbein, E., & Patterson, T. (1993). Error-weighted maximum likelihood (EWML): A new statistically based method to cluster quantitative micropaleontological data. Journal of Paleontology, 67(3), 475–486.
Fisher, R. A., Corbet, A. S., & Williams, C. B. (1943). The relation between the number of species and the number of individuals in a random sample of an animal population. Journal of Animal Ecology, 12, 42–58.
Folk, R., & Word, W. (1957). Brazors River bar. A study in significance of grain size parameters. Journal of Sedimentology and Petrology, 27, 13–27.
Frontalini, F., & Coccioni, R. (2008). Benthic foraminifera for heavy metal pollution monitoring: A case study from the central Adriatic Sea coast of Italy. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 76, 404–417.
Hayward, B. W., Holzmann, M., Grenfell, H. R., Pawlowski, J., & Triggs, C. M. (2004). Morphological distinction of molecular types in Ammonia towards a taxonomic revision of the world’s most commonly misidentified foraminifera. Marine Micropaleontology, 50, 237–272.
Loeblich, A. R., & Tappan, H. (1987). Foraminiferal genera and their classification. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold.
Loring, D.H. (199l). Normalization of heavy-metal data from estuarine and coastal sediments. ICESJ. Marine Science, 48, 101–115.
Louati, A., Elleuch, B., Kallel, M., Saliot, A., Dagaut, J., & Oudot, J. (2001). Hydrocarbon contamination of coastal sediments from the Sfax area (Tunisia), Mediterranean Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 42, 444–451.
Massart, D. L., & Kaufman, L. (1989). Hierarchical clustering methods. In R. E. Krieger (Ed.), The interpretation of analytical chemical data by the use of cluster analysis (pp. 75–99). Malabar: Krieger.
Mohamed, M. (1972). Study of foraminifera in recent marine sediments on the Mediterranean continental shelf off the Nile Delta (p. 175). Unpublished Ph.D. thesis, Faculty of Science, Alexandria University.
Murray, J. W. (1968). Living foraminifera of lagoons and estuaries. Micropaleontology, 14, 435–455.
Murray, J. W. (1991). Ecology and paleoecology of benthic foraminifera (p. 397). Harlow: Longman.
Nagy, J., & Alve, E. (1987). Temporal changes in foraminiferal faunas and impact of pollution in Sandebukta, Oslo Fjord. Marine Micropaleontology, 12, 109–128.
Patterson, R. T. (1990). Intertidal benthic foraminiferal biofacies on the Fraser River Delta British Columbia. Modern distribution and paleoecological importance. Micropaleontology, 36, 229–234.
Pekey, H., Karakas, D., Ayberk, S., Tolun, L., & Bakõglu, M. (2004). Ecological risk assessment using trace elements from surface sediments of Izmit Bay (Northeastern Marmara Sea) Turkey. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 48, 946–953.
Phleger, F. B. (1960). Ecology and distribution of recent foraminifera (p. 297). Baltimore: Johns Hopkins.
Rao, K. K., & Rao, T. S. (1979). Studies of pollution ecology of foraminifera of the Trivandrum coast. Indian Journal of Marine Sciences, 8, 31–35.
Resig, J. M. (1960). Foraminiferal ecology around ocean outfalls off southern California. In E. Person (Ed.), Disposal in the marine environment (pp. 104–121). London: Pergamon.
Rubio, B., Nombela, M. A., & Vilas, F. (2000). Geochemistry of major and trace elements in sediments of the Ria de Vigo (NW Spain): An assessment of metal pollution. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 40(11), 968–980.
Samir, A. M., & El-Din, A. B. (2001). Benthic foraminiferal assemblages and morphological abnormalities as pollution proxies in two Egyptian bays. Marine Micropaleontology, 41, 193–227.
Schafer, C. T. (1970). Studies of benthonic foraminifera in the Restigouche estuary. Faunal distribution patterns near pollution sources. Maritime Sediments, 6(3), 121–134.
Schafer, C. T. (1973). Distribution of foraminifera near pollution sources in Chaleur Bay. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 2, 219–233.
Schafer, C. T., & Cole, F. E. (1974). Distribution of benthic foraminifera: Their use in delimiting local near shore environments. Offshore Geology of Canada, Eastern Canada, Geological Survey of Canada, 103–108, 74–30.
Scott, D. B., & Medioli, F. S. (1980). Living vs. total foraminiferal populations: Their relative usefulness in paleoecology. Journal of Paleontology, 54, 814–831.
Seiglie, G. A. (1968). Foraminiferal assemblages as indicators of high organic carbon content in sediments and of polluted waters. The American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin, 52(11), 2231–2241.
Seiglie, G. A. (1975). Foraminifers of Guayanilla bay and their use as environmental indicators. Revista Espanola de Micropaleontologia, 7(3), 453–487.
Setty, M. G. A. P. (1976). The relative sensitivity of benthonic foraminifera in the polluted marine environment of Cola Bay, Goa. Indian Colloque of Micropaleontological Stratigraphy. Proceeding, 6, 225–234.
Setty, M. G. A. P., & Nigam, R. (1984). Benthic foraminifera as pollution indices in the marine environment of west coast of India. Revue Itay Paleontology Stratigraphy, 89, 421–436.
Sharifi, A. R., Crouda, I. W., & Austin, R. L. (1991). Benthonic foraminiferids as pollution indicators in Southampton water, Southern England, UK. Journal of Micropaleontology, 10, 109–113.
Szefer, P., Kusak, A., & Szefer, K. (1998). Evaluation of the anthropogenic influx of metallic pollutants into Puck Bay, southern Baltic. Applied Geochemistry, 13, 293–304.
Taylor, S. R., & McLennan, S. M. (1995). The geochemical evolution of the continental crust. Revue Geophysique, 33(2), 241–265.
Tsujimoto, A., Nomura, R., Yasuhara, M., Yamazaki, H., & Yoshikawa, S. (2006). Impact of eutrophication on shallow marine benthic foraminifers over the last 150 years in Osaka Bay, Japan. Marine Micropaleontology, 60, 258–268.
USEPA (1996). SW-846 reference methodology: Method 6010B. Inductively Coupled Plasma-Atomic Emission Spectrometry. Washington: Dublin Core (DC).
USEPA (1999). Integrated Risk Information System (IRIS). Washington: National Center for Environmental Assessment, Office of Research and Development.
Walton, W. R. (1952). Techniques of recognition of living foraminifera. Contribution from the Cushman Foundation, 3, 56–60.
Watkins, J. G. (1961). Foraminiferal ecology around the Orange County, California, ocean sewer outfall. Micropaleontology, 7, 199–206.
W.D.O.E. (1995). Sediment management standards. Olympia: Washington State Department of Ecology (Chapter 173-204-320) WAC.
Yanko, V., & Flexer, A., (1991). Foraminiferal benthonic assemblages as indicators of pollution (an example of Northwestern shelf of the Black Sea). In Proceedings of third annual symposium on the Mediterranean margin of Israel, Institute Oceanography and Limnology, Haifa, Israel (Abstract Vol., p. 5).
Yanko, V., & Flexer, A. (1992). Microfauna as possible indicator of hydrocarbon seepages. Method for oil–gas trap reconnaissance. In Proceedings annual meeting Israel Geological Society, Askelon, Israel (pp. 69–170).
Yanko, V., Kronfeld, J., & Flexer, A. (1994). Response of benthic foraminifera to various pollution sources: Implications for pollution monitoring. Journal of Foraminiferal Research, 24, 1–17.
Zaghden, H., Kallel, M., Louati, A., Elleuch, B., Oudot, J., & Saliot, A. (2005). Hydrocarbons in surface sediments from the Sfax coastal zone, (Tunisia) Mediterranean Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 50, 1287–1294.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aloulou, F., EllEuch, B. & Kallel, M. Benthic foraminiferal assemblages as pollution proxies in the northern coast of Gabes Gulf, Tunisia. Environ Monit Assess 184, 777–795 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2001-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2001-2