Abstract
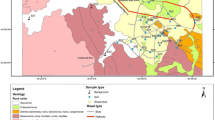
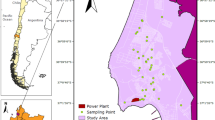
The soil quality of urban parks is of vital importance as the children playing in the parks get themselves easily contaminated. A study was conducted to assess the level of elemental pollution caused by constant urbanization and industrialization, in various parks of Islamabad and Rawalpindi. The soil samples, collected from 14 urban parks of Islamabad and Rawalpindi areas, were analysed for their elemental concentrations. In each sample, 32 elements were quantified using semi-absolute k 0-instrumental neutron activation analysis and flame atomic absorption spectrophotometry. The quality of analysis was assured by analysing the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) reference material IAEA-S7 (soil). The pollution level was assessed by enrichment factor, pollution load index and our suggested indicator called “average toxic element concentration”. The elemental concentrations measured in the parks of two cities were compared by t test. Four sources of different elements in the soils were identified by employing principal component analysis and cluster analysis. The results of multivariate techniques grouped all parks into four classes. The use of enrichment factor indicated the presence of Ni at slightly higher level in all parks while the pollution load index revealed that the parks of Rawalpindi were relatively more polluted as compared to that of Islamabad. The hot spot areas of elemental concentration were closely related to high traffic conditions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batjargal, T., Otgonjargal, E., Baek, K., & Yang, J. S. (2010). Assessment of metals contamination of soils in Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia. Journal of Hazardous Material, 184(1–3), 872–876.
Biasioli, M., Barberis, R., & Ajmone-Marsan, F. (2006). The influence of a large city on some soil properties and metals content. Science of the Total Environment, 356, 154–164.
Bowen, H. J. M. (1979). Environmental chemistry of the elements. London: Academic.
Boyer, K. W., Horwitz, W., & Albert, R. (1985). Interlaboratory variability in trace element analysis. Analytical Chemistry, 57, 454–459.
Bradley, M. P., & Stolt, M. H. (2003). Subaqueous soil–landscape relationships in a Rhode Island estuary. Soil Science Society of American Journal, 67, 1487–1495.
Brereton, R. G. (2003). Chemometrics: data analysis for the laboratory and chemical plant. Chichester: Wiley.
Carr, R., Zhang, C., Moles, N., & Harder, M. (2008). Identification and mapping of heavy metal pollution in soils of a sports ground in Galway City, Ireland, using a portable XRF analyser and GIS. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 30, 45–52.
Chen, T. B., Zheng, Y. M., Lei, M., Huang, Z. C., Wu, H. T., Chen, H., et al. (2005). Assessment of heavy metal pollution in surface soils of urban parks in Beijing, China. Chemosphere, 60, 542–551.
Chon, H., & Kim, K. (1995). Metal contamination in soil and dust in Seoul metropolitan city, Korea. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 17, 139–146.
Councell, T. B., Duckenfield, K. U., Landa, E. R., & Callender, E. (2004). Tire-wear particles as a source of zinc to the environment. Environmental Science and Technology, 38, 4206–4214.
Daud, M., Wasim, M., Khalid, N., Zaidi, J. H., & Iqbal, J. (2009). Assessment of elemental pollution in soil of Islamabad city using instrumental neutron activation analysis and atomic absorption spectrometry techniques. Radiochimica Acta, 97, 117–119.
Faiz, Y., Tufail, M., Javed, M. T., Chaudhry, M. M., & Siddique, N. (2009). Road dust pollution of Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn along Islamabad expressway, Pakistan. Microchemical Journal, 92, 186–192.
Fong, F. T., Chee, P. S., Mahmood, A. A., & Tahir, N. M. (2008). Possible source and pattern distribution of heavy metals content in urban soil at Kuala Terengganu town center. Malaysian Journal of Analytical Sciences, 12, 458–467.
Gingerich, P. D., Arif, M., Bhatti, M. A., Raza, H. A., & Raza, M. (1995). Protosiren and babiacetus (Mammalia, Sirenia and Cetacea) from the middle Eocene Drazinda formation, Sulaiman Range, Punjab (Pakistan). Contributions from the Museum of Paleontology, The University of Michigan, 29, 331–357.
Guitao, S., Zhenlou, C., Shiyuan, Xu, Zhang, Ju, Wang, L., Chunjuan, B., et al. (2008). Potentially toxic metal contamination of urban soils and roadside dust in Shanghai, China. Environmental Pollution, 156, 251–260.
Hopke, P. K., Gladney, E. S., Garden, G. E., William, H. Z., & Jones, A. G. (1976). The use of multivariate analysis to identify sources of selected elements in the Boston urban aerosol. Atmospheric Environment, 10, 1015–1025.
Hou, H., Takamatsu, T., Koshikawa, M. K., & Hosomi, M. (2005). Trace metals in bulk precipitation and through fall in a suburban area of Japan. Atmospheric Environment, 39, 3583–3595.
Imperato, M., Adamo, P., Naimo, D., Arienzo, M., Stanzione, D., & Violante, P. (2003). Spatial distribution of heavy metals in urban soils of Naplescity (Italy). Environmental Pollution, 124, 247–256.
Juma, N. G. (2001). Introduction to soil science and soil resources (the pedosphere and its dynamics: a systems approach to soil science). Alberta: Salman Productions.
Lam, K. C., Ng, S. L., Hui, W. C., & Chan, P. K. (2005). Environmental quality of urban parks and open spaces in Hong Kong. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 111, 55–73.
Lee, C. S., Li, X., Shi, W., Cheung, S. C., & Thornton, I. (2006). Metal contamination in urban, suburban and country park soils of Hong Kong: a study based on GIS and multivariate statistics. Science of the Total Environment, 356, 45–61.
Li, X., Poon, C. S., & Liu, P. S. (2001). Heavy metal contamination of urban soils and street dusts in Hong Kong. Applied Geochemistry, 16, 1361–1368.
Li, X., Lee, S. L., Wong, S. C., Shi, W., & Thornton, I. (2004). The study of metal contamination in urban soils of Hong Kong using a GIS-based approach. Environmental Pollution, 129, 113–124.
Lu, X., Wang, L., Lei, K., Huang, J., & Zhai, Y. (2009). Contamination assessment of copper, lead, zinc, manganese and nickel in street dust of Baoji, NW China. Journal of Hazardous Material, 161, 1058–1062.
Madrid, L., Diaz-Barrientos, E., & Madrid, F. (2002). Distribution of heavy metal contents of urban soils in park of Seville. Chemosphere, 49, 1301–1308.
Manta, D. S., Angelone, M., Bellanca, A., Neri, R., & Sprovieri, M. (2002). Heavy metals in urban soils: A case study from the city of Palermo (Sicily), Italy. Science of the Total Environment, 300(1–3), 229–243.
Marjanović, M. D., Vukčević, M. M., Antonović, D. G., Dimitrijević, S. I., Jovanović, Đ. M., Matavulj, M. N., et al. (2009). Heavy metals concentration in soils from parks and green areas in Belgrade. Journal of the Serbian Chemical Society, 74, 697–706.
Mason, B., & Moore, C. B. (1982). Principles of geochemistry (4th ed.). New York: Wiley.
Massart, D. L., Vandeginste, B. G. M., Buydens, L. M. C., DeJong, S., Lewi, P. J., & Smeyers-Verbeke, J. (2003). Handbook of chemometrics and qualimetrics: Part A. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Moller, A., Muller, H. W., Abdullah, A., Abdelgawad, G., & Utermann, J. (2005). Urban soil pollution in Damascus, Syria: Concentrations and patterns of heavy metals in the soils of the Damascus Ghouta. Geoderma Journal, 25, 1443–1446.
Parr, R. M., & Toro, E. C. (1990). Applications of nuclear analytical methods in the life sciences as exemplified by recent research programs of the IAEA. Biological Trace Element Research, 26–27, 671–681.
Rasmussen, P. E., Subramanian, K. S., & Jessiman, B. J. (2001). A multi-element profile of house dust in relation to exterior dust and soils in the city of Ottawa, Canada. Science of the Total Environment, 267, 125–140.
Salonen, V., & Korkka-Niemi, K. (2007). Influence of parent sediments on the concentration of heavy metals in urban and suburban soils in Turku, Finland. Applied Geochemistry, 22, 906–918.
Scheyer, J. M., & Hipple, K. W. (2005). Urban soil primer. Lincoln: United States Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service, National Soil Survey Centre.
Severson, R. C., Gough, L. P., & Boom, G. (1992). Baseline element concentrations in soils and plants, Wattenmeer National Park, North and East Frisian Islands, Federal Republic of Germany. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 61, 169–184.
Sezgin, N., Ozcan, H. K., Demir, G., Nemlioglu, S., & Bayat, C. (2004). Determination of heavy metal concentrations in street dusts in Istanbul E-5 highway. Environment International, 29, 979–985.
Shah, M. H., Shaheen, N., & Jaffar, M. (2006). Characterization, source identification and apportionment of selected materials in TSP in an urban atmosphere. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 114, 573–587.
Shaikh, A. M. (2009). Economic geography report on introduction to Pakistan, European geotechnical and environmental course, 2008–2010. Hungary: University of Miskolc.
Skjelkvale, B. L., Andersen, T., Fjeld, E., Mannio, J., Wilander, A., Johansson, K., et al. (2001). Heavy metal surveys in Nordic lakes, concentrations, geographic patterns and relation to critical limits. AMBIO Journal of Human Environment, 30, 2–10.
Sparks, D. L. (2003). Environmental soil chemistry (2nd ed.). London: Academic.
Sun, Y., Zhou, Q., Xie, X., & Liu, R. (2010). Spatial, source and risk assessment of the heavy metal contamination of urban soils in a typical regions of Shenyang, china. Journal of Hazardous Material, 174, 455–462.
UNEP (United Nations Environment Program). (2010a). Final review of scientific information on cadmium. Nairobi: UNEP.
UNEP (United Nations Environment Program). (2010b). Final review of scientific information on lead. Nairobi: UNEP.
Vandeginste, B. G. M., Massart, D. L., Buydens, L. M. C., DeJong, S., Lewi, P. J., & Verbeke, J. S. (2003). Handbook of chemometrics and qualimetrics: Part B. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Verheijen, R., Jeffery, S., Bastos, A. C., van der Velde, M., & Diafas, I. (2009). Biochar application to soils: A critical scientific review of effects on soil properties, processes and functions (p. 166). Luxembourg: Office for the Official Publications of the European Communities. EUR 24099 EN.
Wang, X. S., Qin, Y., & Sang, S. X. (2005). Accumulation and sources of heavy metals in urban topsoils: A case study from the city of Xuzhou, China. Environmental Geology, 48, 101–107.
Wasim, M., Zaidi, J. H., Arif, M., & Fatima, I. (2008). Development and implementation of k 0 -INAA standardization at PINSTECH. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 277, 525–529.
Wasim, M., Arif, M., Zaidi, J. H., & Anwar, Y. (2009). Development and implementation of k 0 -INAA standardization at 10 MW Pakistan research reactor-1. Radiochimica Acta, 97, 651–655.
Wilcke, W., Muller, S., Kanchanakool, N., & Zech, W. (1998). Urban soil contamination in Bangkok: Heavy metal and aluminium partitioning in topsoils. Geoderma Journal, 86, 211–228.
Wold, S., Esbensen, K., & Geladi, P. (1987). Principal component analysis. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory System, 2, 37–52.
Wong, C. S. C., Li, X., & Thornton, I. (2006). Urban environmental geochemistry of trace metals. Environmental Pollution, 142, 1–16.
Xinghui, X., Chen, X., Ruimin, L., & Hong, L. (2011). Heavy metals in urban soils with various types of land use in Beijing. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 186, 2043–2050.
Yongfeng, W., Congqiang, L., & Chenglong, T. (2008). Distribution and sequential extraction of some heavy metals in urban soils of Guiyang City, China. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 27, 401–406.
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to Dr. M. Daud, Mr. A. Majid and Ms. M. Zainab for helping during the experimentation and manuscript preparation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iqbal, S., Wasim, M., Tufail, M. et al. Elemental contamination in urban parks of Rawalpindi/Islamabad—a source identification and pollution level assessment study. Environ Monit Assess 184, 5497–5510 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2356-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2356-4