Abstract
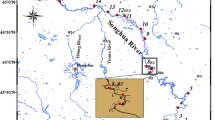
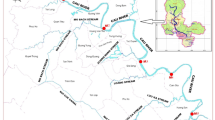
The distribution of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) was investigated in a total of 15 water and sediment samples from the Yellow River Estuary, China in April 2011. The results indicated that the concentrations of PFOS in the water and sediment samples averaged 157.5 ng/L and 198.8 ng/g and ranged from 82.30 to 261.8 ng/L and 75.48 to 457.0 ng/g, respectively. The concentrations of PFOS in the sediment column increased from 45.32 to 379.98 ng/g with the decrease of the sampling depth, which showed that the increased PFOS pollution in the sediment appeared in this region in over recent years. The distribution coefficient (K d) of PFOS between water and sediment linearly increased from 0.37 to 4.80 L/g as the salinity (S‰) increased from 0.18 to 4.47. Correlation analysis revealed that K d was significantly and positively correlated to the contents of total organic carbon and clay of the sediment, and salinity. Therefore, salinity was an important parameter in controlling the sediment–water interactions and the fate or transport of PFOS in the aquatic environment. The results of this study showed that the estuary was an important sink for PFOS and suggested that PFOS might be carried with the river water and transported for long distances before it reached to the sea and largely scavenged to the sediment in the estuaries due to the change in salinity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ankley, G. T., Kuehl, D. W., Kahl, M. D., Jensen, K. M., Butterworth, B. C., & Nichols, J. W. (2004). Partial life-cycle toxicity and bioconcentration modeling of perfluorooctanesulfonate in the northern leopard frog (Rana pipiens). Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 23, 2745–2755.
Beach, S. A., Newsted, J. L., Coady, K., & Giesy, J. P. (2006). Ecotoxicological evaluation of perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS). Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 186, 133–174.
Becker, A. M., Gerstmann, S., & Frank, H. (2008). Perfluorooctane surfactants in waste waters, the major source of hydrosphere pollution. Chemosphere, 72, 115–121.
Boulanger, B., Vargo, J., Schnoor, J. L., & Hornbuckle, K. C. (2004). Detection of perfluorooctane surfactants in Great Lakes water. Environmental Science and Technology, 38, 4064–4070.
Boulanger, B., Vargo, J. D., Schnoor, J. L., & Hornbuckle, K. C. (2005). Evaluation of perfluorooctane surfactants in wastewater treatment system and in commercial surface protection product. Environmental Science and Technology, 39, 5524–5530.
Brunk, B. K., Jirka, G. H., & Lion, L. W. (1997). Effects of salinity changes and the formation of dissolved organic matter coatings on the sorption of phenanthrene: implications for pollutant trapping in estuaries. Environmental Science and Technology, 31, 119–125.
Dinglasan, M., Ye, Y., Edwards, E., & Mabury, S. (2004). Fluorotelomer alcohol yields poly and perfluorinated acids. Environmental Science and Technology, 38, 2857–2864.
Ellis, D. A., Martin, J. W., De Silva, A. O., Mabury, S. A., Hurley, M. D., Sulbaek Andersen, M. P., et al. (2004). Degradation of fluorotelomer alcohols: a likely source of perfluorinated carboxylic acids. Environmental Science and Technology, 38, 3316–3321.
Giesy, J. P., & Kannan, K. (2001). Global distribution of perfluorooctane sulfonate in wildlife. Environmental Science and Technology, 35, 1339–1342.
Giesy, J. P., & Kannan, K. (2002). Perfluorochemical surfactants in the environment. Environmental Science and Technology, 36, 146A–152A.
Guo, R., Zhou, Q. F., Cai, Y. Q., & Jiang, G. B. (2008). Determination of perfluorooctanesulfonate and perfluorooctanoic acid in sewage sludge samples using liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Talanta, 75, 1394–1399.
Hansen, K. J., Johnson, H. O., Eldridge, J. S., Butenhoff, J. L., & Dick, L. A. (2002). Quantitative characterization of trace levels of PFOS and PFOA in the Tennessee River. Environmental Science and Technology, 36, 1681–1685.
Hegemen, W. J. M., Van der Weijden, C. H., & Loch, J. P. G. (1995). Sorption of benzo[a]pyrene and phenanthrene on suspended harbor sediment as a function of suspended sediment concentration and salinity: a laboratory study using the cosolvent partition coefficient. Environmental Science and Technology, 29, 363–371.
Hekster, F. M., & Voogt, P. D. (2003). Perfluoroalkylated substances: aquatic environmental assessment (Rep. RIKZ 2002.043). Amsterdam: University of Amsterdam.
Hekster, F. M., Laane, R. W. P. M., & de Voogt, P. (2003). Environmental and toxicity effects of perfluoroalkylated substances. Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 179, 99–121.
Higgins, C. P., & Luthy, R. G. (2006). Sorption of perfluorinated surfactants on sediments. Environmental Science and Technology, 40, 7251–7256.
Higgins, C. P., Field, J. A., Criddle, C. S., & Luthy, R. G. (2005). Quantitative determination of perfluorochemicals in sediments and domestic sludge. Environmental Science and Technology, 39, 3946–3956.
Hu, B. Q., Li, G. G., Li, J., Yang, M., Wang, L. B., & Bu, R. Y. (2011). Spatial variability of the 210 Pb sedimentation rates in the Bohai and Huanghai Seas and its influencing factors. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 33, 125–133 (In Chinese with English abstract).
Hui, Y. M., Zheng, M. H., Liu, Z. T., & Gao, L. R. (2009). Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments from Yellow River Estuary and Yangtze River Estuary, China. Journal of Environmental Science, 21, 1625–1631.
Kennish, M. J. (2002). Environmental threats and environmental future of estuaries. Environmental Conservation, 29, 78–107.
Lange, C. C. (2000). The aerobic biodegradation of N-EtFOSE alcohol by the microbial activity present in municipal wastewater treatment sludge: report CA058 USEPA Docket AR226-1030a078. St. Paul, MN: 3M Environmental Laboratory.
Liu, F., Li, X. Q., Dong, G. C., Qin, Y. G., Chen, Y. G., Wang, Z. Z., et al. (2011). Water pollution of Yellow River Estuary coastal wetland. Chinese Environmental Science, 31, 1705–1710 (In Chinese with English abstract).
Lotze, H. K., Lenihan, H. S., Bourque, B. J., Bradbury, R. H., Cooke, R. G., Kay, M. C., et al. (2006). Depletion, degradation, and recovery potential of estuaries and coastal seas. Science, 312, 1805–1809.
Luo, X. J., Mai, B. X., Yang, Q. S., Chen, S. J., & Zeng, E. Y. (2008). Distribution and partition of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon in surface water of the Pearl River Estuary, South China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 145, 427–436.
Martin, J. W., Whittle, D. M., Muir, D. C., & Mabury, S. A. (2004). Perfluoroalkyl contaminants in a food web from Lake Ontario. Environmental Science and Technology, 38, 5379–5385.
Olsen, G. W., Burris, J. M., Ehresman, D. J., Froehlich, J. W., Seacat, A. M., Butenhoff, J. L., et al. (2007). Half-life of serum elimination of perfluorooctanesulfonate, perfluorohexanesulfonate, and perfluorooctanoate in retired fluorochemical production workers. Environmental Health Perspectives, 115, 1298–1305.
Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development. (2002). Environment directorate joint meeting of the chemicals committee and the working party on chemicals: co-operation on existing chemicals hazard assessment of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and its salts. Paris: Pesticides and Biothechnology
Pan, G., & You, C. (2010). Sediment–water distribution of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) in Yangtze River Estuary. Environmental Pollution, 158, 1363–1367.
Prevedouros, K., Cousins, I. T., Buck, R. C., & Korzeniowski, S. H. (2006). Sources, fate, and transport of perfluorocarboxylates. Environmental Science and Technology, 40, 32–44.
Saito, N., Sasaki, K., Nakatome, K., Harada, K., Yoshinaga, T., & Koizumi, A. (2003). Perfluorooctane sulfonate concentrations in surface water in Japan. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 45, 149–158.
Schultz, M. M., Barofsky, D. F., & Field, J. A. (2006). Quantitative determination of fluorinated alkyl substances by large-volume-injection liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry-characterization of municipal wastewaters. Environmental Science and Technology, 40, 289–295.
Senthilkumar, K., Ohi, E., Sajwan, K., Takasuga, T., & Kannan, K. (2007). Perfluorinated compounds in river water, river sediment, market fish, and wildlife samples from Japan. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 79, 427–431.
Sinclair, E., & Kannan, K. (2006). Mass loading and fate of perfluoroalkyl surfactants in wastewater treatment plants. Environmental Science and Technology, 40, 1408–1414.
So, M. K., Miyake, Y., Yeung, W. Y., Ho, Y. M., Taniyasu, S., Rostkowski, P., et al. (2007). Perfluorinated compounds in the Pearl River and Yangtze River of China. Chemosphere, 68, 2085–2095.
Sun, T., Yang, Z. F., & Cui, B. S. (2008). Critical environmental flows to support integrated ecological objectives for the Yellow River Estuary, China. Water Resources Management, 22, 973–989.
Takazawa, Y., Nishino, T., Sasaki, Y., Yamashita, H., Suzuki, N., Tanabe, K., et al. (2009). Occurrence and distribution of perfluorooctane sulfonate and perfluorooctanoic acid in the rivers of Tokyo. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 202, 57–67.
Voogt, P. D., & Roon, A. V. (2005). Perfluorinated chemicals in sediments, particulate matter, soil and water samples from The Netherlands. Organohalogen Compounds, 67, 790–793.
Wang, H. J., Bi, N. S., Saito, Y., Wang, Y., Sun, X. X., Zhang, J., et al. (2010). Recent changes in sediment delivery by the Huanghe (Yellow River) to the sea: causes and environmental implications in its estuary. Journal of Hydrology, 391, 302–313.
You, C., Jia, C. X., & Pan, G. (2010). Effect of salinity and sediment characteristics on the sorption and desorption of perfluorooctane sulfonate at sediment–water interface. Environmental Pollution, 158, 1343–1347.
Yu, J., Hu, J. Y., Tanaka, S. H., & Fujii, S. G. (2009). Perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) in sewage treatment plants. Water Research, 43, 2399–2408.
Acknowledgments
The study is supported by the Encouraging Foundation for Outstanding Youth Scientists of Shandong Province, China (BS2012HZ006) and the Program of International S&T Cooperation of Chinese MOST (2010DFA92090).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Wang, H. & Deng, W. Perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) distribution and effect factors in the water and sediment of the Yellow River Estuary, China. Environ Monit Assess 185, 8517–8524 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3192-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3192-5