Abstract
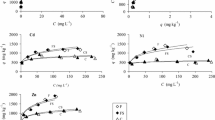
The objectives of this study were to investigate competitive sorption behaviour of heavy metals (Cd, Cu, Mn, Ni, Pb and Zn) under different management practices and identify soil characteristics that can be correlated with the retention and mobility of heavy metals using 65 calcareous soil samples. The lowest sorption was found for Mn and Ni in competition with the other metals, indicating the high mobility of these two cations. The Freundlich equation adequately described heavy metals adsorption. On the basis of Freundlich distribution coefficient, the selectivity sequence of the metal adsorption was Cu > Pb > Cd > Zn > Ni > Mn. The mean value of the joint distribution coefficient (K dΣsp) was 182.1, 364.1, 414.7, 250.1, 277.7, 459.9 and 344.8 l kg−1 for garden, garlic, pasture, potato, vegetables, wheat and polluted soils, respectively. The lowest observed K dΣsp in garden soil samples was due to the lower cation exchange capacity and lower carbonate content. The results of the geochemical modelling under low and high metal addition indicated that Cd, Ni, Mn and Zn were mainly retained via adsorption, while Pb and Cu were retained via adsorption and precipitation. Stepwise forward regression analysis showed that clay, organic matter and CaCO3 were the most important soil properties influencing competitive adsorption of Cd, Mn, Ni and Zn. The results in this study point to a relatively easy way to estimate distribution coefficient values.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhikari, R., & Singh, M. V. (2003). Sorption characteristics of lead and cadmium in some soils of India. Geoderma, 114, 81–92.
Adriano, D. C. (2001). Trace elements in the terrestrial environments: biogeochemistry, bioavailability and risks of metals (2nd ed.). New York: Springer.
Allison, J.D., Brown, D.S., Novo-Gradac, K.J. (1991). MINTEQA2/PRODEFA2, A Geochemical Assessment Model for Environmental Systems: Version 3.0 Users Manual. US Environmental Protection Agency, Athens, GA. (EPA/600/3-91/021).
Antoniadis, V., & Alloway, B. J. (2002). The role of dissolved organic carbon in the mobility of Cd, Ni and Zn in sewage sludge-amended soils. Environmental Pollution, 117, 515–521.
Appel, C., & Ma, L. (2002). Concentration, pH, and surface charge effects on cadmium and lead adsorption in three tropical soils. Journal of Environmental Quality, 31, 581–589.
Berti, W. R., & Jacobs, L. W. (1996). Distribution of trace elements in soil from repeated sewage sludge application. Journal of Environmental Quality, 27, 1280–1286.
Bradl, H. B. (2004). Adsorption of heavymetal ions on soils and soils constituents. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 277, 1–18.
Brümmer, G. W., Gerth, J., & Tiller, K. G. (1988). Reaction kinetics of the adsorption and desorption of nickel, zinc and cadmium by goethite: I. Adsorption and diffusion of metals. Journal of Soil Science, 39, 37–52.
Carlon, C., Dalla Valle, M., & Marcomini, A. (2004). Regression models to predict water–soil heavy metals partition coefficients in risk assessment studies. Environmental Pollution, 127, 109–115.
Cavallaro, N., & McBride, M. B. (1984). Zinc and copper sorption and fixation by an acid soil clay: effect of selective dissolutions. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 48, 1050–1054.
Covelo, E. F., Andrade, M. L., & Vega, F. A. (2004). Heavy metal adsorption by humic Umbrisols: selectivity sequences and competitive sorption kinetics. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 280, 1–8.
de Matos, A. T., Fontes, M. P. F., da Costa, L. M., & Martínez, M. A. (2001). Mobility of heavy metals as related to soil chemical and mineralogical characteristics of Brazilian soils. Environmental Pollution, 111, 429–435.
Doula, M., Ioannou, A., & Dimirkou, A. (1999). Influence of ionic strength and pH on Cu2+ adsorption and on Mg2+, Ca2+, Mn2+, Zn2+ release by kaolinite. Agrochimica, 43, 215–222.
Elliott, H. A., Liberati, M. R., & Huang, C. P. (1985). Effects of iron oxide removal on heavy metal sorption by acid subsoils. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 27, 379–389.
Elzahabi, M., & Yong, R. N. (2001). pH influence on sorption characteristics of heavy metal in the vadose zone. Engineering Geologists, 60, 61–68.
Fontes, M. P. F., de Matos, A. T., da Costa, L. M., & Neves, J. C. L. (2000). Competitive adsorption of Zn, Cd, Cu and Pb in three highly weathered Brazilian soils. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 31, 2939–2958.
Gao, S., Walker, W. J., Dahlgren, R. A., & Bold, J. (1997). Simultaneous sorption of Cd, Cu, Ni, Zn, Pb and Cr on soils treated with sewage sludge supernatant. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 93, 331–345.
Gerriste, R. G., & van Driel, W. (1984). The relationship between adsorption of trace metal, organic matter and pH in temperate soil. Journal of Environmental Quality, 13, 197–204.
Gil-García, C. J., Rigol, A., & Vidal, M. (2011). The use of hard- and soft-modelling to predict radiostrontium solid–liquid distribution coefficients soils. Chemosphere, 85, 1400–1405.
Gomes, P. C., Fontes, M. P., da Silva, A. G., Mendoca, E. S., & Netto, A. R. (2001). Selectivity sequence and competitive adsorption of heavy metal by Brazilian soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 65, 1115–1121.
Gurel, A. (2006). Adsorption characteristics of heavy metals in soil zones developed on spilite. Environmental Geology, 51, 333–340.
Harter, R. D. (1979). Adsorption of copper and lead by Ap and B2 horizons of several northeastern United States soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 43, 679–683.
Harter, R. D. (1992). Competitive sorption of cobalt, copper, and nickel ions by a calcium-saturated soil. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 56, 444–449.
Harter, R. D., & Naidu, R. (2001). An assessment of environmental and solution parameter impact on trace-metal sorption by soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 65, 597–612.
Havlin, L., Beaton, J. D., Tisdale, S. L., & Nelson, W. L. (1999). Soil fertility and fertilizers: an introduction to nutrient management (p. 499). Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall.
Jalali, M. (2005). Nitrates leaching from agricultural land in Hamadan, western Iran. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 110, 210–218.
Jalali, M. (2007). A study of the Quantity = Intensity relationships of potassium in some calcareous soils of Iran. Arid and Land Research Management, 21, 133–141.
Jalali, M., & Khanlari, Z. V. (2008). Major ion chemistry of groundwaters in the Damagh area, Hamadan, western Iran. Environmental Geology, 54, 87–93.
Jalali, M., & Moharami, S. (2007). Competitive adsorption of trace metals in calcareous soils of western Iran. Geoderma, 140, 156–163.
Jalali, M., & Sajad Ttabar, S. (2011). Chemical fractionation of phosphorus in calcareous soils of Hamadan, western Iran under different land use. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 174, 523–531.
Jalali, M., & Sajadi Tabar, S. (2013). Kinetics extractions of nickel and lead from some contaminated calcareous soils. Soil and Sediment Contamination, 22, 56–71.
Kaizer, K., & Zech, W. (1997). Competitive sorption of dissolved organic matter fractions to soils and related mineral phases. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 61, 64–69.
Kinniburgh, D. G., Jackson, M. L., & Syers, J. K. (1976). Adsorption of alkaline earth, transition and heavy metals cation by hydrus oxide gel of iron and aluminium. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 40, 796–799.
Loeppert, R. H., & Inskeep, W. P. (1996). Iron. In D. L. Sparks (Ed.), Methods of soil analysis: chemical methods, part 3 (pp. 639–664). Madison: ASA and SSSA.
Lu, S. G., & Xu, Q. F. (2009). Competitive adsorption of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn by different soils of Eastern China. Environmental Geology, 57, 685–693.
Mahdavi, S. H. (2002). Kinetics of non-exchangeable potassium release and its correlation with plant uptake in dominant soils series in Hamadan province. M.Sc thesis. Tehran University, Tehran, Iran.
McBride, M., Sauve, S., & Hendershot, W. (1997). Solubility control of Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb in contaminated soils. European Journal of Soil Science, 48, 337–346.
MINITAB (2000). User’s Guide 2: Data Analysis and Quality Tools. Minitab, State College, Pa.
Mouni, L., Merabet, D., Robert, D., & Bouzaza, A. (2009). Batch studies for the investigation of the sorption of the heavy metals Pb2+ and Zn2+ onto Amizor soil (Algeria). Geoderma, 154, 30–35.
Naidu, R., Summer, M. E., & Harter, R. D. (1998). Sorption of heavy metals in strongly weathered soils: an overview. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 20, 5–9.
Nakamaru, Y., & Uchida, S. (2008). Distribution coefficients of tin in Japanese agricultural soils and the factors affecting tin sorption behaviour. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 99, 1003–1010.
Pansu, M., & Gautheyrou, J. (2006). Handbook of soil analysis, mineralogical, organic and inorganic analysis. Berlin: Springer.
Plassard, F., Winiarski, T., & Petit-Ramel, M. (2000). Retention and distribution of three previous heavy metals in a carbonated soil: comparison between batch and unsaturated column studies. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 42, 99–111.
Rowell, D. L. (1994). Soil science: methods and applications (p. 345). Harlow: Longman Group.
Sastre, J., Rauret, G., & Vedal, M. (2006). Effect of the cationic composition of sorption solution on the quantification of sorption–desorption parameters of heavy metals in soils. Environmental Pollution, 140, 322–339.
Sauvé, S., Hendershot, W., & Allen, H. E. (2000). Solid-solution partitioning of metals in contaminated soil: dependence on pH, total metal burden, and organic matter. Environmental Science and Technology, 34, 1125–1131.
Serrano, S., Garrido, F., Campbell, C. G., & Garcia-Gonzalez, M. T. (2005). Competitive sorption of cadmium and lead in acid soils of Central Spain. Geoderma, 124, 91–104.
Sidle, R. C., & Kardod, L. T. (1997). Aqueous release of heavy metals from two sewage sludges. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 8, 453–459.
Sipos, P., Németh, T., Kovács Kis, V., & Mohai, I. (2008). Sorption of copper; zinc and lead on soil mineral phases. Chemosphere, 73, 461–469.
Spark, K. M., Wells, J. D., & Johnson, B. B. (1995). Characterizing trace metal adsorption on kaolinite. European Journal of Soil Science, 46, 633–640.
Sposito, G., Lund, J., & Chang, A. C. (1983). Trace metal chemistry in arid zone field soils amended with sewage sludge: I. Fractionation of Ni, Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb in soild phases. Soil Sci Society of America Journal, 46, 260–264.
Usman, A. R. A. (2008). The relative adsorption selectivites of Pb, Cu, Zn, Cd and Ni by soils developed on shale in New Valley. Egyptian Geoderma, 144, 334–343.
Veeresh, H., Tripathy, S., Chaudhuri, D., Hart, B. R., & Powell, M. A. (2003). Sorption and distribution of adsorbed metals in three soils of India. Applied Geochemistry, 18, 1723–1731.
Vega, F. A., Covelo, E. F., & Andrade, M. L. (2006). Competitive sorption and desorption of heavy metals in mine soils: influence of mine soil characteristics. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 298, 582–592.
Vidal, M., Santos, M. J., Abroa, T., Rodriguez, J., & Rigol, A. (2009). Modeling competitive metal sorption in a mineral soil. Geoderma, 149, 189–198.
Zhu, B., & Alva, A. K. (1993). Differential adsorption of trace metals by soils as influenced by exchangeable cations and ionic strength. Soil Science, 155, 61–67.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jalali, M., Moradi, F. Competitive sorption of Cd, Cu, Mn, Ni, Pb and Zn in polluted and unpolluted calcareous soils. Environ Monit Assess 185, 8831–8846 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3216-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3216-1