Abstract
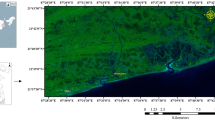
This paper deals with a systematic hydrogeological, geophysical, and hydrochemical investigations carried out in SIPCOT area in Southern India to demarcate groundwater pollution and saline intrusion through Uppanar River, which flows parallel to sea coast with high salinity (average TDS 28, 870 mg/l) due to back waters as well as discharge of industrial and domestic effluents. Hydrogeological and geophysical investigations comprising topographic survey, self-potential, multi-electrode resistivity imaging, and water quality monitoring were found the extent of saline water intrusion in the south and pockets of subsurface pollution in the north of the study area. Since the area is beset with highly permeable unconfined quaternary alluvium forming potential aquifer at shallow depth, long-term excessive pumping and influence of the River have led to lowering of the water table and degradation of water quality through increased salinity there by generating reversal of hydraulic gradient in the south. The improper management of industrial wastes and left over chemicals by closed industries has led surface and subsurface pollution in the north of the study area.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdollahi-Nasab, A., Boufadel, M. C., Li, H. L., & Weaver, J. W. (2010). Saltwater flushing by freshwater in a laboratory beach. Journal of Hydrology, 386(1–4), 1–12.
Alpar, B. (2009). Vulnerability of Turkish coasts to accelerated sea-level rise. Geomorphology, 107(1–2), 58–63.
American Public Health Association (APHA). (1985). Standard methods for the examination of water and waste (16th ed., p. 100). Washington: Am Public Health Assoc.
Appelo, C. A. J., & Postma, D. (2005). Geochemistry, groundwater and pollution (2nd ed.). Rotterdam: Balkema.
Aubert, M., & Atangana, Q. Y. (1996). Self-potential method in hydrogeological exploration of volcanic areas. Ground Water, 34, 1010–1016.
Balaram, V., & Rao, T. G. (2004). Rapid determination of REEs and other trace elements in geological samples by microwave acid digestion and ICP-MS. Atomic Spectroscopy, 24(6), 206–212.
Brown, E., Skougstad, M. W., & Fishmen, M. J. (1983). Method for collection and analyzing of water samples for dissolved minerals and gases (p. 75). Washington: U.S. Govt. Printing Office.
CAMP (2000). Integrated aquifer management plan: Final Report. Gaza coastal aquifer management program. Metcalf and Eddy Inc. in cooperation with the Palestinian Water Authority (PWA). United States Agency for International Development, USAID Contract No. 294-C-00-99-00038-00.
Chapellier, D., Fitterman, D., Parasnis, D., & Valla, P. (1991). Application of geophysics to water prospecting in arid and semi-arid areas. Geoexploration, 27(1–2), R7–R7.
Chidambaram, S., Kumar, G. S., Prasanna, M. V., Peter, A. J., Ramanthan, A. L., & Srinivasamoorthy. (2008). A study on the hydrogeology and hydrogeochemistry of groundwater from different depths in a coastal aquifer: Annamalai Nagar, Tamilnadu, India. Environmental Geology, 57(1), 59–73.
Choudhury, K., & Saha, D. K. (2004). Integrated geophysical and chemical study of saline water intrusion. Groundwater, 42(5), 671–677.
Choudhury, K., Saha, D. K., & Chakraborty, P. (2001). Geophysical study for saline water intrusion in a coastal alluvial terrain. Journal of Geophysics, 46, 189–200.
Custodio, E. (2010). Coastal aquifers of Europe: An overview. Hydrogeology Journal, 18(1), 269–280.
de Lima, O. A. L., Sato, H. K., & Porsani, M. J. (1995). Imaging industrial contaminant plumes with resistivity techniques. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 34(2), 93–108.
Dey, A., & Morrison, H. F. (1979). Resistivity modelling for arbitrary shaped two-dimensional structures. Geophysical Prospecting, 27, 106–136.
Domenico, P. A., & Schwartz, F. W. (1990). Physical and chemical hydrogeology. New York: Wiley.
Doussan, C., Jouniaux, L., & Thony, J. L. (2002). Temporal variations of SP and unsaturated water flow in loam and clay soils: a seasonal field study. Journal of Hydrology, 267, 173–185.
Falgas, E., Ledo, J., Marcuello, A., & Queralt, P. (2009). Monitoring freshwater–seawater interface dynamics with audiomagnetotelluric data. Near Surface Geophysics, 7(5–6), 391–399.
Frohlich, R. K., Urish, D. W., Fuller, J., & Reilly, M. O. (1994). Use of geoelectrical method in groundwater pollution surveys in a coastal environment. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 32, 139–154.
Frohlich, R. K., Barosh, P. J., & Boving, T. (2008). Investigating changes of electrical characteristics of the saturated zone affected by hazardous organic waste. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 64(1–2), 25–36.
Gimenez, E., & Morell, I. (1997). Hydrogeochemical analysis of salinization processes in the coastal aquifer of Oropesa (Castellon, Spain). Environmental Geology, 29, 118–131.
Giordana, G., & Montginoul, M. (2006). Policy instruments to fight against seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers: An overview. Vie Et Milieu Life and Environment, 56(4), 287–294.
Hem, J. D. (1989). Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water. U.S.G.S. Water-Supply Paper, vol. 2254. Washington: US Government Printing Office.
Hidalgo, M. C., & Cruz-Sanjulian, J. (2001). Groundwater composition, hydrochemical evolution and mass transfer in a regional detrital aquifer (Baza basin, southern Spain). Applied Geochemistry, 16(7–8), 745–758.
Hounslow, A. W. (1995). Water quality data analysis and interpretation. Boca Raton: Lewis.
Ibrahim, D. E., & Hussein, M. T. (1998). Integrated hydrogeophysical methods for detecting and mapping the fresh–saline interface in Wadi Fatimah, Saudi Arabia. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 23(2A), 129–146.
Jayaprakash, M., Giridharan, L., Venugopal, T., Krishna Kumar, S. P., & Periakali, P. (2008). Characterization and evaluation of the factors affecting the geochemistry of groundwater in Neyveli, Tamil Nadu, India. Environmental Geology, 54, 855–867.
Jonathan, M. P., Srinivasalu, S., Thangadurai, N., Ayyamperumal, T., Armstrong-Altrin, J. S., & Ram-Mohan, V. (2008). Contamination of Uppanar River and coastal waters off Cuddalore, southeast coast of India. Environmental Geology, 53(7), 1391–1404.
Jouniaux, L., Maineult, A., Naudet, V., Pessel, M., & Sailhac, P. (2009). Review of self-potential methods in hydrogeophysics. Comptes Rendus Geosciences, 341, 928–936.
Kilty, K. T. (1984). On the origin and interpretation of self-potential anomalies. Geophysical Prospecting, 32, 51–62.
Lambrakis, N. (2006). Multicomponent heterovalent chromatography in aquifers. Modelling salinization and freshening phenomena in field conditions. Journal of Hydrology, 323(1–4), 230–243.
Lee, S. H., Kim, K. W., Ko, I. W., Lee, S. G., & Hwang, H. S. (2002). Geochemical and geophysical monitoring of saline water intrusion in Korean paddy fields. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 24(4), 277–291.
Loke, M. H., & Barker, R. D. (1996). Rapid least-squares inversion of apparent resistivity pseudosections using a quasi-Newton method. Geophysical Prospecting, 44, 131–152.
Maineult, A., Strobach, E., & Renner, J. (2008). Self-potential signals induced by periodic pumping tests. Journal of Geophysical Research, 113, B01203.
Mondal, N. C., & Singh, V. P. (2011). Hydrochemical analysis of salinization for a tannery belt in Southern India. Journal of Hydrology, 405(2–3), 235–247.
Mondal, N. C., Singh, V. P., Singh, V. S., & Saxena, V. K. (2010). Determining the interaction between groundwater and saline water through groundwater major ions chemistry. Journal of Hydrology, 388(1–2), 100–111.
Mondal, N. C., Singh, V. P., Singh, S., & Singh, V. S. (2011). Hydrochemical characteristic of coastal aquifer from Tuticorin, Tamil Nadu, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 175(1–4), 531–550.
Moreira, C. A., & Braga, A. C. D. (2009). Applications of geophysical methods in monitoring contaminated area under natural attenuation. Engenharia Sanitaria E Ambiental, 14(2), 257–264.
Nguyen, F., Kemna, A., Antonsson, A., Engesgaard, P., Kuras, O., Ogilvy, R., et al. (2009). Characterization of seawater intrusion using 2D electrical imaging. Near Surface Geophysics, 7(5–6), 377–390.
Ortega-Guerrero, A., Cherry, J. A., & Aravena, R. (1997). Origin of pore water and salinity in the lacustrine aquitard overlying the regional aquifer of Mexico City. Journal of Hydrology, 197(1–4), 47–69.
Park, S. C., Yun, S. T., Chae, G. T., Yoo, I., Shin, K. S., Heo, C. H., et al. (2005). Regional hydrochemical study on salinization of coastal aquifers, western coastal area of South Korea. Journal of Hydrology, 313(3–4), 182–194.
Radhakrishna, I. (2001). Saline water interface structure in Mahanadi Delta region, Orissa, India. Environmental Geology, 40(3), 369–380.
Revil, A., Titov, K., Doussan, C., & Lapenna, V. (2006). Applications of the self-potential method to hydrological problems. Applied Hydrogeophysics, 71, 255–292. Springer Netherlands, NATO Ser. IV.
Sanford, W. E., & Pope, J. P. (2010). Current challenges using models to forecast seawater intrusion: Lessons from the Eastern Shore of Virginia, USA. Hydrogeology Journal, 18(1), 73–93.
Sankaran, S., Saheb Rao, S., Krishnakumar, K. (2009). Micro level groundwater quality/groundwater movement in Cuddalore SIPCOT, Tamilnadu (pp.67). Technical Report No. NGRI-2009-GW-689.
Sarwade, D. V., Nandakumar, M. V., Kesari, M. P., Mondal, N. C., Singh, V. S., & Singh, B. (2007). Evaluation of seawater ingress into an Indian Attoll. Environmental Geology, 52(2), 1475–1483.
Sato, M., & Mooney, H. M. (1960). The electrochemical mechanism of sulfide self-potentials. Geophysics, 25, 226–249.
Singh, V. S., Sarwade, D. V., Mondal, N. C., & Singh, B. (2009). Evaluation of groundwater resources in a tiny Andrott Island, Union Territory of Lakshadweep, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 158(1–4), 145–154.
Stewart, M. T. (1982). Evaluation of electromagnetic methods for rapid mapping of salt–water interfaces in coastal aquifers. Groundwater, 20(5), 538–545.
Urish, D. W. (1983). The practical application of surface electrical resistivity to detection of groundwater pollution. Groundwater, 21(2), 144–152.
Vengosh, A., Spivack, A. J., Artzi, Y., & Ayalon, A. (1999). Geochemical and boron, strontium, and oxygen isotopic constraints on the origin of the salinity in groundwater from the Mediterranean coast of Israel. Water Resources Research, 35(6), 1877–1894.
Vengosh, A., Kloppmann, W., Marei, A., Livshitz, Y., Gutierrez, A., Banna, M., et al. (2005). Sources of salinity and boron in the Gaza strip: Natural contaminant flow in the southern Mediterranean coastal aquifer. Water Resources Research, 41(W01013), 1–19.
Wanfang, Z., Beck, B. F., & Spephenson, J. B. (1999). Investigation of groundwater flow in karst area using component separation of natural potential measurements. Environmental Geology, 37, 19–25.
Ward, N. I. (1995). Trace elements. In F. W. Fifield, & P. J. Haines (Eds.), Environmental analytical chemistry. Chapman and Hall: Blackie.
World Health Organization (WHO). (1984). Guideline of drinking quality (pp. 333–335). Washington: World Health Organization.
Zilberbrand, M., Rosenthal, E., & Shachnai, E. (2001). Impact of urbanization on hydrochemical evolution of groundwater and on unsaturated-zone gas composition in the coastal city of Tel Aviv, Israel. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 50(3–4), 175–208.
Zohdy, A. R., Martin, P., Bisdorf, R. J. (1993). A study of seawater intrusion using direct-current soundings in the southeastern part of the Oxnard Plain, California (p.139). USGS Open-File Report 93–524.
Acknowledgements
The SIPCOT authority, Cuddalore cooperated during the field work. Director, NGRI, Hyderabad had given support and permission to publish this paper. The associate editor, Professor Yu-Pin Lin and three anonymous reviewers had suggested their constructive comments to improve the paper. The authors are thankful to them.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sankaran, S., Sonkamble, S., Krishnakumar, K. et al. Integrated approach for demarcating subsurface pollution and saline water intrusion zones in SIPCOT area: a case study from Cuddalore in Southern India. Environ Monit Assess 184, 5121–5138 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2327-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2327-9